回文自动机
回文自动机
PAM 是一种处理回文串的工具,每个节点都表示一个本质不同的回文串。
PAM 由两棵树组成,分别表示奇数长度的回文串与偶数长度的回文串。称两棵树的根为奇根和偶根,分别表示长度为 \(-1, 0\) 的字符串,不表示任何实际的字符串,仅作为初始状态。
定义:
- \(fail\) 指针:指向当前状态的最长回文真后缀所对应的节点。
- 转移边 \(c\) :在首尾各加一个字符 \(c\) 。
- \(\mathrm{len}\) :当前状态的回文串长度。
规定偶根的 \(fail\) 指针指向奇根,而奇根的 \(fail\) 指针并不重要,因为奇根转移出的下一个状态长度为 \(1\) 一定是回文串,即奇根不可能失配。
在线构建
考虑在线添加字符,同时维护每个节点的信息。
新加入一个字符 \(S[n] = c\) 后,就会产生若干以 \(c\) 结尾的回文串,即原先的回文后缀前后各加 \(c\) 。
在 PAM 上从以 \(n - 1\) 结尾的最长回文子串所对应的节点开始,不断走 \(fail\) 指针,直到走到一个点 \(p\) 满足 \(S[n] = S[n - 1 - \mathrm{len}(p)]\) ,即当前状态的上一个字符为 \(c\) 。因为一直跳 \(fail\) 指针最终会跳到奇根,所以这个式子一定会成立。
设第一个满足条件的节点为 \(p\) 。若 \(p\) 没有 \(c\) 的转移,则新建节点 \(q\) ,考虑信息的维护:
- \(\mathrm{len}(q) = \mathrm{len}(p) + 2\) 。
- \(fail_q\) :从 \(fail_p\) 走到的第一个有 \(c\) 的转移边的 \(c\) 的转移。
可以证明总时间复杂度均摊 \(O(n)\) 。
每次加入字符时,至多新增一个点和一个转移,因此状态数上界为 \(n\) ,下面证明每次跳 \(fail\) 的复杂度均摊线性。
设当前 \(fail\) 链长度为 \(k\) ,若需要跳 \(d\) 步才能有出边,则新的状态的深度为 \(k - d + 1\) 。而深度只会增加 \(n\) 次,因此最多只会跳 \(2n\) 次 \(fail\) 指针。
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - len[x] - 1] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
len[++tot] = len[p] + 2;
fail[tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
ch[p][c] = tot;
}
las = ch[p][c];
}
} // namespace PAM
可持久化
注意到经典的构造方式依赖于势能分析,这在存在删除末端字符时复杂度会退化到平方级别。因为可以对于一次势能减少很多的操作不断插入、删除,使得跳 \(fail\) 的复杂度为 \(O(n)\) 。
考虑寻找一个复杂度不依赖于均摊的构建方法。可以发现跳 \(fail\) 链的目的就是找祖先中第一个左边有某字符的点,不妨在每个点上对于每个字符都存下这个位置,每次新建节点时就是继承父亲+单点修改。
可以用主席树做到 \(O(n \log |\sum|)\) ,并且支持可持久化,该算法可以用于构建一个 Trie 的 PAM。
回文理论
串 \(s\) 的本质不同回文子串数量上界为 \(|s|\) 。
若 \(t\) 是回文串 \(s\) 的后缀,则 \(t\) 是 \(s\) 的 border 当且仅当 \(t\) 是回文串。
必要性:对于 \(i \in [1, |t|]\) ,有 \(s[i] = s[|s| - |t| + i] = s[|s| - i + 1]\) ,因此 \(t\) 是回文串。
充分性:对于 \(i \in [1, |t|]\) ,有 \(s[i] = s[|s| - i + 1] = s[|s| - |t| + i]\) ,因此 \(t\) 是 \(s\) 的 border 。
\(t\) 是串 \(s\) 的 border 且满足 \(|s| \le 2|t|\) , \(s\) 是回文串当且仅当 \(t\) 是回文串。
必要性:直接用上面的结论即可得证。
充分性:对于 \(i \in [1, |t|]\) ,有 \(s[i] = s[|s| - |t| + i] = s[|t| - i + 1] = s[|s| - i + 1]\) ,又 \(|s| \le 2|t|\) ,因此 \(s\) 是回文串。
\(|s| - |t|\) 是 \(s\) 的最小周期当且仅当 \(t\) 是 \(s\) 的最长回文真后缀。
考虑回文串 \(x\) , \(y\) 是 \(x\) 的最长回文真后缀, \(z\) 是 \(y\) 的最长回文真后缀,记 \(x = uy, y = vz\) ,则 \(|u| \ge |v|\) ,进一步有:
- 若 \(|u| > |v|\) ,则 \(|u| > |z|\) 。
- 若 \(|u| = |v|\) ,则 \(u = v\) 。
先证明 \(|u| \ge |v|\) ,由上条得 \(|u|\) 是 \(x\) 的最小周期,\(|v|\) 是 \(y\) 的最小周期。由于 \(y\) 是 \(x\) 的后缀,因此 \(|u|\) 也是 \(y\) 的周期,因此 \(|u| \ge |v|\) 。
若 \(|u| > |v|\) ,设 \(x = vw\) ,则 \(z\) 是 \(w\) 的 border。考虑反证法,若 \(|u| \le |z|\) ,则 \(|w| = |zu| \le 2 |z|\) ,因此 \(w\) 是回文串且 \(w\) 是 \(x\) 的 border,由 \(|u| > |v|\) 推得 \(|w| > |y|\) ,矛盾。
若 \(|u| = |v|\) ,由于 \(u, v\) 都是 \(x\) 的前缀,因此 \(u = v\) 。
Palindrome Series :\(s\) 的所有回文后缀按照长度排序后可以划分为 \(\log|s|\) 段等差数列。
每个回文后缀都是一个 border,直接用 border 理论证明即可。
若回文串 \(s\) 有周期 \(p\) ,则一个循环节必然可以被拆成两个长度分别为 \(s \bmod p\) 和 \(p - s \bmod p\) 的回文串。
记循环节为 \(t\) ,将 \(s\) 记为 \(t^k t_1\) ,其中 \(t_1\) 是 \(t\) 的真前缀,记作 \(t = t_1 t_2\) ,则 \(t_2 t_1\) 是 \(s\) 的后缀。
记 \(t\) 的反转为 \(t'\) ,则 \(t' = t_2' + t_1'\) ,又因为 \(s\) 是回文串,因此 \(t'\) 是 \(s\) 的后缀,因此 \(t' = t_2 + t_1\) ,故 \(t_1, t_2\) 均为回文串。
设 \(v\) 为回文串 \(u\) 的最长回文真前/后缀,若 \(|v| \ge \frac{|u|}{2}\) ,则 \(v\) 只会在 \(u\) 中恰好匹配两次,分别作为前缀和后缀。
考虑反证法,若匹配次数超过 \(3\) ,由 border 理论,\(v\) 在 \(u\) 中的匹配位置构成等差序列,且公差为 \(v\) 的周期。
由上条,记 \(v = (v_1 v_2)^k v_1\) ,则相邻两个匹配位置的并为 \((v_1 v_2)^{2k} v_1\) ,而这是一个更长的回文前缀,矛盾。
回文划分
最小回文划分:将 \(S\) 划分为若干回文串的拼接,最小化回文串数量。
考虑 DP,记 \(f_i\) 表示 \(S[1, i]\) 的最小划分数,转移只需要枚举 \(S[1, i]\) 的所有回文后缀即可,直接做可以做到 \(O(n^2)\) 。
