| 这个作业属于哪个课程 |
软件工程 |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 |
结对项目 |
| 这个作业的目标 |
与搭档共同熟悉结对流程,完成结对项目 |
| 姓名 |
吴鸿洲 |
杨宝烨 |
| 学号 |
3122004496 |
3122004497 |
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning |
计划 |
30 |
40 |
| Estimate |
估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
300 |
400 |
| Development |
开发 |
200 |
200 |
| Analysis |
需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
30 |
60 |
| Design Spec |
生成设计文档 |
30 |
40 |
| Design Review |
设计复审 |
10 |
10 |
| Coding Standard |
代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
20 |
| Design |
具体设计 |
60 |
50 |
| Coding |
具体编码 |
300 |
400 |
| Code Review |
代码复审 |
30 |
60 |
| Test |
测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
30 |
40 |
| Reporting |
报告 |
30 |
30 |
| Test Repor |
测试报告 |
60 |
60 |
| Size Measurement |
计算工作量 |
20 |
20 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
50 |
50 |
| 合计 |
|
1450 |
1400 |
设计过程
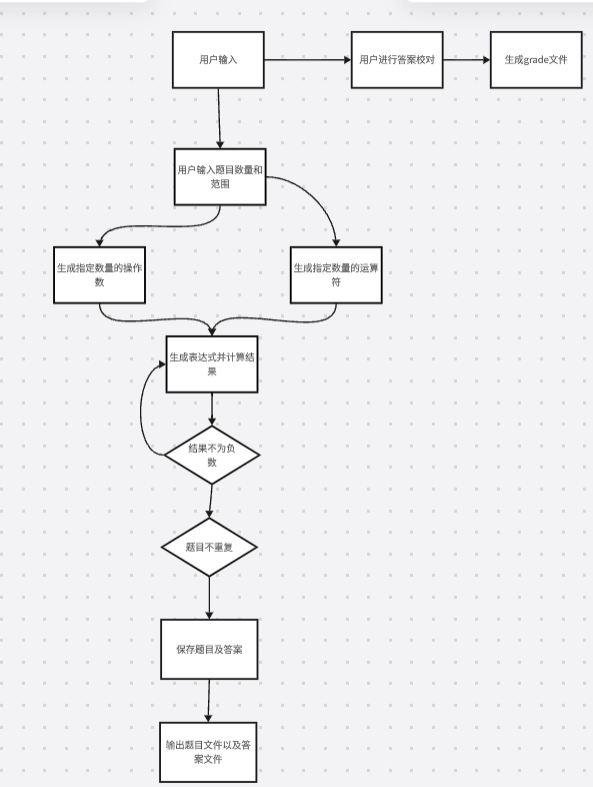
实现过程
- 主要分三个模块对该项目进行其功能的实现,三个模块为生成题目与结果模块、用户模块、以及答案批阅模块
生成题目与结果模块
用户模块

答案批阅模块

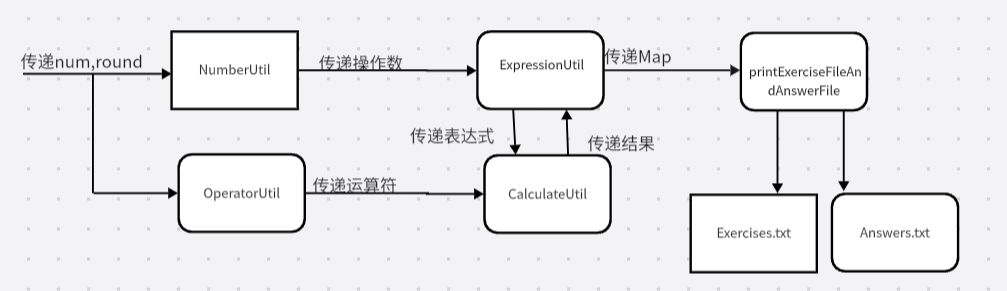
代码设计
generate: 获取表达式与结果的集合的方法
点击查看代码
public static Map<String,String> generate(int n,int round){
//运算式和结果的集合
Map<String,String> questionAndResultMap = new HashMap<>();
//结果集合,用于判断是否重复
Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//随机获取运算符的个数(1~3个)
int num = (int)(Math.random()*3)+1;
//随机获取num个运算符
Character[] curOperators = OperatorUtil.getOperators(num);
//随机获取num+1个操作数
String[] curNumbers = NumberUtil.getNumbers(round,num+1);
//获取运算式表达式
String[] questionAndResult = getExpressStr(curOperators, curNumbers);
if(questionAndResult==null||questionAndResult[1].contains("-")){
//判断是否为负数
i--;
}else if (result.contains(questionAndResult[1])){
//判断是否重复
i--;
}else {
result.add(questionAndResult[1]);
questionAndResultMap.put(questionAndResult[0],questionAndResult[1]);
}
}
return questionAndResultMap;
}
getExpressStr: 获取单个运算式及结果的方法
点击查看代码
ublic static String[] getExpressStr(Character[] curOperators, String[] curNumbers){
//操作数的数量
int number = curNumbers.length;
//随机判断是否生成带括号的运算式
int isAddBracket = (int)(Math.random()*10) % 2;
//随机生成器
Random random = new Random();
if(isAddBracket==1){
//生成带括号的表达式
//当标记为1时代表该操作数已经添加了左括号
int[] lStamp = new int[number];
