dsc使用方法
1. 安装dsc
yum install -y libpcap-devel
wget https://www.dns-oarc.net/files/dsc/dsc-2.13.0.tar.gz
tar -xf dsc-2.13.0.tar.gz
cd dsc-2.13.0
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/dsc
make
make install2. 启动dsc
cp /usr/local/dsc/etc/dsc/dsc.conf.sample /usr/local/dsc/etc/dsc/dsc.conf
vim /usr/local/dsc/etc/dsc/dsc.conf
dsc -i /usr/local/dsc/etc/dsc/dsc.conf
dsc配置根据实际需要修改

[root@bogon home]# cat /usr/local/dsc/etc/dsc/dsc.conf # local_address # # Specifies a local IP address with an optional mask/bits for local # networks. Used to determine the "direction" of an IP packet: sending # or receiving or other. Repeat any number of times for all local # addresses. # local_address 127.0.0.1; local_address ::1; #local_address 127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0; #local_address 192.168.0.0 24; #local_address 10.0.0.0 8; # run_dir # # dsc passes this directory to chdir() after starting. # run_dir "/usr/local/dsc/var/lib/dsc"; # minfree_bytes # # If the filesystem has less than this amount of free # space, then dsc will not write its XML files to disk. # The data will be lost. # minfree_bytes 5000000; # pid_file # # filename where DSC should store its process-id # pid_file "/run/dsc.pid"; # bpf_program # # a berkely packet filter program. it can be used to limit # the number and type of queries that the application receives # from the kernel. note if you limit it to "udp port 53" the # IP-based collectors do not work # # NOTE: bpf_program must GO BEFORE interface # # use this to see only DNS messages #bpf_program "udp port 53"; # # use this to see only DNS *queries* #bpf_program "udp dst port 53 and udp[10:2] & 0x8000 = 0"; # dns_port # # DSC will only parse traffic coming to or leaving the DNS port (default 53), # this option lets you control which port that is in case it's not standard. #dns_port 53; # pcap_buffer_size # # Set the buffer size (in bytes) for pcap, increasing this may help # if you see dropped packets by the kernel but increasing it too much # may have other side effects # # NOTE: pcap_buffer_size must GO BEFORE interface #pcap_buffer_size 4194304; # pcap_thread_timeout # # Set the internal timeout pcap-thread uses when waiting for packets, # the default is 100 ms. # # NOTE: pcap_thread_timeout must GO BEFORE interface #pcap_thread_timeout 100; # drop_ip_fragments # # Drop all packets that are fragments # # NOTE: drop_ip_fragments must GO BEFORE interface #drop_ip_fragments; # interface # # specifies a network interface to sniff packets from or a pcap # file to read packets from, can specify more than one. # # Under Linux (kernel v2.2+) libpcap can use an "any" interface which # will include any interfaces the host has but these interfaces will # not be put into promiscuous mode which may prevent capturing traffic # that is not directly related to the host. # interface ens33; #interface fxp0; #interface any; #interface /path/to/dump.pcap; # DNSTAP # # specify DNSTAP input from a file, UNIX socket, UDP or TCP connections # (dsc will listen for incoming connections). # # This type of input is delivered directly from the DNS software itself # as encapsulated DNS packets as seen or as made by the software. # See https://dnstap.info for more information about DNSTAP. # # dnstap_unixsock can have additional optional options to control access # to the socket: [user][:group] [umask] # # dnstap_unixsock /path/to/unix.sock user:group 0007; # # NOTE: # - Only one DNSTAP input can be specified at a time currently. # - Configuration needs to match that of the DNS software. # - Don't use these values as default values, no default port for DNSTAP! # #dnstap_file /path/to/file.dnstap; #dnstap_unixsock /path/to/unix.sock; #dnstap_tcp 127.0.0.1 5353; #dnstap_udp 127.0.0.1 5353; # DNSTAP network information filler # # per DNSTAP specification, some information may be not included such as # receiver or sender of DNS. To be able to produce statistics, dsc needs # to know what to put in place when that information is missing. # This is configured by dnstap_network and should be the primary IP # addresses and port of the DNS software. # # dnstap_network <IPv4> <IPv6> <port>; # #dnstap_network 