考虑利用 Palindrome Series 优化枚举结构,建立 PAM 结构后,考虑对每个状态额外维护:
- \(diff_u\) :\(u\) 与 \(fail_u\) 的长度差,即 \(\mathrm{len}(u) - \mathrm{len}(fail_u)\) 。
- \(slink_u\) :\(u\) 跳 fail 跳到的第一个满足 \(diff\) 与 \(u\) 不同的点,即 \(u\) 所在等差数列中长度最小的点。
由 Palindrome Series ,跳 \(slink\) 的复杂度是 \(O(\log |S|)\) 的,考虑将一个等差数列表示的所有回文串的 DP 值合并到最长的回文串上。
设 \(g_u\) 表示 \(u\) 所在等差数列的 DP 值贡献和,其中 \(u\) 是这个等差数列中长度最长的节点。
假设当前枚举到 \(i\) ,PAM 上对应状态为 \(x\) 。如图,\(g_x\) 包含的 DP 值是橙色位置( \(slink_x\) 被算在下一个等差数列中)。\(fail_x\) 上一次出现的结束位置是 \(i - diff_x\) ,\(g_{fail_x}\) 包含的 DP 值是蓝色位置。
观察可以发现 \(g_x\) 实际相当于 \(g_{fail_x}\)和多出来一个位置的 DP 值之和,多出来的位置是 \(i - diff_x - \mathrm{len}(slink_x)\) 。
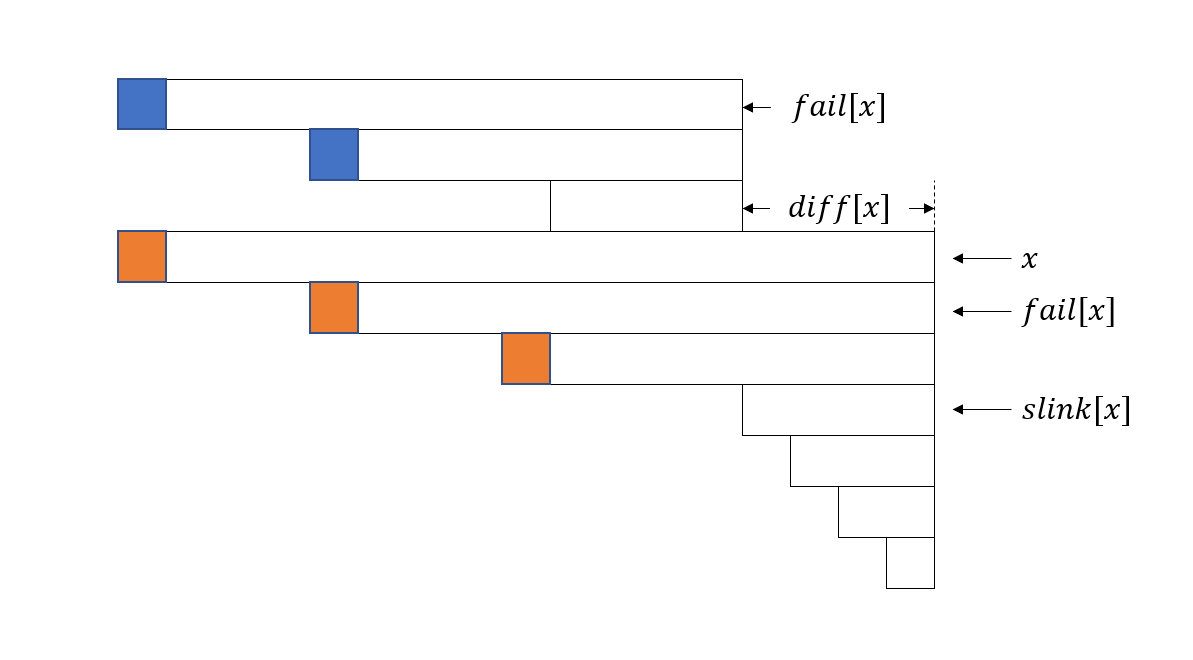
最后再用 \(g_x\) 去更新当前的 DP 值,这部分等差数列的贡献就算完了,不断跳 \(slink_x\) 重复这个过程即可,时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\) 。
应用
基本应用
P5496 【模板】回文自动机(PAM)
给出长度为 \(n\) 的字符串 \(S\) ,求以每个 \(i \in [1, n]\) 结尾的回文串数量。
\(n \le 5 \times 10^5\) ,强制在线
对每个状态 \(u\) 记录其回文后缀的数量 \(sum(u)\) ,则有转移 \(sum(u) = sum(fail_u) + 1\) ,直接做即可做到线性。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 7, S = 26;
char str[N];
int n;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], len[N], fail[N], cnt[N];
int tot, las, n;
inline void prework() {
str[n = 0] = -1, tot = las = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1, fail[0] = 1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline int extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
cnt[tot] = cnt[fail[tot]] + 1;
}
return cnt[las = ch[p][c]];
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s", str + 1), n = strlen(str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1, lstans = 0; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%d ", lstans = PAM::extend((str[i] - 'a' + lstans) % 26));
return 0;
}
P4555 [国家集训队] 最长双回文串
定义双回文串为可以分割为两个回文串的串,求最长双回文串的长度。
\(n \le 10^5\)
对正串反串都建立 PAM ,求出 \(L_i\) 表示以 \(i\) 结尾的最长回文串长度,\(R_i\) 表示以 \(i\) 开始的最长回文串长度,答案为 \(\max(L_i + R_{i + 1})\) ,时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。
类似的题目:
- CF17E Palisection :补集转化即可用类似的方法解决。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 7, S = 26;
int L[N], R[N];
char str[N];
int n;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N];
int tot, las, n;
inline int newnode() {
++tot, fail[tot] = len[tot] = 0;
memset(ch[tot], 0, sizeof(int) * S);
return tot;
}
inline void prework() {
memset(ch[0], 0, sizeof(int) * S), memset(ch[1], 0, sizeof(int) * S);
las = tot = 1, str[n = 0] = -1;
fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
int q = newnode();
fail[q] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[q] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = q;
}
las = ch[p][c];
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s", str + 1), n = strlen(str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a'), L[i] = PAM::len[PAM::las];
PAM::prework();
for (int i = n; i; --i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a'), R[i] = PAM::len[PAM::las];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
ans = max(ans, L[i] + R[i + 1]);
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
P3649 [APIO2014] 回文串
求所有回文子串中出现次数乘子串长度的最大值。
\(n \le 3 \times 10^5\)
考虑插入一个 \(S[i]\) 后每个状态出现次数的变化,发现就是 fail 树上到根的链加,因此可以树上差分后转化为单点加与子树查询。
由于 PAM 构造过程中,节点本身就是按照拓扑序插入,因此只要逆序枚举所有状态,将当前状态出现次数加到其 \(fail\) 指针对应状态的出现次数上即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 7, S = 26;
char str[N];