//当标记为1时代表该操作数已经添加了右括号
int[] rStamp = new int[number];
//遍历操作数数组,随机添加括号
for (int index=0;index<number-1;index++) {
int n = (int)(Math.random()*10) % 2;
//判断当前操作数是否标记了左括号
if(n == 0 && rStamp[index] != 1) {
//标记左括号
lStamp[index] = 1;
//操作数之前加上左括号
curNumbers[index] = "(" + curNumbers[index];
int k = number - 1;
//生成右括号的位置
int rbracketIndex = random.nextInt(k)%(k-index) + (index+1);
//如果当前操作数有左括号,则重新生成优括号位置
while (lStamp[rbracketIndex] == 1){
rbracketIndex = random.nextInt(k)%(k-index) + (index+1);
}
rStamp[rbracketIndex] = 1;
curNumbers[rbracketIndex] = curNumbers[rbracketIndex] +")";
}
}
}
//将运算符数组和操作数数组拼成一个运算式字符串
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(curNumbers[0]);
for (int k = 0; k < curOperators.length; k++) {
str.append(curOperators[k]).append(curNumbers[k + 1]);
}
//生成的运算式
String express = str.toString();
//获取运算式结果
String value = CalculateUtil.getExpressResult(express);
if("#".equals(value)){
//运算过程出现负数
return null;
}
return new String[]{express,value};
}
NumberUtil: 生成随机操作数
OperatorUtil :生成随机运算符
printExerciseFileAndAnswerFile :生成练习文件与答案文件
点击查看代码
public static void printExerciseFileAndAnswerFile(Map<String, String> questionAndResultMap) {
File dir = new File(SymbolConstant.PRINT_FILE_URL);
//解决FileNotFound
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdir();
}
File exerciseFile = new File(SymbolConstant.PRINT_FILE_URL, "Exercises.txt");
File answerFile = new File(SymbolConstant.PRINT_FILE_URL, "Answers.txt");
try {
OutputStream exerciseFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(exerciseFile);
OutputStream answerFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(answerFile);
StringBuilder exerciseBuffer = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder answerFileBuffer = new StringBuilder();
System.out.println("正在写出到文件...");
int count =1;
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry:questionAndResultMap.entrySet()){
exerciseBuffer.append(count).append("、");
exerciseBuffer.append(entry.getKey()).append("\r\n");
answerFileBuffer.append(count).append("、");
answerFileBuffer.append(entry.getValue()).append("\r\n");
count++;
}
exerciseFileOutputStream.write(exerciseBuffer.toString().getBytes());
answerFileOutputStream.write(answerFileBuffer.toString().getBytes());
