WordCount基础功能
作业链接:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xnsy/2018Systemanalysisanddesign/homework/2120
码云项目地址:https://gitee.com/hhhhhhh2/WordCount
PSP表格
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
20 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
20 |
|
Development |
开发 |
120 |
200 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
100 |
60 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
0 |
0 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
0 |
0 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
0 |
0 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
90 |
50 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
120 |
100 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
0 |
0 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
90 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
90 |
50 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
60 |
30 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
10 |
10 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
10 |
10 |
|
|
合计 |
750 |
610 |
总结:在PSP这块,预计耗时和实际耗时相差比较大,尤其是在测试、需求分析等上,是预估的时间更长。原因一主要有刚开始对整体项目的难度把握不够,所以对于各部分预估的时间都比较长。原因二是在实际耗时中,开发和具体编码阶段耗时最长。开发阶段主要用在了学习上,通过查询资料对Java io流文件输入输出的复习和学习命令行内容后,才开始设计程序。而具体编码阶段前并没有完整地设计出程序就开始敲代码,所以是一小部分逐步实现的,经过了不断修改所以耗时较长。
概述
1.作业要求
根据WordCount的需求描述,先编程实现,再编写单元测试,最后撰写博客。
2.功能需求
WordCount项目分为三个阶段:基本功能、扩展功能、高级功能。
·基本功能:-c输出字符数,-w输出单词总数,-l输出总行数,-o输出结果到指定文件;
·扩展功能:-s递归处理目录下符合条件的文件,-a输出更复杂的数据(代码行/空行/注释行),-e停用词表(统计文件单词总数时不统计该表中的单词);
·高级功能:-x显示图形界面,可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、单词数、行数等全部统计信息。
本周只要求实现基本功能,其具体需求为:
·对程序设计语言源文件统计字符数、单词数、行数,统计结果以指定格式输出到默认文件中,以及其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
·可执行程序命名为:wc.exe,该程序处理用户需求的模式为:wc.exe [parameter] [input_file_name]
·存储统计结果的文件默认为result.txt,放在与wc.exe相同的目录下。
解题思路
在刚拿到题目后,我选择了自己相对比较熟悉的Java语言来编程。
(1)对于题目中涉及的统计字符数、单词数、行数且需将结果输出到指定文件中,我首先考虑到这里要考查的是对字符串和java io流(对文件进行操作)的使用。
(2)在java程序实现统计等基础功能后,需要转成exe在cmd下输入命令执行,所以还要查询如何加入命令到cmd下的命令行和如何在Eclipse中将java程序打包成exe文件。
程序设计实现过程
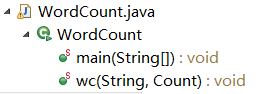
WordCount程序中一共设计了两个类,分别是:
①类:public class Count{}
属性有字符数、单词数、行数(为实现扩展功能有代码行、空行、注释行等属性,暂未实现);
用于接收文件统计后的各数据结果。

②类:public class WordCount{}
main(String[]) 是程序入口,分析判断指令格式;
wc(String, Count)对输入文件进行统计(字符数、单词数、行数)。
代码说明
1.Count类,内含字符数、单词数、行数等属性(包括扩展功能中的属性),用于接受文件统计后的结果。
1 package WordCount; 2 3 /* 4 * Count类,属性有字符数,单词数,行数,代码行,注释行,空行 5 * 用于接收文件统计后的各数据结果 6 */ 7 8 public class Count 9 { 10 public int charCount; //字符个数 11 public int wordCount; //单词总数 12 public int lineCount; //行数 13 public int codeCount; //代码行 14 public int noteCount; //注释行 15 public int emptyCount; //空行 16 17 //基础功能 18 public Count(int charCount, int wordCount, int lineCount){ 19 this.charCount = charCount; 20 this.wordCount = wordCount; 21 this.lineCount = lineCount; 22 } 23 24 //扩展功能 25 public Count(int charCount, int wordCount, int lineCount, int codeCount, int noteCount, int emptyCount){ 26 this.charCount = charCount; 27 this.wordCount = wordCount; 28 this.lineCount = lineCount; 29 this.codeCount = codeCount; 30 this.noteCount = noteCount; 31 this.emptyCount = emptyCount; 32 } 33 34 //getter方法 35 public int getCodeCount() { 36 return codeCount; 37 } 38 39 public int getNoteCount() { 40 return noteCount; 41 } 42 43 public int getEmptyCount() { 44 return emptyCount; 45 } 46 47 public int getCharCount() { 48 return charCount; 49 } 50 51 52 public int getWordCount() { 53 return wordCount; 54 } 55 56 public int getLineCount() { 57 return lineCount; 58 } 59 }
2.统计功能:wc(String,Count)函数内含核心算法,需读取文件后统计单词数、行数、字符数。
对文件的操作主要是用BufferedReader读取文件,生成缓冲字符输入流,之后都取每行字符串进行统计操作。
1 public static void wc(String targetFile, Count count) throws IOException 2 { 3 String Sline = null; 4 File dir = new File(targetFile); 5 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(dir));//读取文件,生成缓冲字符输入流 6 7 //readLine()每次读取一行,br.readLine()=null代表数据读取完毕 8 while((Sline = br.readLine()) != null) 9 { 10 count.charCount += Sline.length(); //字符个数就是每行字符串长度 11 count.wordCount += Sline.split(" ").length; //split()把一个字符串分割成以空格为界限的字符串数组 12 count.lineCount++; //每次读取一行则总行数+1 13 }//of while 14 15 System.out.println("字符数:" + count.charCount + ",单词数:" + count.wordCount + ",行数:"+ count.lineCount); 16 br.close(); 17 }