int n;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], cnt[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
}
++cnt[las = ch[p][c]];
}
inline ll solve() {
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = tot; i > 1; --i)
ans = max(ans, 1ll * cnt[i] * len[i]), cnt[fail[i]] += cnt[i];
return ans;
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s", str + 1), n = strlen(str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a');
printf("%lld", PAM::solve());
return 0;
}
P5555 秩序魔咒
求两个串的最长公共回文子串即方案数。
\(n, m \le 3 \times 10^5\)
对两个串分别建出 PAM 后一起在上面跑转移边即可,时间复杂度 \(O(n |\sum|)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 7, S = 26;
char a[N], b[N];
int n, m, ans1, ans2;
struct PAM {
int ch[N][S], [N], fail[N], len[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
}
las = ch[p][c];
}
} A, B;
void dfs(int u, int v) {
if (A.len[u] > ans1)
ans1 = A.len[u], ans2 = 1;
else if (A.len[u] == ans1)
++ans2;
for (int i = 0; i < S; ++i)
if (A.ch[u][i] && B.ch[v][i])
dfs(A.ch[u][i], B.ch[v][i]);
}
signed main() {
scanf("%d%d%s%s", &n, &m, a + 1, b + 1);
A.prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
A.extend(a[i] - 'a');
B.prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
B.extend(b[i] - 'a');
dfs(0, 0), dfs(1, 1);
printf("%d %d", ans1, ans2);
return 0;
}
P5685 [JSOI2013] 快乐的 JYY
求两个串相等的回文子串对数,出现位置不同算不同。
\(n, m \le 5 \times 10^4\)
建出一个串的 PAM,然后用另一个串跑匹配,匹配到的点的贡献就是 fail 链的 \(cnt\) 和。
注意扩展时两个串两端的字符都要判断是否相等,时间复杂度线性。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 7, S = 26;
char a[N], b[N];
int n, m;
namespace PAM {
ll sum[N];
int ch[N][S];
int a[N], fail[N], len[N], cnt[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
a[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (a[n - 1 - len[x]] != a[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
a[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
}
++cnt[las = ch[p][c]];
}
inline void build() {
for (int i = tot; i >= 2; --i)
cnt[fail[i]] += cnt[i];
cnt[0] = cnt[1] = sum[0] = sum[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= tot; ++i)
sum[i] = sum[fail[i]] + cnt[i];
}
inline ll query(char *str, int m) {
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 1, x = 0; i <= m; ++i) {
int c = str[i] - 'A';
while (x != 1 && (!ch[x][c] || !(i - 1 - len[x]) || b[i] != b[i - 1 - len[x]]))
x = fail[x];
if (ch[x][c])
x = ch[x][c];
res += sum[x];
}
return res;
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s%s", a + 1, b + 1);
n = strlen(a + 1), m = strlen(b + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(a[i] - 'A');
PAM::build();
printf("%lld\n", PAM::query(b, m));
return 0;
}
Fail 指针的推广
P4287 [SHOI2011]双倍回文
定义一个串为双倍回文串当且仅当其可以写作 \(ww^Rww^R\) 的形式,其中 \(w^R\) 表示 \(w\) 翻转的结果。求最长双倍回文子串的长度。
\(n \le 5 \times 10^5\)
定义指针 \(hf\) 指向长度不超过当前状态一半的最长回文后缀的节点,求法与 \(fail\) 指针类似:
- 新建一个节点后,若其长度 \(\le 2\) ,那么其 \(hf\) 指针指向其 \(fail\) 节点。
- 否则从它父亲的 \(hf\) 指针指向节点开始跳 \(fail\) ,直到跳到某个节点所表示的回文串的两侧都可以扩展这个字符且扩展后的长度不超过当前节点长度的一半,则令 \(hf\) 指针就指向该节点的儿子。
求解 \(hf\) 指针均摊也是线性的。
一个字符串满足双倍回文,当且仅当其长度是 \(4\) 的倍数且 \(hf\) 指针指向的节点所表示的回文串长度刚好是这个字符串长度的一半。
枚举每个节点更新答案即可,时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 7, S = 26;
char str[N];
int n;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], hf[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
if (len[tot] <= 2)
hf[tot] = fail[tot];
else {
int x = hf[p];
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n] || len[x] + 2 > len[tot] / 2)