127.0.0.1 ::1 53; # qname_filter # # Defines a custom QNAME-based filter for DNS messages. If # you refer to this named filter on a dataset line, then only # queries or replies for matching QNAMEs will be counted. # The QNAME argument is a regular expression. For example: # #qname_filter WWW-Only ^www\. ; #dataset qtype dns All:null Qtype:qtype queries-only,WWW-Only ; # datasets # # please see dsc.conf(5) man-page for more information. dataset qtype dns All:null Qtype:qtype queries-only; dataset rcode dns All:null Rcode:rcode replies-only; dataset opcode dns All:null Opcode:opcode queries-only; dataset rcode_vs_replylen dns Rcode:rcode ReplyLen:msglen replies-only; dataset client_subnet dns All:null ClientSubnet:client_subnet queries-only max-cells=200; dataset qtype_vs_qnamelen dns Qtype:qtype QnameLen:qnamelen queries-only; dataset qtype_vs_tld dns Qtype:qtype TLD:tld queries-only,popular-qtypes max-cells=200; dataset certain_qnames_vs_qtype dns CertainQnames:certain_qnames Qtype:qtype queries-only; dataset client_subnet2 dns Class:query_classification ClientSubnet:client_subnet queries-only max-cells=200; dataset client_addr_vs_rcode dns Rcode:rcode ClientAddr:client replies-only max-cells=50; dataset chaos_types_and_names dns Qtype:qtype Qname:qname chaos-class,queries-only; #dataset country_code dns All:null CountryCode:country queries-only; #dataset asn_all dns IPVersion:dns_ip_version ASN:asn queries-only max-cells=200; dataset idn_qname dns All:null IDNQname:idn_qname queries-only; dataset edns_version dns All:null EDNSVersion:edns_version queries-only; dataset edns_bufsiz dns All:null EDNSBufSiz:edns_bufsiz queries-only; dataset do_bit dns All:null D0:do_bit queries-only; dataset rd_bit dns All:null RD:rd_bit queries-only; dataset idn_vs_tld dns All:null TLD:tld queries-only,idn-only; dataset ipv6_rsn_abusers dns All:null ClientAddr:client queries-only,aaaa-or-a6-only,root-servers-net-only max-cells=50; dataset transport_vs_qtype dns Transport:transport Qtype:qtype queries-only; dataset client_port_range dns All:null PortRange:dns_sport_range queries-only; #dataset second_ld_vs_rcode dns Rcode:rcode SecondLD:second_ld replies-only max-cells=50; #dataset third_ld_vs_rcode dns Rcode:rcode ThirdLD:third_ld replies-only max-cells=50; dataset direction_vs_ipproto ip Direction:ip_direction IPProto:ip_proto any; #dataset dns_ip_version_vs_qtype dns IPVersion:dns_ip_version Qtype:qtype queries-only; dataset response_time dns All:null ResponseTime:response_time; #dataset label_count dns All:null LabelCount:label_count any; #dataset encryption dns All:null Encryption:encryption queries-only; # datasets for collecting data on priming queries at root nameservers #dataset priming_queries dns Transport:transport EDNSBufSiz:edns_bufsiz priming-query,queries-only; #dataset priming_responses dns All:null ReplyLen:msglen priming-query,replies-only; # dataset for monitoring an authoritative nameserver for DNS reflection attack #dataset qr_aa_bits dns Direction:ip_direction QRAABits:qr_aa_bits any; # dataset for servfail response for dnssec validation fail. #dataset servfail_qname dns ALL:null Qname:qname servfail-only,replies-only; # dataset for successful validation. #dataset ad_qname dns ALL:null Qname:qname authentic-data-only,replies-only; # bpf_vlan_tag_byte_order # # Set this to 'host' on FreeBSD-4 where the VLAN id that we # get from BPF appears to already be in host byte order. #bpf_vlan_tag_byte_order host; # match_vlan # # A whitespace-separated list of VLAN IDs. If set, only the # packets with these VLAN IDs will be analyzed by DSC. # #match_vlan 100 200; # statistics_interval # # Specify how often we write statistics, default to 60 seconds. # statistics_interval 60; # no_wait_interval # # Do not wait on interval sync to start capturing, normally DSC will # sleep for time() % statistics_interval to align with the minute # (as was the default interval before) but now if you change the interval # to more then a minute you can use with option to begin capture right # away. # no_wait_interval; # output_format # # Specify the output format, can be give multiple times to output in more then # one format. Default output