async 和await 的用法
https://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/p/9249390.html
① 传统的同步方式:
public class HttpService { /// <summary> /// 后台跨域请求发送代码 /// </summary> /// <param name="url">eg:http://ac.guojin.org/jeesite/regist/saveAppAgentAccount </param> ///<param name="postData"></param> /// 参数格式(手拼Json) string postData = "{\"name\":\"" + vip.comName + "\",\"shortName\":\"" + vip.shortName + + "\"}"; /// <returns></returns> public static string PostData(string postData, string url) { HttpWebRequest req = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);//后台请求页面 Encoding encoding = Encoding.GetEncoding("utf-8");//注意页面的编码,否则会出现乱码 byte[] requestBytes = encoding.GetBytes(postData); req.Method = "POST"; req.ContentType = "application/json"; req.ContentLength = requestBytes.Length; Stream requestStream = req.GetRequestStream(); requestStream.Write(requestBytes, 0, requestBytes.Length); requestStream.Close(); HttpWebResponse res = (HttpWebResponse)req.GetResponse(); StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(res.GetResponseStream(), System.Text.Encoding.GetEncoding("utf-8")); string backstr = sr.ReadToEnd();//可以读取到从页面返回的结果,以数据流的形式。 sr.Close(); res.Close(); return backstr; }
/// <summary> /// 耗时方法 耗时3s /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public ActionResult GetMsg1() { Thread.Sleep(3000); return Content("GetMsg1"); } /// <summary> /// 耗时方法 耗时5s /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public ActionResult GetMsg2() { Thread.Sleep(5000); return Content("GetMsg2"); }
#region 案例1(传统同步方式 耗时8s左右) { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); string t1 = HttpService.PostData("", "http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1"); string t2 = HttpService.PostData("", "http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2"); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); Console.WriteLine($"{t1},{t2}"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
这样的耗时就会是3+5=8s
② 开启新线程分别执行两个耗时操作
需要的时间大约为:Max(3s,5s) = 5s ,如下面【案例2】
#region 案例2(开启新线程分别执行两个耗时操作 耗时5s左右) { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); var task1 = Task.Run(() => { return HttpService.PostData("", "http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1"); }); var task2 = Task.Run(() => { return HttpService.PostData("", "http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2"); }); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); //主线程进行等待 Task.WaitAll(task1, task2); Console.WriteLine($"{task1.Result},{task2.Result}"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
既然②方式可以解决同步方法串行耗时间的问题,但这种方式存在一个弊端,一个业务中存在多个线程,且需要对线程进行管理,相对麻烦,从而引出了异步方法。
③ 使用系统类库自带的异步方法
#region 案例3(使用系统类库自带的异步方法 耗时5s左右) { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); //执行业务 var r1 = http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1", httpContent); var r2 = http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2", httpContent); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); //通过异步方法的结果.Result可以是异步方法执行完的结果 Console.WriteLine(r1.Result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result); Console.WriteLine(r2.Result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
二. 利用async和await封装异步方法
① async和await关键字是C# 5.0时代引入的,它是一种异步编程模型
②它们本身并不创建新线程,但是可以在自行封装的async中利用ask.Run开启新线程
③利用async关键字封装的方法中如果全部都是一些串行业务,且不用await关键字,那么即使使用async封装,也并没什么用,起不到异步方法的作用
//利用async封装同步业务的方法 private static async Task<string> NewMethod5Async() { Thread.Sleep(3000); //其它同步业务 return "Msg1"; } private static async Task<string> NewMethod6Async() { Thread.Sleep(5000); //其它同步业务 return "Msg2"; }
#region 案例4(async关键字封装的方法中如果写全部都是一些串行业务 耗时8s左右) { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); Task<string> t1 = NewMethod5Async(); Task<string> t2 = NewMethod6Async(); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); Console.WriteLine($"{t1.Result},{t2.Result}"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
从上面③中可以得出一个结论,async中必须要有await运算符才能起到异步方法的作用,且await 运算符只能加在 系统类库默认提供的异步方法或者新线程(如:Task.Run)前面
// 将系统类库提供的异步方法利用async封装起来 private static async Task<String> NewMethod1Async() { HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1", httpContent); return r1.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; } private static async Task<String> NewMethod2Async() { HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2", httpContent); return r1.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; } //将await关键字加在新线程的前面 private static async Task<string> NewMethod3Async() { var msg = await Task.Run(() => { return HttpService.PostData("", "http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1"); }); return msg; } private static async Task<string> NewMethod4Async() { var msg = await Task.Run(() => { return HttpService.PostData("", "http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2"); }); return msg; }