x = fail[x];
hf[tot] = ch[x][c];
}
}
las = ch[p][c];
}
inline int solve() {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= tot; ++i)
if (!(len[i] & 3) && len[hf[i]] == len[i] / 2)
ans = max(ans, len[i]);
return ans;
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%d%s", &n, str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a');
printf("%d", PAM::solve());
return 0;
}
P4762 [CERC2014] Virus synthesis
初始有一个空串,利用下面的操作构造出给定串 \(S\) 。
串开头或末尾加一个字符。
串开头或末尾加一个该串的逆串。
最小化操作数。
\(|S| \le 10^5\),字符集为 \(\{ A, T, C, G \}\)
显然操作二越多越好,而经过操作二之后的串必定是一个回文串,所以最后的答案肯定是由一个回文串后面不断暴力添加字符得来。
先建 PAM ,记 \(f_i\) 表示转移到 \(i\) 的最少操作次数,答案即为 \(f_i + n - \mathrm{len}(i)\) 。
对于 \(f\) 的转移,先令 \(f_i = \mathrm{len}(i)\) 表示仅用操作一。然后考虑操作二,对于一个 \(2 | \mathrm{len}\) 的状态 \(u\) ,有:
-
DAG 上的转移:对于一个转移边 \(u \to v\) ,在形成 \(u\) 之前先在前面加一个字符后再操作二,有 \(f_u + 1 \to f_v\) 。
-
fail 树上的转移:先填好一部分再用操作二,发现可以这样操作的串的长度不能超过当前串长度的一半,有 \(f_{hf_u} + \frac{\mathrm{len}(u)}{2} - \mathrm{len}(hf_u) + 1 \to f_u\) 。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 7, S = 4;
char str[N];
int n;
inline int trans(char c) {
if (c == 'A')
return 0;
else if (c == 'C')
return 1;
else if (c == 'G')
return 2;
else
return 3;
}
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], hf[N], f[N];
int tot, las, n;
inline void prework() {
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(int) * S * (tot + 1));
las = tot = 1, str[n = 0] = -1;
fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
if (len[tot] <= 2)
hf[tot] = fail[tot];
else {
int x = hf[p];
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n] || len[x] + 2 > len[tot] / 2)
x = fail[x];
hf[tot] = ch[x][c];
}
}
las = ch[p][c];
}
inline void solve() {
memcpy(f, len, sizeof(int) * (tot + 1));
f[0] = 1, f[1] = 0;
for (int u = 0; u <= tot; ++u) {
if (len[u] & 1)
continue;
f[u] = min(f[u], f[hf[u]] + len[u] / 2 - len[hf[u]] + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < S; ++i)
if (ch[u][i])
f[ch[u][i]] = min(f[ch[u][i]], f[u] + 1);
}
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
scanf("%s", str + 1), n = strlen(str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(trans(str[i]));
PAM::solve();
int ans = n;
for (int i = 2; i <= PAM::tot; ++i)
ans = min(ans, PAM::f[i] + n - PAM::len[i]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
CF835D Palindromic characteristics
递归定义 \(k\) 阶回文串 \(S\) :
- 若 \(k = 1\) ,则要求 \(S\) 是回文串。
- 否则要求 \(S\) 长度为 \(\lfloor \frac{|s|}{2} \rfloor\) 的前半部分和后半部分为相等的 \(k - 1\) 阶回文串。
给定长度为 \(n\) 的字符串 \(S\) ,对于 \(i \in [1, n]\) ,求 \(i\) 阶回文子串数量。
\(n \le 5000\)
首先不难发现,一个 \(k\) 阶回文串同时是一个 \(k - 1\) 阶回文串,因此只要求出回文串二点最高阶数即可。
建出 PAM,设 \(f_i\) 表示 \(i\) 状态的最高阶数,则有转移:
不难做到线性。
类似的题目:Palindromeness
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e3 + 7, S = 26;
int ans[N];
char str[N];
int n;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], fail[N], len[N], cnt[N], hf[N], f[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
if (len[tot] <= 2)
hf[tot] = fail[tot];
else {
int x = hf[p];
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n] || len[x] + 2 > len[tot] / 2)
x = fail[x];
hf[tot] = ch[x][c];
}
}
++cnt[las = ch[p][c]];
}
inline void solve() {
for (int i = tot; i > 1; --i)
cnt[fail[i]] += cnt[i];
for (int i = 2; i <= tot; ++i)
ans[f[i] = (len[hf[i]] == len[i] / 2 ? f[hf[i]] + 1 : 1)] += cnt[i];
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s", str + 1), n = strlen(str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a');