exerciseFileOutputStream.close();
answerFileOutputStream.close();
System.out.println("操作成功!!!");
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件操作异常,请重试");
}
}
validateAnswerFile :进行答案校对,生成成绩文件
点击查看代码
public static void validateAnswerFile(String exerciseFileUrl, String answerFileUrl) {
//SymbolConstant.PRINT_FILE_URL, exerciseFileUrl);
File exerciseFile = new File(ValidateUtil.improvePath(exerciseFileUrl));
File answerFile = new File(ValidateUtil.improvePath(answerFileUrl));
File gradeFile = new File(SymbolConstant.PRINT_FILE_URL, "Grade.txt");
if (exerciseFile.isFile() && answerFile.isFile()) {
BufferedReader exerciseReader = null;
BufferedReader answerReader = null;
OutputStream gradeFileOutputStream = null;
List<Integer> Correct = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> Wrong = new ArrayList<>();
try {
exerciseReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(exerciseFile)));
answerReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(answerFile)));
String exerciseStr;
String answerStr;
//记录行数
int line = 0;
int tag=0;
System.out.println("开始验证...");
while ((exerciseStr = exerciseReader.readLine()) != null && (answerStr = answerReader.readLine()) != null) {
//获取运算式的正确答案
StringBuffer answersBuffer =new StringBuffer(answerStr);
//消除答案文件中的序号
int count=1;
tag++;
int flag=tag;
while(flag/10!=0){
flag=flag/10;
count++;
}
for(int i=0;i<=count;i++)
{
answersBuffer.deleteCharAt(0);
}
answerStr =answersBuffer.toString();
String realAnswer = CalculateUtil.getExpressResult(exerciseStr);
if (realAnswer.equals(answerStr)) {
line++;
Correct.add(line);
} else {
line++;
Wrong.add(line);
}
}
String result = "Correct:" + Correct.size() + Correct + "\r\n" + "Wrong:" + Wrong.size() + Wrong;
//保存成绩文件
gradeFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(gradeFile);
gradeFileOutputStream.write(result.getBytes());
//打印结果
System.out.print(result);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (exerciseReader != null) {
try {
exerciseReader.close();
} catch (IOException ignored) {
}
}
if (answerReader != null) {
try {
answerReader.close();
} catch (IOException ignored) {
}
}
if (gradeFileOutputStream != null) {
try {
gradeFileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException ignored) {