#region 案例5(将系统类库提供的异步方法利用async封装起来 耗时5s左右) //并且先输出“我是主业务”,证明t1和t2是并行执行的,且不阻碍主业务 { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); Task<string> t1 = NewMethod1Async(); Task<string> t2 = NewMethod2Async(); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); Console.WriteLine($"{t1.Result},{t2.Result}"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
2 几个规则和约定
① async封装的方法中,可以有多个await ,这里的await代表等待该行代码执行完毕
② 我们通常自己封装的方法也要以Async结尾,方便识别
③ 异步返回类型主要有三种:Task<T> 、Task、Void
3 测试得出其他几个结论
① 如果async封装的异步方法里既有同步业务又有异步业务,name同步犯法的那部分的时间在调用的时候是会阻塞主线程额的,即主线程要等待这部分同步业务执行完才能往下执行。
//同步耗时操作和异步方法同时封装 private static async Task<String> NewMethod7Async() { //调用异步方法之前还有一个耗时操作 Thread.Sleep(2000); //下面的操作耗时3s HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1", httpContent); return r1.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; } private static async Task<String> NewMethod8Async() { //调用异步方法之前还有一个耗时操作 Thread.Sleep(2000); //下面的操作耗时5s HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2", httpContent); return r1.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; }
#region 案例7(既有普通的耗时操作,也有系统本身的异步方法,耗时9s左右) //且大约4s后才能输出 “我是主业务”,证明同步操作Thread.Sleep(2000); 阻塞主线程 { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); Task<string> t1 = NewMethod7Async(); Task<string> t2 = NewMethod8Async(); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); Console.WriteLine($"{t1.Result},{t2.Result}"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion

② 如果封装的异步方法中存在等待的问题,而且不能阻塞主线程(不能用Thread.Sleep) , 这个时候可以用Task.Delay,并在前面加await关键字 耗时:Max(2+3 , 5+2)=7s
//利用Task.Delay(2000);等待 private static async Task<String> NewMethod11Async() { //调用异步方法之前需要等待2s await Task.Delay(2000); //下面的操作耗时3s HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1", httpContent); return r1.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; } private static async Task<String> NewMethod12Async() { //调用异步方法之前需要等待2s await Task.Delay(2000); //下面的操作耗时5s HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg2", httpContent); return r1.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; }
#region 案例8(利用Task.Delay执行异步方法的等待操作) //结果是7s,且马上输出“我是主业务”,说明Task.Delay(),不阻塞主线程。 { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); Task<string> t1 = NewMethod11Async(); Task<string> t2 = NewMethod12Async(); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); Console.WriteLine($"{t1.Result},{t2.Result}"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
三. 异步方法返回类型
1. Task<T>,处理含有返回值额异步方法,通过.Result等待异步方法执行完,且获取到返回值。
2. Task:调用方法不需要从异步方法中取返回值,但是希望检查异步方法的状态,那么可以选择可以返回Task类型的对象。不过,就算异步方法中含return语句,也不会返回任何东西
//返回值为Task的方法 private static async Task NewMethod9Async() { //下面的操作耗时3s HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1", httpContent); Console.WriteLine("NewMethod9Async执行完成"); }
#region 案例9(返回值为Task的异步方法) //结果是5s,说明异步方法和主线程的同步方法 在并行执行 { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); Task t = NewMethod9Async(); Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(t.Status)}: {t.Status}"); //任务状态 Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(t.IsCompleted)}: {t.IsCompleted}"); //任务完成状态标识 Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(t.IsFaulted)}: {t.IsFaulted}"); //任务是否有未处理的异常标识 //执行其他耗时操作,与此同时NewMethod9Async也在工作 Thread.Sleep(5000); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); t.Wait(); Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(t.Status)}: {t.Status}"); //任务状态 Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(t.IsCompleted)}: {t.IsCompleted}"); //任务完成状态标识 Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(t.IsFaulted)}: {t.IsFaulted}"); //任务是否有未处理的异常标识 Console.WriteLine($"所有业务执行完成了"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
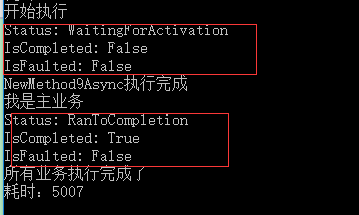
PS:对于Task返回值的异步方法,可以调用Wait(),等 待该异步方法执行完,他和await不同,await必须出现在async关键字封装的方法中。
3.void :调用异步执行方法,不需要做任何交互
//返回值是Void的方法 private static async void NewMethod10Async() { //下面的操作耗时5s HttpClient http = new HttpClient(); var httpContent = new StringContent("", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json"); //执行业务,假设这里主需要请求,不需要做任何交互 var r1 = await http.PostAsync("http://localhost:2788/Home/GetMsg1", httpContent); Console.WriteLine("NewMethod10Async执行完成"); }
#region 案例10(返回值为Void的异步方法) //结果是5s,说明异步方法和主线程的同步方法 在并行执行 { Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); Console.WriteLine("开始执行"); NewMethod10Async(); //执行其他耗时操作,与此同时NewMethod9Async也在工作 Thread.Sleep(5000); Console.WriteLine("我是主业务"); Console.WriteLine($"所有业务执行完成了"); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine($"耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); } #endregion
四. 几个结论
1.异步方法到底开不开起新线程?
异步和等待关键字不会导致其他线程创建,因为异步方法本身不会运行线程,异步方法不需要多线程。只有+当方法处于活动状态,则方法在当前同步上下文中运行并使用在线程的时间。可以使用Task.Run移动CPU工作移到后台线程,但是,后台线程不利于等待结果变得可用处理
2 async 和await是一种异步编程模型,它本身并不能开启新线程,多用于将一些非阻止API或者开启新线程的操作封装起来,使其调用的时候像同步方法一样使用。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号