PAM::solve();
for (int i = n - 1; i; --i)
ans[i] += ans[i + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
动态维护 PAM
CF1738H Palindrome Addicts
初始有一空串,\(n\) 次操作,每次在前端删除一个字符或在末端插入一个字符,每次操作后求本质不同回文串数量。
\(n \le 10^6\)
考虑增量维护忽略删除操作得到的 PAM,每个结点维护其最后一次出现的右端点。
加入字符时,暴力将 PAM 的指针向上跳到第一个没有被删除的回文串,那么这个点在 \(fail\) 树上到根的路径都要进行一次标记。
删除字符时,只需将最后一次出现的左端点在当前位置的所有点删掉。
但是如果直接跳 \(fail\) 标记整条链,复杂度并不优秀。观察 PAM 结构可以发现删除一定是从叶子开始,因此标记可以只打在当前点上,删除当前点时再推到 \(fail\) 上。
实现可以动态维护一个 vector 表示每个左端点被删时可能会被删掉的状态,同时维护每个状态的度数,若一个状态最后一次出现的左端点为当前端点且其为叶子,则删去。如果不维护度数可能会出现儿子的信息还没推上来就被删除的情况。
时间复杂度均摊 \(O(n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 7, S = 26;
namespace PAM {
vector<int> vec[N];
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], deg[N], mxr[N];
ll sum;
int tot = 1, las = 1, tl = 1, tr;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[tr - 1 - len[x]] != str[tr])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void spread(int x, int k) {
if (x <= 1)
return;
if (!mxr[x])
++sum, ++deg[fail[x]];
if (mxr[x] < k)
vec[k - len[x] + 1].emplace_back(x), mxr[x] = k;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++tr] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
len[++tot] = len[p] + 2;
fail[tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
ch[p][c] = tot;
}
las = ch[p][c];
while (len[las] > tr - tl + 1)
las = fail[las];
spread(las, tr);
}
inline void pop_front() {
for (int x : vec[tl])
if (mxr[x] - len[x] + 1 == tl && !deg[x])
spread(fail[x], mxr[x]), --deg[fail[x]], --sum, mxr[x] = 0;
++tl;
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
PAM::prework();
while (n--) {
string op;
cin >> op;
if (op == "push") {
char c;
cin >> c;
PAM::extend(c - 'a');
} else
PAM::pop_front();
cout << PAM::sum << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
HDU5421 Victor and String
初始有一个空串 \(S\) ,\(n\) 次操作:
- 在开头加一个字符。
- 在结尾加一个字符。
- 求本质不同回文串数量。
- 求回文串数量。
\(n \le 10^5\)
考虑维护 \(fail'\) 指针表示自动机中串的最长回文前缀。不难发现回文前缀同时也是回文后缀,所以总有 \(fail' = fail\) ,不必额外维护。
额外记录一个前端插入的 \(las\) 即可,前端插入和后端插入操作是类似的。
所以,只需要记下正反两条终止链的末端就可以实现两侧插入了。
注意当整个串变成回文串的时候,要更新另一侧的末端。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 7, S = 26;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], dep[N];
ll sum;
int tot, lasl, lasr, tl, tr;
inline void prework(int mid) {
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(int) * (tot + 1) * S);
fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
lasl = lasr = tot = 1, sum = 0;
tl = mid + 1, tr = mid;
}
inline int getfail_front(int x) {
while (tl + 1 + len[x] > tr || str[tl + 1 + len[x]] != str[tl])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend_front(int c) {
str[--tl] = c;
int p = getfail_front(lasl);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail_front(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
dep[tot] = dep[fail[tot]] + 1;
}
sum += dep[lasl = ch[p][c]];
if (len[lasl] == tr - tl + 1)
lasr = lasl;
}
inline int getfail_back(int x) {
while (tr - 1 - len[x] < tl || str[tr - 1 - len[x]] != str[tr])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend_back(int c) {
str[++tr] = c;
int p = getfail_back(lasr);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail_back(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
dep[tot] = dep[fail[tot]] + 1;
}
sum += dep[lasr = ch[p][c]];
if (len[lasr] == tr - tl + 1)
lasl = lasr;
