![]()
package com.study.lock.locks1;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class JamesReadWriteLock {
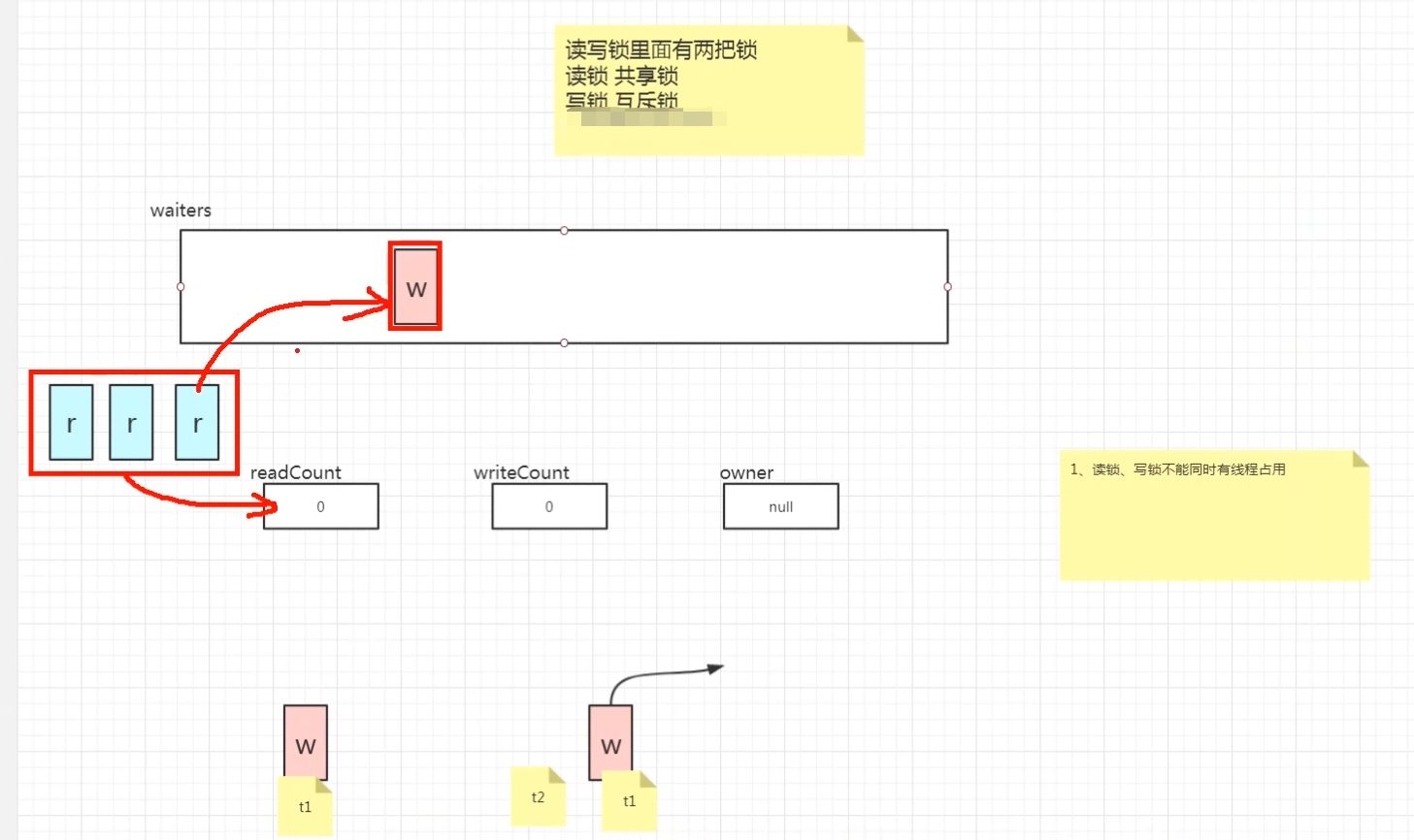
volatile AtomicInteger readCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
AtomicInteger writeCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
//独占锁 拥有者
AtomicReference<Thread> owner = new AtomicReference<>();
//等待队列
public volatile LinkedBlockingQueue<WaitNode> waiters = new LinkedBlockingQueue<WaitNode>();
class WaitNode{
int type = 0; //0 为想获取独占锁的线程, 1为想获取共享锁的线程
Thread thread = null;
int arg = 0;
public WaitNode(Thread thread, int type, int arg){
this.thread = thread;
this.type = type;
this.arg = arg;
}
}
//获取独占锁
public void lock() {
int arg = 1;
//尝试获取独占锁,若成功,退出方法, 若失败...
