【LCA】最近公共祖先
【LCA】最近公共祖先
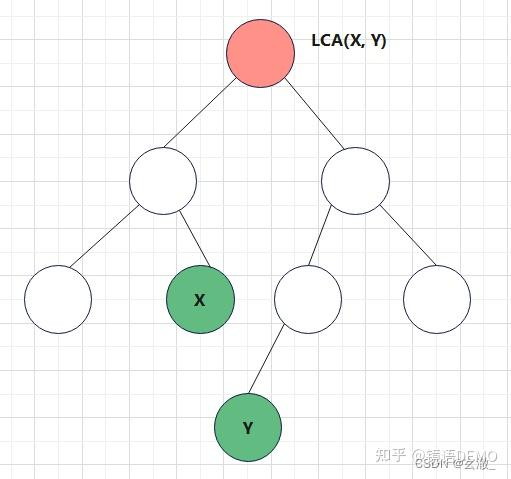
LCA(x,y)
模版代码
模版题 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3379
树上倍增
基础封装:针对无权图
把空间开到全局
struct Tree {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> ver, val;
vector<int> lg, dep;
void init(int n) {
this->n = n;
ver.resize(n + 1);
val.resize(n + 1, vector<int>(30));
lg.resize(n + 1);//满足 2^(lg[i]-1) ≤ i 的最大整数
dep.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //预处理 log
lg[i] = lg[i - 1] + (1 << lg[i - 1] == i);
}
}
void add(int x, int y) { // 建立双向边
ver[x].push_back(y);
ver[y].push_back(x);
}
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
val[x][0] = fa; // 储存 x 的父节点
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[dep[x]]; i++) {
val[x][i] = val[val[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for (auto y : ver[x]) {
if (y == fa) continue;
dfs(y, x);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) swap(x, y);
while (dep[x] > dep[y]) {//先从深度大的节点往上跳
x = val[x][lg[dep[x] - dep[y]] - 1];
}
if (x == y) return x;//调整完深度大的节点,两者相遇说明是答案
for (int k = lg[dep[x]] - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (val[x][k] == val[y][k]) continue;//保证两节点深度不同且不相会
x = val[x][k];
y = val[y][k];
}
return val[x][0];
}
int clac(int x, int y) { // 倍增查询两点间距离
return dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[lca(x, y)];
}
void work(int root = 1) { // 在此初始化
dfs(root, 0);
}
void clear() {
n = 0;
ver.clear();
val.clear();
lg.clear();
dep.clear();
}
}tree;
注意init和work,使用完要clear
针对有权图,支持“倍增查询两点路径上的最大边权”
struct Tree {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> val, Max;
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> ver;
vector<int> lg, dep;
void init(int n) {
this->n = n;
ver.resize(n + 1);
val.resize(n + 1, vector<int>(30));
Max.resize(n + 1, vector<int>(30));
lg.resize(n + 1);
dep.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //预处理 log
lg[i] = lg[i - 1] + (1 << lg[i - 1] == i);
}
}
void add(int x, int y, int w) { // 建立双向边
ver[x].push_back({y, w});
ver[y].push_back({x, w});
}
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
val[x][0] = fa;
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[dep[x]]; i++) {
val[x][i] = val[val[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
Max[x][i] = max(Max[x][i - 1], Max[val[x][i - 1]][i - 1]);
}
for (auto [y, w] : ver[x]) {
if (y == fa) continue;
Max[y][0] = w;
dfs(y, x);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) swap(x, y);
while (dep[x] > dep[y]) {
x = val[x][lg[dep[x] - dep[y]] - 1];
}
if (x == y) return x;
for (int k = lg[dep[x]] - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (val[x][k] == val[y][k]) continue;
x = val[x][k];
y = val[y][k];
}
return val[x][0];
}
int clac(int x, int y) { // 倍增查询两点间距离
return dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[lca(x, y)];
}
int query(int x, int y) { // 倍增查询两点路径上的最大边权(带权图)
auto get = [&](int x, int y) -> int {
int ans = 0;
if (x == y) return ans;
for (int i = lg[dep[x]]; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dep[val[x][i]] > dep[y]) {
ans = max(ans, Max[x][i]);
x = val[x][i];
}
}
ans = max(ans, Max[x][0]);
return ans;
};
int fa = lca(x, y);