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n;
while (cin >> n) {
PAM::prework(n);
while (n--) {
int op;
cin >> op;
if (op == 1) {
char c;
cin >> c;
PAM::extend_front(c - 'a');
} else if (op == 2) {
char c;
cin >> c;
PAM::extend_back(c - 'a');
} else if (op == 3)
cout << PAM::tot - 1 << '\n';
else
cout << PAM::sum << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
回文理论
HDU6320 Cut The String
定义串 \(t\) 的回文切分为二元串组 \((a, b)\) ,其中 \(t = a + b\) 且 \(a, b\) 均为回文串。
给出一个字符串 \(s\) ,每次询问一个子串的回分切分方案数。
\(n \le 10^5\)
对原串正反跑两次 PAM,求出在每个位置开始/结尾的回文串长度集合。
对于每组询问,取出在 \(l\) 开头的长度集合 \(L_1\) ,在 \(r\) 结尾的长度集合 \(L_2\) ,要选出 \(t_1 \in L_1, t_2 \in L_2\) 使得 \(t_1 + t_2 = r - l + 1\) 。
直接暴力是不行的,利用回文 Border 理论,在某点开始/结尾的回文串长度集合可以被划分成 \(O(\log n)\) 个等差数列。
现在就是要对 \(O(\log^2 n)\) 对等差数列,计算有多少种方案各选一数和为定值。不难转化为等差序列求交集。
又能发现,由于 Border 的长度区间可以按照 \([2^k, 2^{k + 1})\) 划分,实际上每个等差序列只能对应到 \(O(1)\) 个,所以只需要求 \(O(\log n)\) 次交。
等差序列求交集相当于求同余方程在一定范围内的解的个数,可以用 exCRT 求解。
时间复杂度 \(O(n \log^2 n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 7, S = 27;
struct Node {
int l, r, d;
};
struct PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], len[N], fail[N], diff[N], slink[N], id[N];
int tot, las, n;
inline void prework() {
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(int) * (tot + 1) * S);
str[n = 0] = -1, tot = las = 1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - len[x] - 1] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
diff[tot] = len[tot] - len[fail[tot]];
slink[tot] = (diff[tot] == diff[fail[tot]] ? slink[fail[tot]] : tot);
}
id[n] = las = ch[p][c];
}
inline vector<Node> query(int x) {
vector<Node> vec;
for (x = id[x]; x > 1; x = fail[slink[x]])
vec.emplace_back((Node){len[slink[x]], len[x], diff[x]});
return vec;
}
} A, B;
char str[N];
int n, m;
template <class T = int>
inline T read() {
char c = getchar();
bool sign = (c == '-');
while (c < '0' || c > '9')
c = getchar(), sign |= (c == '-');
T x = 0;
while ('0' <= c && c <= '9')
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c & 15), c = getchar();
return sign ? (~x + 1) : x;
}
inline ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (b) {
ll g = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return g;
} else
return x = 1, y = 0, a;
}
inline ll inv(ll a, ll p) {
ll x, y;
exgcd(a, p, x, y);
return (x % p + p) % p;
}
inline pair<ll, ll> merge(pair<ll, ll> a, pair<ll, ll> b) {
ll a1 = a.first, m1 = a.second, a2 = b.first, m2 = b.second,
x, y, g = exgcd(m1, m2, x, y), m = m1 / g * m2, c = ((a2 - a1) % m + m) % m;
return c % g ? make_pair(-1ll, -1ll) : make_pair((a1 + 1ll * x * (c / g) % m * m1 % m) % m, m);
}
inline int calc(Node a, Node b) {
auto res = merge(make_pair(a.l % a.d, a.d), make_pair(b.l % b.d, b.d));
if (res == make_pair(-1ll, -1ll))
return 0;
ll x = res.first, m = res.second;
if (x < max(a.l, b.l))
x += (max(a.l, b.l) - x + m - 1) / m * m;
if (x > min(a.r, b.r))
return 0;
return (min(a.r, b.r) - x) / m + 1;
}
signed main() {
int T = read();
while (T--) {
n = read(), m = read();
scanf("%s", str + 1);
A.prework(), B.prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
A.extend(str[i] - 'a'), B.extend(str[n - i + 1] - 'a');
while (m--) {
int l = read(), r = read(), len = r - l + 1;
vector<Node> vec1 = A.query(r), vec2 = B.query(n - l + 1);
for (Node &it : vec2)
it = (Node){len - it.r, len - it.l, it.d};
int ans = 0;
for (Node it1 : vec1)
for (Node it2 : vec2)
