【双指针】
【双指针】
思路
先从暴力开始写
然后思考暴力如何优化
一般都是遍历一个找另一个
【模版题】找最长连续不重复子序列
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/20960/1014
思路
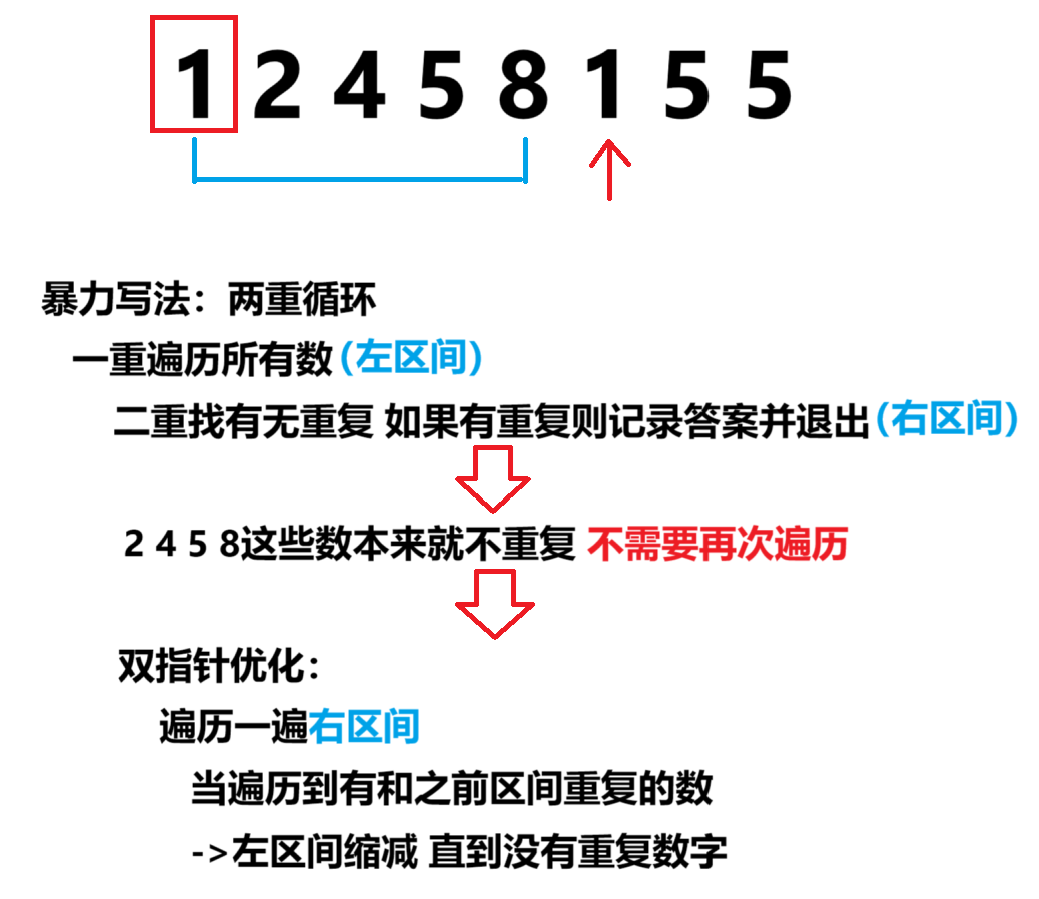
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
const int N=200010;
int n,a[N];
map<int,int> q;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
/*
【思路】
前面的指针遍历一次
如果出现重复:后面的指针一直往前跑,直到不重复
*/
vector<array<int,3>> tmp;
int ans=-1;
for(int i=1,j=1;i<=n;i++){
q[a[i]]++;
while(q[a[i]]>1){
q[a[j]]--;
j++;
}
tmp.push_back({j,i,i-j+1});
ans=max(ans,i-j+1);
}
vector<PII> an;
int cnt=0;
for(auto temp:tmp){
if(temp[2]==ans){
cnt++;
an.push_back({temp[0],temp[1]});
}
}
cout<<cnt<<endl;
sort(an.begin(),an.end());
for(auto aa:an){
cout<<aa.first<<" "<<aa.second<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
数组元素的目标和
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/802/
思路
遍历时有三种状态:
(1)a[i]+b[j]>x
(2)a[i]+b[j]<x
(3)a[i]+b[j]==x
->i和j一定要都从小开始找嘛?如果都从小开始遍历 更新状态很麻烦
->从小到大遍历一个 另一个从最大开始找->大于就--
->状态始终只有<和=
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
const int N=100010;
int n,m,x;