return max(get(x, fa), get(y, fa));
}
void work(int root = 1) { // 在此初始化
dfs(root, 0);
}
};
树链剖分
struct HLD {
int n, idx;
vector<vector<int>> ver;
vector<int> siz, dep;
vector<int> top, son, parent;
void init(int n) {
this->n = n;
ver.resize(n + 1);
siz.resize(n + 1);
dep.resize(n + 1);
top.resize(n + 1);
son.resize(n + 1);
parent.resize(n + 1);
}
void add(int x, int y) { // 建立双向边
ver[x].push_back(y);
ver[y].push_back(x);
}
void dfs1(int x) {
siz[x] = 1;
dep[x] = dep[parent[x]] + 1;
for (auto y : ver[x]) {
if (y == parent[x]) continue;
parent[y] = x;
dfs1(y);
siz[x] += siz[y];
if (siz[y] > siz[son[x]]) {
son[x] = y;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int up) {
top[x] = up;
if (son[x]) dfs2(son[x], up);
for (auto y : ver[x]) {
if (y == parent[x] || y == son[x]) continue;
dfs2(y, y);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (dep[top[x]] > dep[top[y]]) {
x = parent[top[x]];
} else {
y = parent[top[y]];
}
}
return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;
}
int clac(int x, int y) { // 查询两点间距离
return dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[lca(x, y)];
}
void work(int root = 1) { // 在此初始化
dfs1(root);
dfs2(root, root);
}
};
Tarjan
注意把空间开到全局
struct Tarjan{
int n;
vector<vector<int>> ver; // 邻接表存储树
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> q; // 存储查询 (另一个节点, 查询编号)
vector<int> parent; // 父节点数组
vector<int> depth; // 节点深度数组
vector<int> visited; // 访问标记: 0-未访问, 1-正在访问, 2-已访问
vector<int> ancestor; // 并查集的祖先数组
vector<int> ans; // 存储查询结果
// 构造函数
void init(int n) {
this->n = n;
ver.resize(n + 1);
q.resize(n + 1);
parent.resize(n + 1);
depth.resize(n + 1, 0); // 初始化深度数组
visited.resize(n + 1, 0);
ancestor.resize(n + 1);
}
// 添加树的边
void add(int x, int y) {
ver[x].push_back(y);
ver[y].push_back(x);
}
// 添加查询
void add_query(int x, int y, int idx) {
if (x == y) {
ans[idx] = x; // 若节点相同,直接记录结果(LCA就是自身)
return;
}
// 节点不同时,正常添加查询
q[x].emplace_back(y, idx);
q[y].emplace_back(x, idx);
}
// 并查集查找操作
int find(int x) {
if (ancestor[x] != x) {
ancestor[x] = find(ancestor[x]);
}
return ancestor[x];
}
// 并查集合并操作
void unite(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x != y) {
ancestor[y] = x;
}
}
// Tarjan算法的核心DFS
void dfs(int x) {
visited[x] = 1; // 标记为正在访问
ancestor[x] = x; // 初始化并查集,祖先为自己
for (int y : ver[x]) {
if (visited[y] == 0) { // 未访问过的子节点
parent[y] = x;
depth[y] = depth[x] + 1; // 计算子节点深度
dfs(y);
unite(x, y); // 回溯时合并
}
}
// 处理与当前节点相关的查询
for (auto &query : q[x]) {
int y = query.first;
int idx = query.second;
if (visited[y] == 2) { // 若另一个节点已访问完毕
ans[idx] = find(y); // 记录LCA结果
}
}
visited[x] = 2; // 标记为已访问完毕
}
// 计算两点间的距离
int calc_distance(int x, int y) {
int common_ancestor = lca(x, y);
return depth[x] + depth[y] - 2 * depth[common_ancestor];
}
// 获取LCA结果
int lca(int x, int y) {
// 为单次查询创建临时存储
ans.resize(1);
add_query(x, y, 0);
work();
return ans[0];
}
// 执行Tarjan算法处理所有查询
void work(int root = 1) {
// 初始化
fill(visited.begin(), visited.end(), 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ancestor[i] = i;
}
parent[root] = 0;
depth[root] = 0; // 根节点深度为0
dfs(root);
}
}tarjan;
初始化预处理
tarjan.init(n);
tarjan.ans.resize(m+1);//注意ans数组也要初始化!