if (it2.l <= it1.r && it1.l <= it2.r)
ans += calc(it1, it2);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
LOJ6070. 「2017 山东一轮集训 Day4」基因
给定一个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串,\(q\) 次询问区间本质不同回文子串数量,强制在线。
\(n \le 10^5\)
先考虑离线的情况,记 \(c_i\) 表示最后出现的位置以 \(i\) 开头的回文串的数量,那么从小到大扫右端点,答案即为 \(\sum_{i = l}^r c_i\) 。
强制在线考虑主席树维护 \(c\) ,需要考虑移动右端点的影响。对于 fail 链上的字符串,需要将其出现处的 \(c_i\) 都减一,然后在新出现处的 \(c_i\) 都加一。
考虑 Palindrome Series,对于一个等差数列,中间的加减都会抵消掉。
证明:由于所有的回文后缀按值域可以划分为若干 \([2^k, 2^{k + 1})\) 的等差序列,因此对于一段等差序列,每一项都长于上一项的一半,因此后一项上一次出现的位置即为前一项的前缀。将这个等差序列用 \((l, r, d)\) 表示,则相当于每一项都从上一项的前缀移动到后缀,移动距离恰好为 \(d\) 。
只要对等差数列中最长串上一次出现的位置的 \(c\) 减一,再对等差链顶新出现的位置的 \(c\) 加一即可。
于是只需支持查询一个节点目前的出现位置。左端点是不好维护的,考虑维护右端点,需要对一条链上的信息取 \(\max\) ,树上差分转化为单点修改、子树查 \(\max\) 即可。
时空复杂度 \(O(n \log^2 n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 7, S = 26;
char str[N];
int tp, n, m;
namespace SGT {
int mx[N << 2];
inline int ls(int x) {
return x << 1;
}
inline int rs(int x) {
return x << 1 | 1;
}
void update(int x, int nl, int nr, int p, int k) {
mx[x] = max(mx[x], k);
if (nl == nr)
return;
int mid = (nl + nr) >> 1;
if (p <= mid)
update(ls(x), nl, mid, p, k);
else
update(rs(x), mid + 1, nr, p, k);
}
int query(int x, int nl, int nr, int l, int r) {
if (l <= nl && nr <= r)
return mx[x];
int mid = (nl + nr) >> 1;
if (r <= mid)
return query(ls(x), nl, mid, l, r);
else if (l > mid)
return query(rs(x), mid + 1, nr, l, r);
else
return max(query(ls(x), nl, mid, l, r), query(rs(x), mid + 1, nr, l, r));
}
} // namespace SGT
namespace SMT {
const int S = 3e7 + 7;
ll s[S];
int rt[N], lc[S], rc[S];
int tot;
int update(int x, int nl, int nr, int p, int k) {
int y = ++tot;
lc[y] = lc[x], rc[y] = rc[x], s[y] = s[x] + k;
if (nl == nr)
return y;
int mid = (nl + nr) >> 1;
if (p <= mid)
lc[y] = update(lc[x], nl, mid, p, k);
else
rc[y] = update(rc[x], mid + 1, nr, p, k);
return y;
}
ll query(int x, int nl, int nr, int l, int r) {
if (l <= nl && nr <= r)
return s[x];
int mid = (nl + nr) >> 1;
if (r <= mid)
return query(lc[x], nl, mid, l, r);
else if (l > mid)
return query(rc[x], mid + 1, nr, l, r);
else
return query(lc[x], nl, mid, l, r) + query(rc[x], mid + 1, nr, l, r);
}
} // namespace SMT
namespace PAM {
struct Graph {
vector<int> e[N];
inline void insert(int u, int v) {
e[u].emplace_back(v);
}
} G;
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], diff[N], slink[N], id[N], in[N], out[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n, dfstime;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
diff[tot] = len[tot] - len[fail[tot]];
slink[tot] = (diff[tot] == diff[fail[tot]] ? slink[fail[tot]] : tot);
}
id[n] = las = ch[p][c];
}
void dfs(int u) {
in[u] = ++dfstime;
for (int v : G.e[u])
dfs(v);
out[u] = dfstime;
}
inline void build() {
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; ++i)
if (i != 1)
G.insert(fail[i], i);
dfs(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
SMT::rt[i] = SMT::rt[i - 1];
for (int x = id[i]; x; x = fail[slink[x]]) {
int r = SGT::query(1, 1, dfstime, in[x], out[x]);
if (r)
SMT::rt[i] = SMT::update(SMT::rt[i], 1, n, r - len[x] + 1, -1);
SMT::rt[i] = SMT::update(SMT::rt[i], 1, n, i - len[slink[x]] + 1, 1);
}
SGT::update(1, 1, dfstime, in[id[i]], i);
}
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%d%d%d%s", &tp, &n, &m, str + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a');
PAM::build();
int lstans = 0;
while (m--) {