3.主函数:主函数的主要作用是得到用户的指令(存储在args中的字符串数组),并判断不同指令下执行不同操作。
在调用wc()统计运算后,对args数组进行遍历分析,找出输入命令和文件名,比如-c、-l、-w后面跟的是输入文件名file.c,-o接输出文件名result.txt。
其中-o指令需要输出结果到指定文件,这里用的是BufferedWriter将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,最后写数据到resultFile中。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
//默认初始化file.c目标文件,result.txt结果输出到指定文件
Count count = new Count(0,0,0); //创建一个Count对象
String targetFile = "f:/file.c";
String resultFile = "f:/result.txt";//存储统计结果的文件默认为result.txt,放在与wc.exe相同的目录下。
//先判断命令,对文件路径变量进行赋值
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
//通过后缀名判断目标文件
if(((args[i].endsWith(".c")) || (args[i].endsWith(".java")) || (args[i].endsWith(".js")) || (args[i].endsWith(".py")) || (args[i].endsWith(".htm")) || (args[i].endsWith(".txt"))) && !(args[i - 1].equals("-o")))
{
targetFile = args[i];
}//of if
//-o输出结果到指定文件
if(args[i].equals("-o")){
if(i != (args.length - 1)){ //检查-o后是否有文件路径
resultFile = args[i+1]; //-o后接的字符串即存储结果的文件
}//of if
}//of if
}//of for i
wc(targetFile, count); //进行统计计算
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++)
{
switch(args[i])
{
case "-c":
System.out.println(targetFile + ", 字符数:" + count.charCount);
break;
case "-w":
System.out.println(targetFile + ", 单词数:" + count.wordCount);
break;
case "-l":
System.out.println(targetFile + ", 行数:" + count.lineCount);
break;
case "-o":
String s = null;
for(int j = 0; j < args.length; j++)
{
if(args[j].equals("-c"))
s += "\r\n" + targetFile + ",字符数:" + count.getCharCount();
if(args[j].equals("-w"))
s += "\r\n" + targetFile + ",单词数:" + count.getWordCount();
if(args[j].equals("-l"))
s += "\r\n" + targetFile + ",行数:" + count.getLineCount();
}//of for j
File f = new File(resultFile); //写数据到resultFile中
f.createNewFile();
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f));
out.write(s);
out.flush();
out.close();
break;
}//of switch
}//of for i
}
测试设计过程
此次程序测试并没有用单元测试框架及课程中介绍的白盒测试用例设计方法来设计测试用例,所以我主要通过的是利用一个内容足够多的目标文件和多种组合命令行进行测试。
1.进行三个基本的测试用例测试:
file.c文件内容:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 int main() 3 { 4 printf("Hello World"); 5 return 0; 6 }
①测试命令-c:输出file.c字符数
![]()
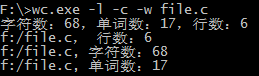
②测试命令-l、-c、-w:输出file.c行数、字符数、单词数。
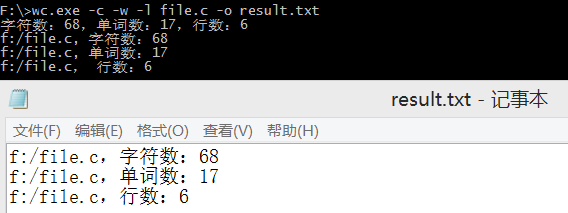
③测试命令-c、-w、-l、-o:输出file.c字符数、单词数、行数,并输出到文件result.txt中。
2.将目标文件内容替换为一个完整的C语言程序文件,含足够多的代码、注释。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 int main(){ 5 FILE *fp; 6 char ch; 7 int i; 8 if((fp = fopen("demo.bin","wb")) == NULL){ 9 printf("Failure to open demo.bin!\n"); 10 exit(0); 11 }//of if 12 for(i = 0; i < 128; ++i){ 13 fputc(i, fp); 14 }//of for i 15 fclose(fp); 16 if((fp = fopen("demo.bin", "rb")) == NULL){ 17 printf("Failure to open demo.bin!\n"); 18 exit(0); 19 }//of if 20 while((ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF){ 21 putchar(ch); //在显示器上显示从文件读出的所有字符 22 }//of while 23 /* 20~22行可以换做: 24 ch = fgetc(fp); 25 while(!feof(fp)){ 26 putchar(ch); 27 ch = fgetc(fp); 28 }//of while 29 */ 30 fclose(fp); 31 return 0; 32 }//of main
3.命令行参数测试用例(默认输出文件为根目录下的result.txt文件下)
- wc.exe -w file.c
- wc.exe -c file.c
- wc.exe -l file.c
- wc.exe -c -w -l file.c
- wc.exe -w -c filec -o result.txt
- wc.exe -l -w -c file.c -o result.txt
- wc.exe -o file.c
- wc.exe -o result.txt
- wc.exe file.c
- wc.exe result.txt
心得总结
这是我第一篇关于项目的博客,学习了关于git使用和添加命令行等知识点。首先可见自己对编码的设计能力还很差,无法恰当把握项目难度和进度。此次程序的基础功能还是比较简单的,主要考察的就是文件操作。其次是关于测试还需要进一步学习,这次程序测试是通过自己设计的几个用例而非正确使用单元测试等更系统化的方法。
参考文献链接
- https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/2a138328f3e2b0074a134ffe.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/Who-Named-Cody/p/8609924.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号