离线算法一次处理所有查询
用法
tarjan.add(1, 2);
tarjan.add(2, 3);
tarjan.add(2, 4);
//添加查询
tarjan.add_query(3, 5, 0);
tarjan.add_query(3, 4, 1);
tarjan.add_query(5, 1, 2);
//一次性处理所有查询
tarjan.work(root); //work里面参数写根节点
//从ans数组获取查询结果:注意刚开始自己定义的idx
cout << "LCA(3,5) = " << tarjan.ans[0] << endl;
概念
最近公共祖先
首先树要是无环树
两个节点在这棵树上深度最大的公共的祖先节点
主要用法
(1)处理当两个点仅有唯一一条确定的最短路径时的路径
(2)求解树上两节点距离
(3)求解树上路径问题
求解思路
(1)树上倍增:在线
预处理复杂度O(nlogn)
询问每次复杂度O(logn)
(2)Tarjan:离线
复杂度O(m+n)
(3)利用欧拉序转为RMQ问题,用ST表解决RMQ问题:在线
预处理复杂度O(n+nlogn)
询问每次复杂度O(1)
(4)树链剖分:和LCA类似且较复杂,常数比较小
以下为理论推导
朴素算法
每次找深度比较高的点,开始往上跳直到相遇即可->O(n)
倍增算法
基于朴素算法的优化

参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/594255188
https://www.cnblogs.com/hulean/p/11144059.html
题目积累
小红的树不动点
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/114848/F
题目大意

思路
注意权值:排序后与下标相等
->必须要有1才有2 必须要有1 2才有3...
从1开始找->同时包含1 2 ...的子树->lca
贡献即为深度
代码
int n;
struct Tree {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> ver, val;
vector<int> lg, dep;
void init(int n) {
this->n = n;
ver.resize(n + 1);
val.resize(n + 1, vector<int>(30));
lg.resize(n + 1);//满足 2^(lg[i]-1) ≤ i 的最大整数
dep.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //预处理 log
lg[i] = lg[i - 1] + (1 << lg[i - 1] == i);
}
}
void add(int x, int y) { // 建立双向边
ver[x].push_back(y);
ver[y].push_back(x);
}
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
val[x][0] = fa; // 储存 x 的父节点
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[dep[x]]; i++) {
val[x][i] = val[val[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for (auto y : ver[x]) {
if (y == fa) continue;
dfs(y, x);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) swap(x, y);
while (dep[x] > dep[y]) {//先从深度大的节点往上跳
x = val[x][lg[dep[x] - dep[y]] - 1];
}
if (x == y) return x;//调整完深度大的节点,两者相遇说明是答案
for (int k = lg[dep[x]] - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
if (val[x][k] == val[y][k]) continue;//保证两节点深度不同且不相会
x = val[x][k];
y = val[y][k];
}
return val[x][0];
}
int clac(int x, int y) { // 倍增查询两点间距离
return dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[lca(x, y)];
}
void work(int root = 1) { // 在此初始化
dfs(root, 0);
}
}tree;
void solve(){
cin>>n;
tree.init(n);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
tree.add(u,v);
}
tree.work(n);
i64 ans=(i64)(tree.dep[1]);
int lca=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
lca=tree.lca(lca,i);
ans+=(i64)(tree.dep[lca]);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号