if (!tryLock(arg)){
//标记为独占锁
WaitNode waitNode = new WaitNode(Thread.currentThread(), 0, arg);
waiters.offer(waitNode); //进入等待队列
//循环尝试拿锁
for(;;){
//若队列头部是当前线程
WaitNode head = waiters.peek();
if (head!=null && head.thread == Thread.currentThread()){
if (!tryLock(arg)){ //再次尝试获取 独占锁
LockSupport.park(); //若失败,挂起线程
} else{ //若成功获取
waiters.poll(); // 将当前线程从队列头部移除
return; //并退出方法
}
}else{ //若不是队列头部元素
LockSupport.park(); //将当前线程挂起
}
}
}
}
//释放独占锁
public boolean unlock() {
int arg = 1;
//尝试释放独占锁 若失败返回true,若失败...
if(tryUnlock(arg)){
WaitNode next = waiters.peek(); //取出队列头部的元素
if (next !=null){
Thread th = next.thread;
LockSupport.unpark(th); //唤醒队列头部的线程
}
return true; //返回true
}
return false;
}
//尝试获取独占锁
public boolean tryLock(int acquires) {
//如果read count !=0 返回false
if (readCount.get() !=0)
return false;
int wct = writeCount.get(); //拿到 独占锁 当前状态
if (wct==0){
if (writeCount.compareAndSet(wct, wct + acquires)){ //通过修改state来抢锁
owner.set(Thread.currentThread()); // 抢到锁后,直接修改owner为当前线程
return true;
}
}else if (owner.get() == Thread.currentThread()){
writeCount.set(wct + acquires); //修改count值
return true;
}
return false;
}
//尝试释放独占锁
public boolean tryUnlock(int releases) {
//若当前线程没有 持有独占锁
if(owner.get()!= Thread.currentThread()){
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); //抛IllegalMonitorStateException
}
int wc= writeCount.get();
int nextc = wc - releases; //计算 独占锁剩余占用
writeCount.set(nextc); //不管是否完全释放,都更新count值
if (nextc==0){ //是否完全释放
owner.compareAndSet(Thread.currentThread(), null);
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//获取共享锁
public void lockShared() {
int arg = 1;
if (tryLockShared(arg) < 0){ //如果tryAcquireShare失败
//将当前进程放入队列
WaitNode node = new WaitNode(Thread.currentThread(), 1, arg);
waiters.offer(node); //加入队列
for (;;){
//若队列头部的元素是当前线程
WaitNode head = waiters.peek();
if (head!=null && head.thread == Thread.currentThread()){
if (tryLockShared(arg) >=0){ //尝试获取共享锁, 若成功
waiters.poll(); //将当前线程从队列中移除
WaitNode next = waiters.peek();
if (next!=null && next.type==1){ //如果下一个线程也是等待共享锁
LockSupport.unpark(next.thread); //将其唤醒
}
return; //退出方法
}else{ //若尝试失败
LockSupport.park(); //挂起线程
}
}else{ //若不是头部元素
LockSupport.park();
}
}
}
}
//解锁共享锁
public boolean unLockShared() {
int arg = 1;
if (tryUnLockShared(arg)){ //当read count变为0,才叫release share成功
WaitNode next = waiters.peek();
if (next!=null){
LockSupport.unpark(next.thread);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
//尝试获取共享锁
public int tryLockShared(int acquires) {
for (;;){
if (writeCount.get()!=0 &&
owner.get() != Thread.currentThread())
return -1;
int rct = readCount.get();
if (readCount.compareAndSet(rct, rct + acquires)){
return 1;
}
}
}
//尝试解锁共享锁
public boolean tryUnLockShared(int releases) {
for(;;){
int rc = readCount.get();
int nextc = rc - releases;
if (readCount.compareAndSet(rc, nextc)){
return nextc==0;
}
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号