format is XML. # # Available formats are: # - XML # - JSON # output_format XML; #output_format JSON; # dump_reports_on_exit # # Dump any remaining report before exiting. # # NOTE: Timing in the data files will be off! # #dump_reports_on_exit; # geoip # # Following configuration is used for MaxMind GeoIP Legacy API # if present and enabled during compilation. # #geoip_v4_dat "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIP.dat" STANDARD MEMORY_CACHE MMAP_CACHE; #geoip_v6_dat "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIPv6.dat"; #geoip_asn_v4_dat "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIPASNum.dat" MEMORY_CACHE; #geoip_asn_v6_dat "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoIPASNumv6.dat" MEMORY_CACHE; # ASN/Country Indexer and MaxMind DB # # Following configuration controls what backend the ASN and Country indexer # will use and if/what MaxMind database (GeoIP2) files. # # Available backends: # - geoip # - maxminddb # #asn_indexer_backend geoip; #country_indexer_backend geoip; #maxminddb_asn "/path/to/GeoLite2/ASN.mmdb"; #maxminddb_country "/path/to/GeoList2/Country.mmdb"; # Client Subnet Mask # # Set the IPv4/IPv6 client subnet mask which is used for the # ClientSubnet indexer. # #client_v4_mask 255.255.255.0; #client_v6_mask ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:0000:0000; # Response Time indexer # # These settings are for the response time indexer, it tracks query # to match it with a response and gives statistics about the time it # took to answer the query. # # Available statistical output modes: # - bucket # - log10 (default) # - log2 # #response_time_mode log10; #response_time_max_queries 1000000; # # If the number of queries tracked exceeds max_queries the full_mode # will control how to handle it: # - drop_query: Drop the incoming query. # - drop_oldest: Drop the oldest query being tracked and accept the # incoming one. # #response_time_full_mode drop_query; # # Set the maximum seconds to keep a query but a query can still be # matched to a response while being outside this limit and therefor # there is a mode on how to handle that situation: # - ceil: The query will be counted as successful but the time it took # will be the maximum seconds (think ceiling, or ceil()). # - timed_out: The query will be counted as timed out. # #response_time_max_seconds 5; #response_time_max_sec_mode ceil; # # Control the size of bucket (microseconds) in bucket mode. # #response_time_bucket_size 100; # Known TLDs # # Load known TLDs from a file, see https://data.iana.org/TLD/tlds-alpha-by-domain.txt # #knowntlds_file file; # TLD list (aka Public Suffix List) # # This option changes what DSC considers a TLD (similar to Public Suffix # List) and affects any indexers that gathers statistics on TLDs, such as # the tld, second_ld and third_ld indexers. # The file format is simply one line per suffix and supports commenting out # lines with #. # You can use dsc-psl-convert to convert the Public Suffix List to this # format, see dsc-psl-convert (5) for more information and examples on how # to setup. # #tld_list file;
3. 启动dnsperf
3.1 安装dnsperf
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
yum install dnsperf
3.2 下载测试数据
wget https://github.com/DNS-OARC/sample-query-data/blob/main/queryfile-example-10million-201202_part01.xz
解压后即可使用
3.3 执行压测命令
dnsperf -d queryfile-example-10million-201202_part01 -s 192.168.214.131
4. 安装dsc-datatool
(1). yum方式
cat dsc-datatool.repo [copr:copr.fedorainfracloud.org:group_dnsoarc:dsc] name=Copr repo for dsc owned by @dnsoarc baseurl=https://download.copr.fedorainfracloud.org/results/@dnsoarc/dsc/epel-7-$basearch/ type=rpm-md skip_if_unavailable=True gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://download.copr.fedorainfracloud.org/results/@dnsoarc/dsc/pubkey.gpg repo_gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 enabled_metadata=1
yum install dsc-datatool
(2). pip方式
cd dsc-datatool-1.1.0 python setup.py install
5. 安装influxdb
6. 下载地图数据
https://www.maxmind.com/en/accounts/703068/geoip/downloads 需要输入个人的用户名与密码,根据链接下载即可
根据dsc-datatool源码可以看到,解压后的以.mmdb结尾的地图数据必须放在['/var/lib/GeoIP', '/usr/share/GeoIP', '/usr/local/share/GeoIP']其中一个目录下,