int a[N],b[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m>>x;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) cin>>b[i];
//遍历一个找另一个
//i从小到大 j从大到小:a[i]+b[j]要么<x要么=x
for(int i=1,j=m;i<=n;i++){
while(j>=1 && a[i]+b[j]>x) j--;
if(a[i]+b[j]==x){
cout<<i<<" "<<j;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
字符串
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/18386
注意存状态方式 只要不爆越简单越暴力越好
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
string s;
//涉及到桶的遍历:数量少不用map直接建桶就行
int a[35];
int cnt=0;
//最坏情况1e6*26也不会爆->直接扫就行
bool is_ok(){
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
if(!a[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>s;
int n=s.size();
s='.'+s;
//遍历右端点
int j=1;
int ans=INF;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int t=s[i]-'a';
a[t]++;
while(is_ok()){
ans=min(ans,i-j+1);
int tt=s[j]-'a';
a[tt]--;
j++;
}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
丢手绢
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/problem/207040
注:我觉得题目中对于a数组的描述有点问题 他没说清楚a[0]是最后一个小朋友到第一个小朋友的距离 还是第一个小朋友到第二个小朋友的距离、、、
思路
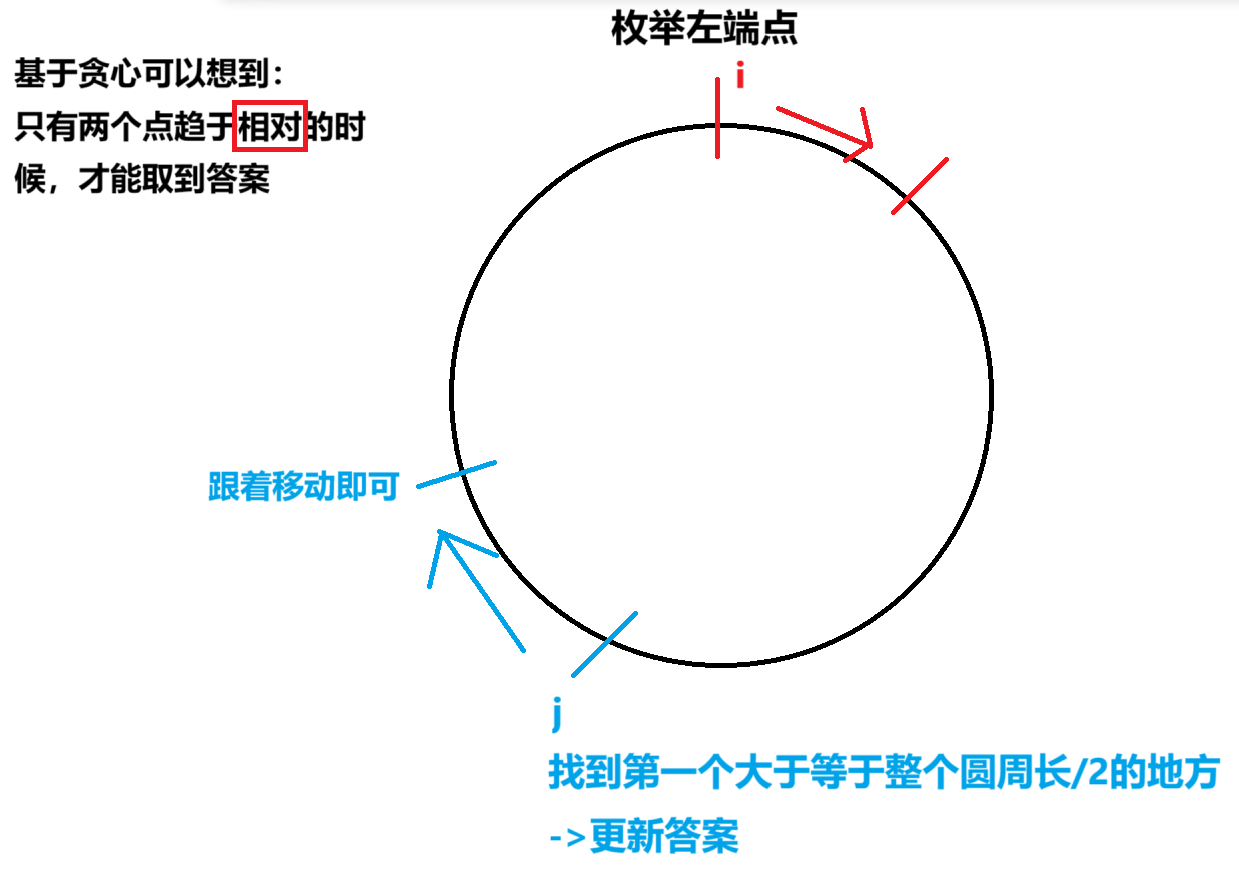
设计圆圈枚举的题目都可以用取余想
※注意首个点应当从0开始!