}
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("文件不存在!!!");
}
}
getExpressResult : 计算运算式的结果
点击查看代码
ublic static String getExpressResult( String express){
//运算符栈,用于存放运算符包括 +、-、*、÷、(、)
Stack<Character> operators = new Stack<>();
//操作数栈,用于存放操作数
Stack<Fraction> fractions = new Stack<>();
//将表达式字符串转成字符数组
char[] chars = express.toCharArray();
//遍历获取处理
for (int i=0;i<chars.length;i++) {
//获取当前的字符
char c = chars[i];
if(c=='('){
//如果是左括号,入栈
operators.push(c);
}else if(c==')'){
//当前字符为右括号
//当运算符栈顶的元素不为‘(’,则继续
while(operators.peek()!='('){
//拿取操作栈中的两个分数
Fraction fraction1 = fractions.pop();
Fraction fraction2 = fractions.pop();
//获取计算后的值
Fraction result = calculate(operators.pop(), fraction1.getNumerator(), fraction1.getDenominator(),
fraction2.getNumerator(), fraction2.getDenominator());
if(result.getNumerator()<0){
//保证运算过程不出现负数
return "#";
}
//将结果压入栈中
fractions.push(result);
}
//将左括号出栈
operators.pop();
}else if(c=='+'||c=='-'||c=='*'||c=='÷'){
//是运算符
//当运算符栈不为空,且当前运算符优先级小于栈顶运算符优先级
while(!operators.empty()&&!priority(c, operators.peek())){
//拿取操作栈中的两个分数
Fraction fraction1 = fractions.pop();
Fraction fraction2 = fractions.pop();
//获取计算后的值
Fraction result = calculate(operators.pop(), fraction1.getNumerator(), fraction1.getDenominator(),
fraction2.getNumerator(), fraction2.getDenominator());
if(result.getNumerator()<0){
return "#";
}
//将结果压入栈中
fractions.push(result);
}
//将运算符入栈
operators.push(c);
}else{//是操作数
if(c>='0'&&c<='9'){
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
//这一步主要是取出一个完整的数值 比如 2/5、9、9/12
while(i< chars.length&&(chars[i]=='/'||((chars[i]>='0')&&chars[i]<='9'))){
buf.append(chars[i]);
i++;
}
i--;
//到此 buf里面是一个操作数
String val = buf.toString();
//标记‘/’的位置
int flag = val.length();
for(int k=0;k<val.length();k++){
if(val.charAt(k)=='/'){
//当获取的数值存在/则标记/的位置,便于接下来划分分子和分母生成分数对象
flag = k;
}
}
//分子
StringBuilder numeratorBuf = new StringBuilder();
//分母
StringBuilder denominatorBuf = new StringBuilder();
for(int j=0;j<flag;j++){
numeratorBuf.append(val.charAt(j));
}
//判断是否为分数
if(flag!=val.length()){
for(int q=flag+1;q<val.length();q++){
denominatorBuf.append(val.charAt(q));
}
}else{
//如果不是分数则分母计为1
denominatorBuf.append('1');
}
//入栈