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
if (tp)
l ^= lstans, r ^= lstans;
printf("%d\n", lstans = SMT::query(SMT::rt[r], 1, n, l, r));
}
return 0;
}
回文划分
CF932G Palindrome Partition
给定一个串 \(S\),把串分为偶数段 \(s_{1 \sim k}\) ,求满足 \(s_i = s_{k - i + 1}\) 的划分方案数。
\(n \le 10^6\)
考虑将 \(s_{k - i + 1}\) 翻转,这样两个串的相等的形式就可以类似于回文。具体的,将 \(S\) 的后半部分翻转,然后逐个插入 \(S\) 的前一半的相邻两个之间,那么字符串将变为 \(S_1 S_n S_2 S_{n - 1} \cdots S_{\frac{n}{2}} S_{\frac{n}{2} + 1}\) 。
可以发现原划分方案恰好对应了对新串进行偶数长度的回文划分的方案,问题转化为求偶数长度的回文划分方案数。
一个简单的处理方式是只在偶数位置更新 DP 数组,时间复杂度 \(O(n \log n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e6 + 7, S = 26;
char str[N];
int n;
inline int add(int x, int y) {
x += y;
if (x >= Mod)
x -= Mod;
return x;
}
inline int dec(int x, int y) {
x -= y;
if (x < 0)
x += Mod;
return x;
}
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], diff[N], slink[N], g[N], f[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1, f[0] = 1;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
diff[tot] = len[tot] - len[fail[tot]];
slink[tot] = (diff[tot] == diff[fail[tot]] ? slink[fail[tot]] : fail[tot]);
}
las = ch[p][c];
for (int x = las; x; x = slink[x]) {
g[x] = f[n - diff[x] - len[slink[x]]];
if (diff[x] == diff[fail[x]])
g[x] = add(g[x], g[fail[x]]);
if (~n & 1)
f[n] = add(f[n], g[x]);
}
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s", str + 1), n = strlen(str + 1);
if (n & 1)
return puts("0"), 0;
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 2; ++i)
PAM::extend(str[i] - 'a'), PAM::extend(str[n - i + 1] - 'a');
printf("%d", PAM::f[n]);
return 0;
}
CF906E Reverses
给出两个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串 \(s\) 和 \(t\) ,求最少翻转 \(t\) 的几个不相交的区间使得 \(s = t\) ,并给出方案。
\(n \le 5 \times 10^5\)
令 \(S = s_1 t_1 s_2 t_2 \cdots\) ,问题转化为 \(S\) 的最小偶回文划分。
转移的时候记一下路径即可,注意长度为 \(2\) 的回文子串不用翻转,不对回文划分数量产生贡献,时间复杂度 \(O(n \log n)\) 。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1e6 + 7, S = 26;
char s[N], t[N];
int n;
namespace PAM {
int ch[N][S], str[N], fail[N], len[N], diff[N], slink[N];
int f[N], pref[N], g[N], preg[N];
int tot = 1, las = 1, n;
inline void prework() {
str[0] = -1, fail[0] = 1, len[0] = 0, len[1] = -1;
memset(f, inf, sizeof(f)), memset(g, inf, sizeof(g));
f[0] = g[0] = 0;
}
inline int getfail(int x) {
while (str[n - 1 - len[x]] != str[n])
x = fail[x];
return x;
}
inline void extend(int c) {
str[++n] = c;
int p = getfail(las);
if (!ch[p][c]) {
fail[++tot] = ch[getfail(fail[p])][c];
len[tot] = len[p] + 2, ch[p][c] = tot;
diff[tot] = len[tot] - len[fail[tot]];
slink[tot] = (diff[tot] == diff[fail[tot]] ? slink[fail[tot]] : fail[tot]);
}
las = ch[p][c];
for (int x = las; x; x = slink[x]) {
g[x] = f[preg[x] = n - diff[x] - len[slink[x]]];
if (diff[x] == diff[fail[x]] && g[fail[x]] < g[x])
g[x] = f[preg[x] = preg[fail[x]]];
if (~n & 1) {
if (g[x] + 1 < f[n])
f[n] = f[pref[n] = preg[x]] + 1;
if (str[n] == str[n - 1] && f[n - 2] < f[n])
f[n] = f[pref[n] = n - 2];
}
}
}
} // namespace PAM
signed main() {
scanf("%s%s", s + 1, t + 1), n = strlen(s + 1);
PAM::prework();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
PAM::extend(s[i] - 'a'), PAM::extend(t[i] - 'a');
if (PAM::f[n * 2] == inf)
return puts("-1"), 0;
printf("%d\n", PAM::f[n * 2]);
for (int x = n * 2; x; x = PAM::pref[x])
if (x - PAM::pref[x] != 2)
printf("%d %d\n", PAM::pref[x] / 2 + 1, x / 2);
return 0;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号