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
ll abss(ll a){return a>0?a:-a;}
ll max_(ll a,ll b){return a>b?a:b;}
ll min_(ll a,ll b){return a<b?a:b;}
bool cmpll(ll a,ll b){return a>b;}
const int N=100010;
int n,a[N];
int pres[N],nxts[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
sum+=a[i];
}
int j=0;//注意这里 右端点从第一个小朋友(重合的状态)开始
int cnt=0;
int ans=-1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){//枚举左端点
while(cnt<sum/2){//基于贪心的策略:使两个点趋于相对的状态
cnt+=a[j];
j=(j+1)%n;//圆圈都可以用取余来操作->注意第一个点应当从0开始
}
ans=max(ans,min(cnt,sum-cnt));
cnt-=a[i];//i移动了所以需要减去
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
小柒的幸运数
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/111921/C
题目大意
统计各区间逆序对数量 与x最接近的数
思路
一眼看上去是个数论/贡献法/前缀和的题目
->逆序对需要遍历区间->双指针 枚举右端点
若逆序对数量大于x->缩短左端点 否则继续往右枚举
如何统计区间逆序对的数量? 数字只有0-25 直接暴力加减统计
代码
string s;
i64 x;
/*
【滑动窗口思想】统计区间逆序对数量
若逆序对:
大于->缩小尾端
小于->扩大顶端
*/
void solve(){
cin>>s;
cin>>x;
i64 ans=inf_i64;
int len=s.size();
s=' '+s;
int l=1;
vector<i64> b(26,0);
i64 res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=len;i++){
for(int k=s[i]-'a'+1;k<26;k++){
res+=b[k];
}
i64 cnt=llabs(x-res);
ans=min_(ans,cnt);
b[s[i]-'a']+=1LL;
while(res>x && l<i){
i64 ress=0;
for(int k=0;k<s[l]-'a';k++){
ress+=b[k];
}
res-=ress;
cnt=llabs(x-res);
ans=min_(ans,cnt);
b[s[l]-'a']--;
l++;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
Make a Palindrome
https://codeforces.com/contest/2124/problem/D
题目大意
每次选择一个连续区间,从区间中删去第k大的数
可以操作无数次,问能不能将序列变成一个回文序列
思路
(1)只能删去第k大的数
->求出序列中第k大的数cutoff
->三种情况:
①a[i]>cutoff 这种数是可以被删去且对序列无影响的->直接默认删去
②a[i]==cutoff 这种数可以被删 也可以不删->当备用
③a[i]<cutoff 这种数删不掉
(2)序列构成回文数
把所有a[i]<=cutoff拿进数组 双指针判断
头尾要相等
如果不相等:
头尾有可以删的(==cutoff)就删
没有可以删的 因为现在数组里的数也删不掉->无法构成回文
代码
int n,k;
void solve(){
cin>>n>>k;
vector<int> a(n+1,0),b(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
b[i]=a[i];
}
if(k==1){
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
return;
}
sort(b.begin()+1,b.end(),cmp);
int cutoff=b[k];
vector<int> c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i]<=cutoff){//注意这里要按照a的原顺序
c.push_back(a[i]);
}
}
//数组至少要保留k-1个元素
int spare=c.size()-(k-1);//能删的次数
int L=0,R=c.size()-1;
while(L<R){
if(c[L]!=c[R]){
if(spare==0){
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return;
}
if(c[L]==cutoff){
L++;
spare--;
}
else if(c[R]==cutoff){
R--;
spare--;
}
else{
//即使中间有cutoff可以删->首尾删不了 那么回文永远无法成立
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return;
}
continue;
}
L++;
R--;
}
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}
Sparse Range
https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc444/tasks/abc444_e
统计区间问题:
可以通过双指针固定快的指针为右区间,这样单点答案就只需要+区间长度
题目大意

思路
①考虑一个合法区间有新数加进来时应该如何操作:multiset维护,找一个或两个最靠近的数看是否满足条件
②考虑如何枚举区间:固定左端点r,找到最靠左的l,这样r~l的每一个点都可以作为答案,直接加就行
->考虑双指针,枚举r,在遇到不满足条件的l时就缩短左端点
AC代码
const int N=4e5+10;
int n;
i64 d;
i64 a[N];
multiset<i64> s;
bool check(i64 x){
if(s.empty()) return true;
auto idx1=s.lower_bound(x);
if(idx1==s.end()){
i64 res1=*s.rbegin();
i64 tmp1=llabs(res1-x);
if(tmp1<d){
return false;
}
else{
return true;
}
}
else if(idx1==s.begin()){
i64 res1=*s.begin();
i64 tmp1=llabs(res1-x);
if(tmp1<d){
return false;
}
else{
return true;
}
}
else{
i64 res1=*idx1;
idx1--;
i64 res2=*idx1;
i64 tmp1=llabs(res1-x);
i64 tmp2=llabs(res2-x);
if(tmp1<d || tmp2<d){
return false;
}
else{
return true;
}
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>d;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
//双指针
int l=1,r=1;
i64 ans=0;
for(r=1;r<=n;r++){
while(!check(a[r]) && l<r){
s.erase(s.find(a[l]));
l++;
}
s.insert(a[r]);
ans+=s.size();
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号