fractions.push(new Fraction(Integer.parseInt(numeratorBuf.toString()), Integer.parseInt(denominatorBuf.toString())));
}
}
}
while(!operators.empty()){
Fraction fraction1 = fractions.pop();
Fraction fraction2 = fractions.pop();
//获取计算后的值
Fraction result = calculate(operators.pop(), fraction1.getNumerator(), fraction1.getDenominator(),
fraction2.getNumerator(), fraction2.getDenominator());
if(result.getNumerator()<0){
return "#";
}
//将结果压入栈中
fractions.push(result);
}
//计算结果
Fraction result = fractions.pop();
//获取最终的结果(将分数进行约分)
return getFinalResult(result);
}
测试运行
运算式

答案

校验结果

不足: 查重设计存在缺陷,导致r过小,n过大时会陷入死循环
单元测试
CalculateUtil类
点击查看代码
@Test
public void getExpressResult() {
CalculateUtil calculateUtil= new CalculateUtil();
int num=1,round=100;
Character[] curOperators = OperatorUtil.getOperators(num);
String[] curNumbers = NumberUtil.getNumbers(round,num+1);
String [] express = ExpressionUtil.getExpressStr(curOperators,curNumbers);
for (int i = 0; i < express.length ; i=i+2) {
System.out.println( calculateUtil.getExpressResult(express[i]));
}
ExpressionUtil类
点击查看代码
@Test
public void generate() {
int n=3,round=100;
Map<String,String> questionAndResultMap = new HashMap<String,String>();
questionAndResultMap = ExpressionUtil.generate(n,round);
}
@Test
public void getExpressStr() {
int num=3,round=100;
Character[] curOperators = OperatorUtil.getOperators(num);
String[] curNumbers = NumberUtil.getNumbers(round,num+1);
String [] express = ExpressionUtil.getExpressStr(curOperators,curNumbers);
}
FileIO类
点击查看代码
@Test
public void printExerciseFileAndAnswerFile() {
int n=10000,round=100;
Map<String,String> questionAndResult = ExpressionUtil.generate(n, round);
FileIO.printExerciseFileAndAnswerFile(questionAndResult);
}
//相对路径查找
@Test
public void validateAnswerFile() {
String exerciseFileUrl="exercises.txt", answerFileUrl="Answers.txt";
FileIO.validateAnswerFile(exerciseFileUrl,answerFileUrl);
}
//绝对路径查找
@Test
public void validateAnswerFile1() {
String exerciseFileUrl="D:/idea/IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3.4/project/caculation/question_bank/exercises.txt";
String answerFileUrl="D:/idea/IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3.4/project/caculation/question_bank/Answers.txt";
FileIO.validateAnswerFile(exerciseFileUrl,answerFileUrl);
}
NumberUtil类
