【ROS2复习】202501
不同节点之间话题订阅发布
https://www.cnblogs.com/whiteink/articles/18595916


要点
(1)消息接口包:写+包含
(2)publisher和subscription:定义、调用+回调函数写实际操作!
(3)launch一次启动多节点
(4)没收到消息的处理方式:Debug操作
发布者 Publisher
rclcpp::Publisher<消息接口名>
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp" //包含消息接口头文件
#include <chrono> //包含时间相关头文件
using namespace std::chrono_literals;//使用时间单位字面量->用s和ms表示时间
//在private下进行变量定义和写回调函数
//在public下写构造函数
class TurtleCircle : public rclcpp::Node{
private:
//【创建指针】
//设置定时器:设置隔几秒发送一次数据
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
//发布者
rclcpp::Publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::Twist>::SharedPtr publisher_;
public:
//都在构造函数下进行编写!
explicit TurtleCircle(const std::string& node_name) : Node(node_name)
{
publisher_=this->create_publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::Twist>("/turtle1/cmd_vel",10);//与海龟订阅的话题名称保持一致
timer_=this->create_wall_timer(1000ms,std::bind(&TurtleCircle::timer_callback,this));
}
//※每1000ms调用一次回调函数
private:
void timer_callback(){
auto msg=geometry_msgs::msg::Twist();
msg.linear.x=1.0;
msg.angular.z=0.5;
publisher_->publish(msg);//发布信息
}
};
订阅者 Subscription
rclcpp::Subscription<消息接口名>
//包含消息接口头文件
#include"geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp"
#include"turtlesim/msg/pose.hpp"
#include"rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
class TurtleController : public rclcpp::Node{
public:
TurtleController() : Node("turtle_controller"){
velocity_publisher_ = this->create_publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::Twist>
("/turtle1/cmd_vel",10);
pose_subscription_ = this->create_subscription<turtlesim::msg::Pose>("turtle1/pose",10,
std::bind(&TurtleController::on_pose_received_,this,std::placeholders::_1));
//※※当后台收到数据时,调用该回调函数处理
}
private:
//收到位置计算误差,发布速度指令
void on_pose_received_(const turtlesim::msg::Pose::SharedPtr pose){
auto message = geometry_msgs::msg::Twist();
//1.记录当前位置
double current_x = pose->x;
double current_y = pose->y;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"当前位置:(x=%f,y=%f)",current_x,current_y);
//2.计算与目标之间的距离,以及与当前海龟朝向的角度差
double distance = std::sqrt((target_x_-current_x)*(target_x_-current_x)
+(target_y_-current_y)*(target_y_-current_y));
//atan2:y/x的反正切值
//与std::atan()函数不同,std::atan2()考虑x和y的符号,可正确确定角度所在的象限
//计算目标点位置相对当前位置的角度,将结果和当前朝向作差
double angle = std::atan2(target_y_-current_y,target_x_-current_x) - pose -> theta;
//3.控制策略:距离大于0.1继续运动,角度差大于0.2原地旋转,否则直行
if(distance > 0.1){
//计算角速度
if(fabs(angle)>0.2){
message.angular.z=fabs(angle);
}
else{
//通过比例控制器计算输出速度
message.linear.x=k_*distance;
}
}
//4.限制最大值并发布消息
if(message.linear.x>max_speed_){
message.linear.x=max_speed_;
}
velocity_publisher_->publish(message);//发布消息
}
private:
// 订阅/turtle1/pose获取海龟实时位置
rclcpp::Subscription<turtlesim::msg::Pose>::SharedPtr pose_subscription_;
//话题发布者
rclcpp::Publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::Twist>::SharedPtr velocity_publisher_;
/*目标点*/
double target_x_{1.0}; //目标位置x 默认值1.0
double target_y_{1.0}; //目标位置y 默认值1.0
double k_{1.0}; //比例系数,控制输出=误差x比例系数
double max_speed_{3.0}; //最大线速度 默认值3.0
};
int main(int argc,char** argv){
rclcpp::init(argc,argv);
auto node=std::make_shared<TurtleController>();
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
自定义通信接口
新建功能包->功能包中建立msg目录->xxx.msg文件->注册
服务端与客户端通信
https://www.cnblogs.com/whiteink/articles/18613483
相关概念
服务端 处理大量来自客户端的请求并管理数据
接收请求,处理请求(比如从数据库中提取相关数据),然后将处理后的结果(如网页内容)发送回客户端
客户端 向服务端发送请求以获取服务或资源
eg 网页浏览器(如 Chrome、Firefox)、手机应用程序
要点
自定义服务接口
创建功能包->创建srv文件夹->xxx.srv文件->注册
# Request 部分
...
---
# Response 部分
...
