文件操作补充 函数 昨日作业回顾
今日内容概要
-
作业讲解
-
文件操作补充
-
文件操作补充
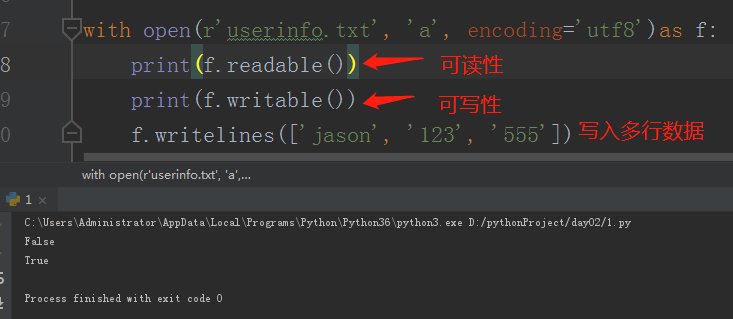
# 方法补充 with open(r'userinfo.txt','a',encoding='utf8') as f: print(f.readable()) # True print(f.writable()) # False f.writelines(['jason','123','555']) """ 1.flush() 将内存中的数据立刻刷到硬盘 相当于保存文件 2.readable() writeable() 判断文件是否可读可写 3.writelines() 括号内放列表 多个元素都会被依次写入 """
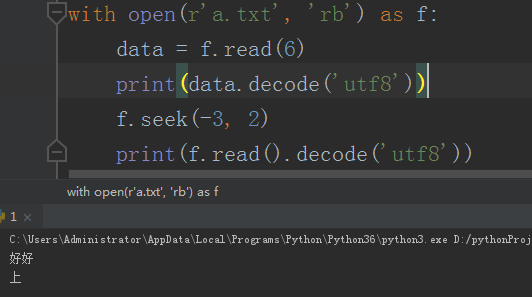
# 文件光标移动 及 文件修改 """ seek方法可以控制光标的移动 seek(offset,whence) offset用来控制移动的位数 whence是操作模式 0:既可以用在文本模式也可以用在二进制模式 文件开头 1:只可以在二进制模式下使用 当前位置 2:只可以在二进制模式下使用 文件末尾 """ # with open(r'a.txt', 'r', encoding='utf8') as f: # data = f.read() # print(data) # # 控制光标移动 # f.seek(1, 0) # 移动到文件开头并往后再移动一个字符 # print(f.read()) # with open(r'a.txt', 'rb') as f: # data = f.read(4) # print(data.decode('utf8')) # # 控制光标移动 # f.seek(-3, 2) # 二进制模式下移动的是字节数,一个中文字符为三个字节 # print(f.read().decode('utf8'))
![]()
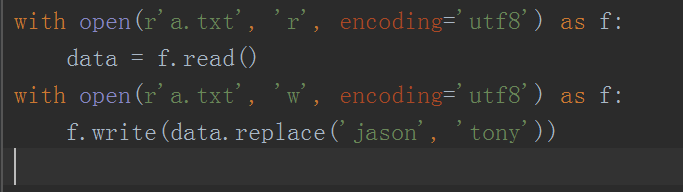
# 文件修改 # with open(r'a.txt','r',encoding='utf8') as f: # data = f.read() # with open(r'a.txt','w',encoding='utf8') as f: # f.write(data.replace('jason','tony'))
# 创建一个新文件 将老文件内容写入新文件 过程中完成修改 # 之后将老文件删除 将新文件命名成老文件 从而达到修改的效果 import os with open(r'a.txt','r',encoding='utf8') as f,open(r'a.txt.backend','w',encoding='utf8') as f1: for line in f: f1.write(line.replace('tony','jason')) os.remove(r'a.txt') os.rename(r'a.txt.backend',r'a.txt')
函数就相当于是工具 提前定义好后续可以反复使用,避免了代码冗余的情况 eg:修理工与工具的案例 函数的语法结构 def 函数名(参数1,参数2): '''函数的注释''' 函数体代码 return 函数的返回值 """ 1.def 定义函数的关键字 2.函数名 函数名的命名与变量名保持一致 见名知意 3.参数 函数在使用之前还可以接收外部传入的参数 4.函数的注释 类似于产品说明书 5.函数体代码 整个函数主要功能逻辑 是整个函数的核心 6.return 执行完函数之后可以给调用者一个反馈结果 """ 函数的基本使用 # 函数的使用一定要先定义后使用!!!
昨日练习回顾
第一题
利用文件操作编写一个简易的文件拷贝系统
让用户输入需要拷贝的文件路径
然后再获取即将拷贝到哪儿的路径
source_file_path = input('source_path>>>:').strip() target_file_path = input('target_path>>>:').strip() with open(r'%s' % source_file_path, 'rb')as read_f, open(r'%s' % target_file_path, 'wb')as write_f: for line in read_f: write_f.write(line)
第二题
while True: print(""" 1.注册 2.登录 """) choice = input("请选择想要执行的功能>>>:").strip() if choice == '1': username = input('username>>>:').strip() password = input('password>>>:').strip() with open(r'userinfo.txt', 'w', encoding='utf8')as f: f.write('%s|%s' % (username, password)) print('%s注册成功' % username) elif choice == '2': username = input('username>>>:').strip() password = input('password>>>:').strip() with open(r'userinfo.txt', 'r', encoding='utf8')as f: data = f.read() real_name, real_pwd = data.split('|') if real_name == username and real_pwd == password: print('登录成功') break else: print('用户名或密码错误') else: print('输入不合法 暂时没有该功能')
第三题
flag = True while flag: username = input('username>>>:').strip() password = input('password>>>:').strip() with open(r'userinfo.txt', 'r', encoding='utf8')as f: for line in f: real_name = line.split('|')[0] if real_name == username: print('用户名已存在') flag = False if flag: with open(r'userinfo.txt', 'a', encoding='utf8')as f: f.write('%s|%s\n' % (username, password)) print('%s注册成功' % username) # 登录 username = input('username>>>:').strip() password = input('password>>>:').strip() with open(r'userinfo.txt', 'r', encoding='utf8')as f: for line in f: real_name, real_pwd = line.split('|') if username == real_name and password == real_pwd.strip('\n'): print('登陆成功') break else: print('用户名或密码错误')



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号