点击查看代码
@Test
public void getNumbersTest() {
int round=100,num=10000;
String [] numbers = new String[num];
numbers = NumberUtil.getNumbers(round, num);
for(int i=0;i< numbers.length;i++)
{
System.out.printf("第%d个数为%s\n",i,numbers[i]);
}
}
OperatoUtil类
点击查看代码
private final static Character[] operatorTypes = new Character[]{SymbolConstant.PLUS, SymbolConstant.MINUS,SymbolConstant.MULTIPLY,SymbolConstant.DIVIDE};
@Test
public void getOperatorsTest() {
int num=3;
Character[] operators = new Character[num];
operators = OperatorUtil.getOperators(num);
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"个符号"+operators[i]);
}
}
ValidateUtil类
点击查看代码
@Test
public void checkParams() {
String command ="-n i -r j";
String[] s=ValidateUtil.checkParams(command);
for (int i = 0; i <s.length ; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
@Test
public void checkParams1() {
String command ="-r i -n j";
String[] s=ValidateUtil.checkParams(command);
for (int i = 0; i <s.length ; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
@Test
public void checkParams2() {
String command ="-e i -a j";
String[] s=ValidateUtil.checkParams(command);
for (int i = 0; i <s.length ; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
@Test
public void checkParams3() {
String command ="-a i -e j";
String[] s=ValidateUtil.checkParams(command);
for (int i = 0; i <s.length ; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
@Test
public void checkParams4() {
String command ="-j i -k j";
String[] s=ValidateUtil.checkParams(command);
if(s!=null)
for (int i = 0; i <s.length ; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
@Test
public void improvePath() {
String path1= "Answers.txt";
String path2= "D:/idea/IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3.4/project/caculation/question_bank/Answers.txt";
System.out.println("输入相对路径后获得的路径:"+(ValidateUtil.improvePath(path1)));
System.out.println("输入绝对路径后获得的路径:"+(ValidateUtil.improvePath(path2)));
}
}
性能分析
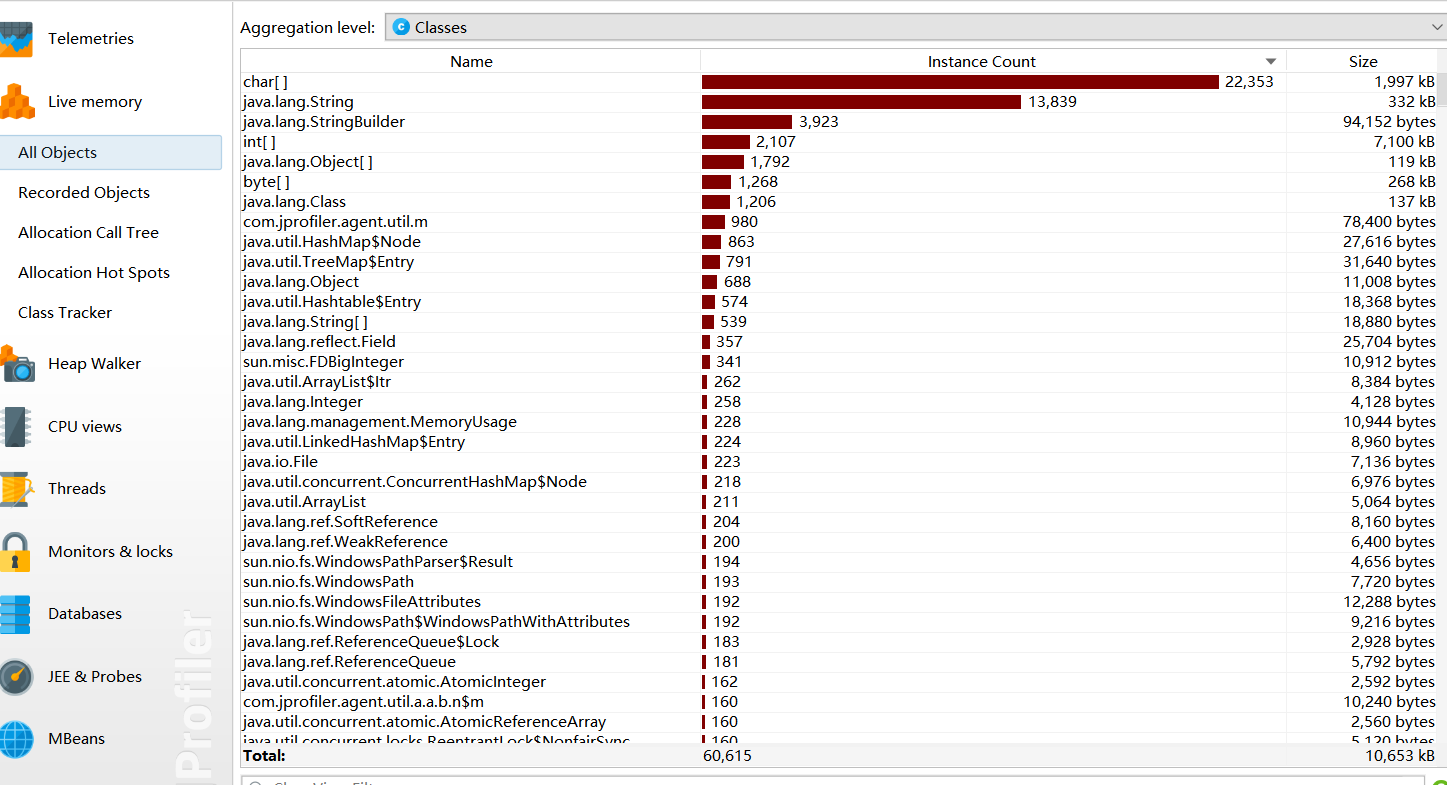
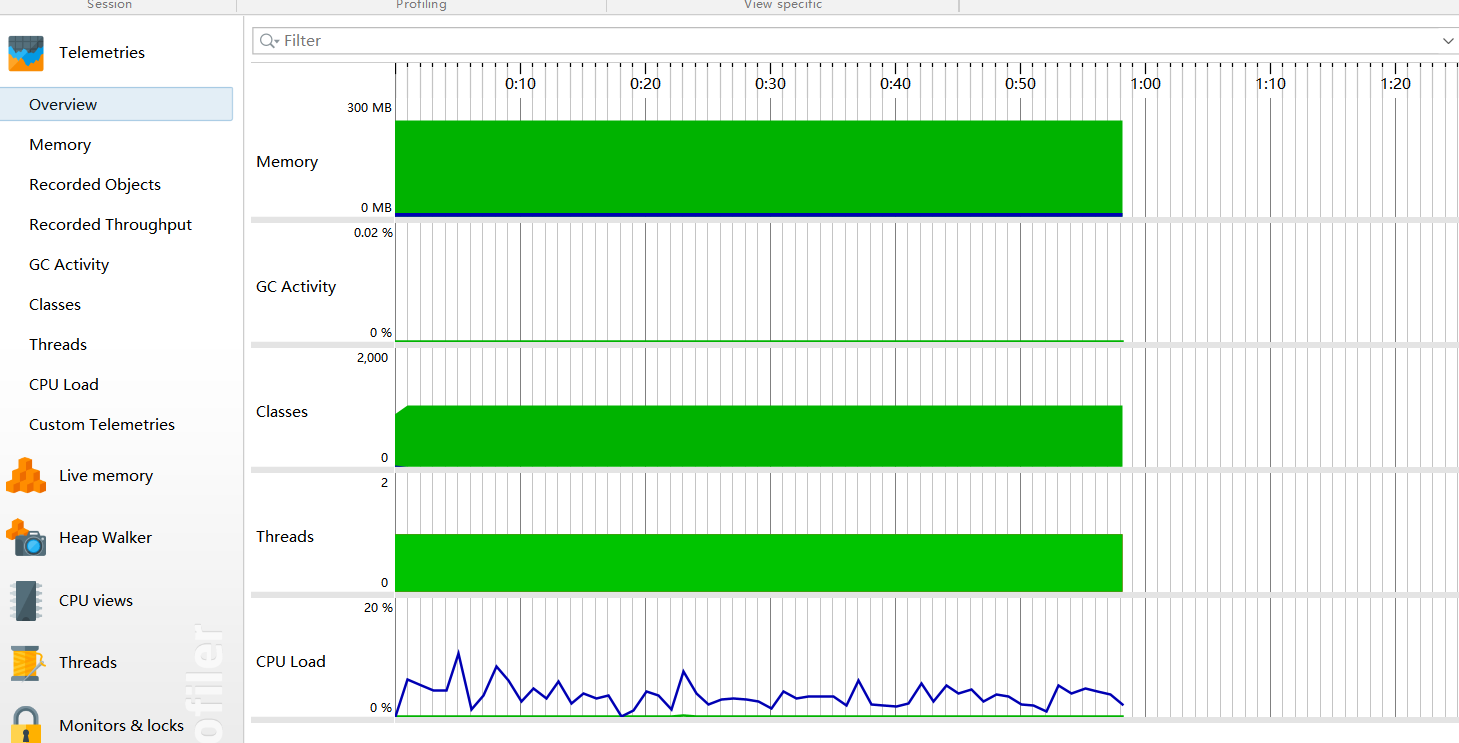
项目小结
- 1、实现了基本的四则运算出题功能,以及答案检验,但是限于两个人编程能力有限,查重算法得不到优化以及提升,导致在特定需求下该项目不能快速完成目标甚至可能完成不了目标
- 2、结对感受:相比于个人项目,结对合作可以实现高效沟通,互相交换想法,讨论算法,了解对方的思维方式,从彼此身上获得启发;不足: 第一次使用git管理代码,可能因为代码管理不当而延缓团队进度。