服务端:对操作进行处理
rclcpp::Service<srv文件名>
#include "chapt4_interfaces/srv/patrol.hpp" //添加服务头文件
//创建服务
patrol_server_ = this->create_service<Patrol>(
"patrol",
//lambda函数作为回调函数:参数为请求和响应对象的共享指针
[&](const std::shared_ptr<Patrol::Request> request,
std::shared_ptr<Patrol::Response> response) -> void{
/*调用srv数据的方式:
(1)变量 request/response->xxx
(2)常量 <消息接口类型>::Request/Response::<常量名>
*/
if((0 < request->target_x && request->target_x < 12.0f)
&& (0 < request->target_y && request->target_y < 12.0f)){
//设置目标点
target_x_ = request -> target_x;
target_y_ = request -> target_y;
response -> result = Patrol::Response::SUCCESS;
}
else{
response -> result = Patrol::Response::FAIL;
}
});
private:
//【创建指针】
rclcpp::Service<Patrol>::SharedPtr patrol_server_;
客户端:写具体是什么操作的地方->请求操作
rclcpp::Client<srv文件名>
class PatrolClient : public rclcpp::Node{
public:
//注意:客户端里构造函数要写请求服务端的回调函数!->定时器
PatrolClient() : Node("patrol_cilent"){
patrol_client_ = this->create_client<Patrol>("patrol");
timer_=this->create_wall_timer(10s,std::bind(&PatrolClient::timer_callback,this));
srand(time(NULL));
}
//实现函数
void timer_callback(){
//1.等待服务端上线 👇超过指定时间
while(!patrol_client_->wait_for_service(std::chrono::seconds(1))){
//检查服务端是否有效
//等待时检测rclcpp状态
if(!rclcpp::ok()){
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(),"等待服务的过程中被打断,,,");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"等待服务端上线中");
}
//2.构造请求对象
auto request = std::make_shared<Patrol::Request>();
request->target_x = rand() % 15;
request->target_y = rand() % 15;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"请求巡逻:(%f,%f)",request->target_x,request->target_y);
//3.※发送异步请求,然后等待返回,返回时调用回调函数(用lambda写)
patrol_client_->async_send_request(
request, // ↓ 获取异步处理的结果
[&](rclcpp::Client<Patrol>::SharedFuture result_future) -> void{
auto response = result_future.get();//获取Response共享指针
if(response -> result == Patrol::Response::SUCCESS){
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"目标点处理成功");
}
else if(response -> result == Patrol::Response::FAIL){
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(),"目标点处理失败");
}
});
}
private:
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
rclcpp::Client<Patrol>::SharedPtr patrol_client_;
};
参数通信
rclcpp::Parameter
装甲板识别改版思路
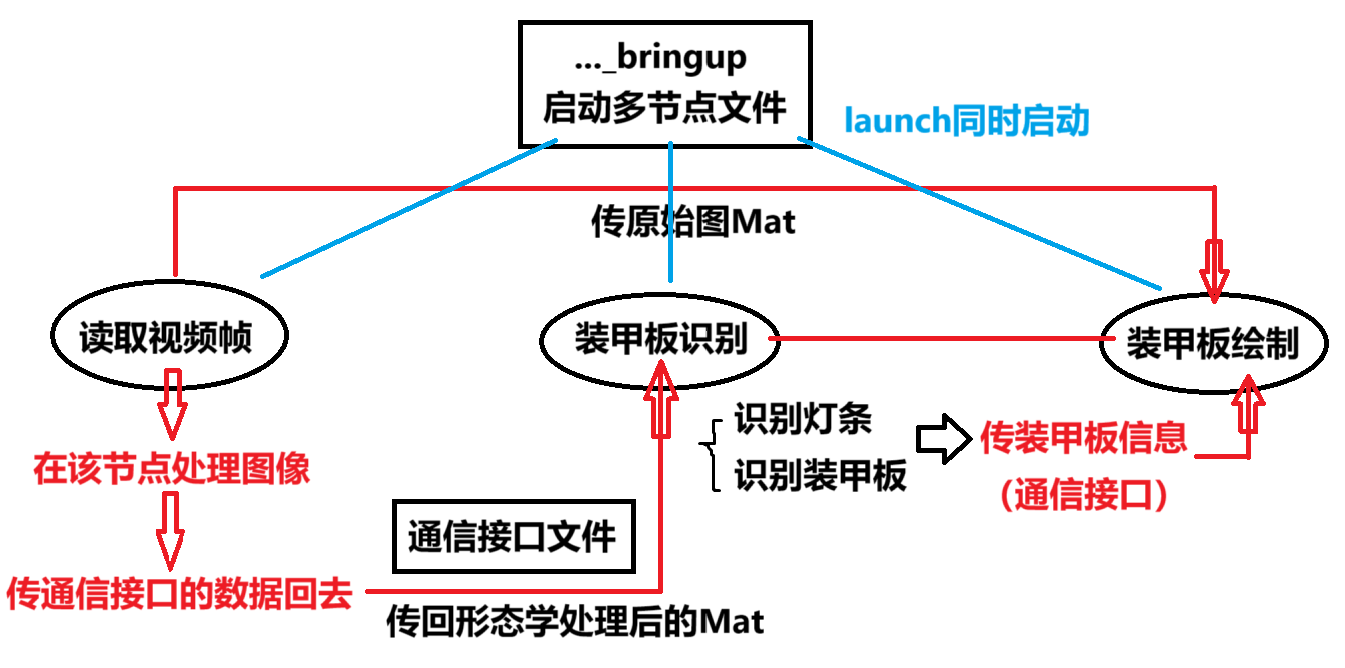
注意点(持续补充)
(1)要写readme.md
包含:
-节点
-发布话题
-订阅话题
-服务
-参数
-各主要功能
(2)待补充


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号