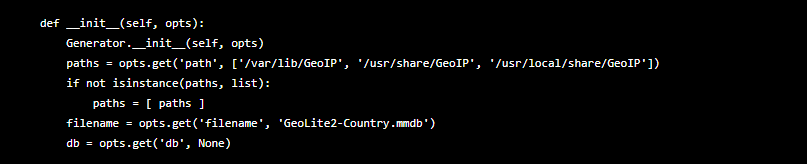
6. 运行dsc-datatool
# 使用influxdb方式:
dsc-datatool --server "192.168.214.131" --node "192.168.214.131" --output ";InfluxDB;file=/home/influx.txt;dml=1;database=dsc" --transform ";Labler;*;yaml=/home/labler.yaml" --transform ";ReRanger;rcode_vs_replylen;range=/64;pad_to=5" --transform ";ReRanger;qtype_vs_qnamelen;range=/16;pad_to=3" --transform ";ReRanger;client_port_range;key=low;range=/2048;pad_to=5" --transform ";ReRanger;edns_bufsiz,priming_queries;key=low;range=/512;pad_to=5;allow_invalid_keys=1" --transform ";ReRanger;priming_responses;key=low;range=/128;pad_to=4" --transform ";NetRemap;client_subnet,client_subnet2,client_addr_vs_rcode,ipv6_rsn_abusers;v4net=24;v6net=48" --generator client_subnet_country --generator ";client_subnet_authority;fetch=no;csv=/usr/local/dsc/iana/ipv4-address-space.csv" --xml "/usr/local/dsc/var/lib/dsc"
参数解释:
--server "192.168.214.131" --node "192.168.214.131": 要监听的机器
--output ";InfluxDB;file=/home/influx.txt;dml=1;database=dsc":输出influxdb需要的数据文件---/home/influx.txt, database就是influxdb的bucket---dsc
--transform ";Labler;*;yaml=/home/labler.yaml": 读取/home/labler.yaml文件,将dns状态码转为文字。
/home/labler.yaml文件的生成方式:
[root@bogon home]# cat iana-dns-params-toyaml.py import yaml import csv from urllib.request import Request, urlopen from io import StringIO rcode = {} qtype = {} opcode = {} for row in csv.reader(StringIO(urlopen(Request('http://www.iana.org/assignments/dns-parameters/dns-parameters-6.csv')).read().decode('utf-8'))): if row[0] == 'RCODE': continue rcode[row[0]] = row[1] for row in csv.reader(StringIO(urlopen(Request('http://www.iana.org/assignments/dns-parameters/dns-parameters-4.csv')).read().decode('utf-8'))): if row[0] == 'TYPE': continue qtype[row[1]] = row[0] for row in csv.reader(StringIO(urlopen(Request('http://www.iana.org/assignments/dns-parameters/dns-parameters-5.csv')).read().decode('utf-8'))): if row[0] == 'OpCode': continue opcode[row[0]] = row[1] y = {} for n in ['rcode', 'client_addr_vs_rcode', 'rcode_vs_replylen']: y[n] = { 'Rcode': {} } for k, v in rcode.items(): y[n]['Rcode'][k] = v for n in ['qtype', 'transport_vs_qtype', 'certain_qnames_vs_qtype', 'qtype_vs_tld', 'qtype_vs_qnamelen', 'chaos_types_and_names', 'dns_ip_version_vs_qtype']: y[n] = { 'Qtype': {} } for k, v in qtype.items(): if v == '*': v = 'wildcard' y[n]['Qtype'][k] = v for n in ['opcode']: y[n] = { 'Opcode': {} } for k, v in rcode.items(): y[n]['Opcode'][k] = v print(yaml.dump(y, explicit_start=True, default_flow_style=False))
[root@bogon home]# python3 iana-dns-params-toyaml.py > /home/labler.yaml # 即可生成
--generator ";client_subnet_authority;fetch=no;csv=/usr/local/dsc/iana/ipv4-address-space.csv": fetch=no表示程序不会去互联网下载ipv4-address-space.csv文件, 通过csv=指定离线下载的ipv4-address-space.csv文件,
可以通过man dsc-datatool-generator client_subnet_authority查看下载链接
https://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv4-address-space/ipv4-address-space.csv
https://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv6-unicast-address-assignments/ipv6-unicast-address-assignments.csv
--xml "/usr/local/dsc/var/lib/dsc": 指定通过dsc软件生成的dns统计数据的目录
使用prometheus形式:
dsc-datatool --server "192.168.214.131" --node "192.168.214.131" --output ";Prometheus;timestamp=hide;file=/home/dns.prom" --transform ";Labler;*;yaml=/home/labler.yaml" --transform ";ReRanger;rcode_vs_replylen;range=/64;pad_to=5" --transform ";ReRanger;qtype_vs_qnamelen;range=/16;pad_to=3" --transform ";ReRanger;client_port_range;key=low;range=/2048;pad_to=5" --transform ";ReRanger;edns_bufsiz,priming_queries;key=low;range=/512;pad_to=5;allow_invalid_keys=1" --transform ";ReRanger;priming_responses;key=low;range=/128;pad_to=4" --transform ";NetRemap;client_subnet,client_subnet2,client_addr_vs_rcode,ipv6_rsn_abusers;net=24" --generator client_subnet_country --generator ";client_subnet_authority;fetch=no;csv=/usr/local/dsc/iana/ipv4-address-space.csv" --xml "/usr/local/dsc/var/lib/dsc"
参数解释:
--output ";Prometheus;timestamp=hide;file=/home/dns.prom" :生成prom文件,将改文件放到textfile目录下让node_exporter读取即可
--xml "/usr/local/dsc/var/lib/dsc" : 这里用单个的xml文件更好,可以改用单个xml文件




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号