数据结构---栈
一、定义
栈是限定在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。因此对栈来说,表尾端有特殊含义,称为栈顶,相应地,表头端称为栈底。不含元素的空表称为空栈。
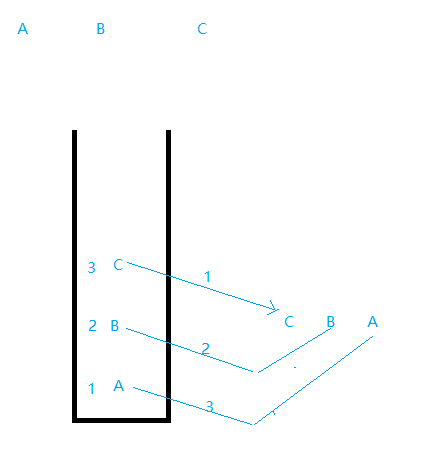
二、栈的实现方式
1、顺序栈
顺序存储结构,利用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素,同时附设指针top指示栈顶元素在顺序栈中的位置。通常的习惯做法是以top=0表示空栈(,鉴于C语言数组下标从0开始),也有以top=-1表示空栈的。另一方面,由于栈在使用过程中所需最大空间的大小很难估计,因此,一般来说,在初始化时,先为栈分配一个基本容量,然后在应用过程中,当栈的空间不够使用时再逐段扩大。为此,可设定两个常量:STACK_INIT_SIZE和STACKINCREMENT
2、链栈
三、代码实现
1、顺序栈
1.1 结构体定义
#define ElemType int
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 8
#define STACK_INC_SIZE 3
typedef struct SeqStack
{
ElemType *base;
int capacity;
int top;
}SeqStack;
1.2 功能代码实现
#include "SeqStack.h"
bool Inc(SeqStack *s)
{
ElemType *newbase = (ElemType *)realloc(s->base, sizeof(ElemType)*(s->capacity + STACK_INC_SIZE));
if(newbase == NULL)
{
printf("内存不足\n");
return false;
}
s->base = newbase;
s->capacity += STACK_INC_SIZE;
return true;
}
void InitStack(SeqStack *s)
{
s->base = (ElemType *)malloc(sizeof(ElemType)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
assert(s->base != NULL);
s->capacity = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
s->top = 0;
}
bool IsFull(SeqStack *s)
{
return s->top >= s->capacity;
}
bool IsEmpty(SeqStack *s)
{
return s->top == 0;
}
void Push(SeqStack *s, ElemType x)
{
if (IsFull(s) && !Inc(s))
{
printf("栈空间已满,%d,不能入栈", x);
return;
}
s->base[s->top++] = x;
}
void Pop(SeqStack *s)
{
if (IsEmpty(s))
{
printf("栈空间已空,不能出栈。\n");
return;
}
s->top--;
}
bool GetTop(SeqStack *s, ElemType *v)
{
if (IsEmpty(s))
{
printf("栈空间已空,不能取栈顶元素\n");
return false;
}
*v = s->base[s->top-1];
return true;
}
int Length(SeqStack *s)
{
return s->top;
}
void Clear(SeqStack *s)
{
s->top = 0;
}
void Destroy(SeqStack *s)
{
free(s->base);
s->base = NULL;
s->capacity = 0;
s->top = 0;
}
void Show(SeqStack *s)
{
for (int i = s->top - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
printf("%d\n", s->base[i]);
}
}
1.3 测试代码实现
#include "SeqStack.h"
void main()
{
SeqStack st;
InitStack(&st);
ElemType v;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
Push(&st, i);
}
Show(&st);
GetTop(&st, &v);
printf("%d 出栈\n", v);
Pop(&st);
Show(&st);
Clear(&st);
Show(&st);
Destroy(&st);
}
1.4、头文件实现
#ifndef __SEQSTACK_H__
#define __SEQSTACK_H__
#include "stdio.h"
#include "malloc.h"
#include "assert.h"
#define ElemType int
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 8
#define STACK_INC_SIZE 3
typedef struct SeqStack
{
ElemType *base;
int capacity;
int top;
}SeqStack;
bool Inc(SeqStack *s);
void InitStack(SeqStack *s);
bool IsFull(SeqStack *s);
bool IsEmpty(SeqStack *s);
void Push(SeqStack *s, ElemType x);
void Pop(SeqStack *s);
bool GetTop(SeqStack *s, ElemType *v);
int Length(SeqStack *s);
void Clear(SeqStack *s);
void Destroy(SeqStack *s);
void Show(SeqStack *s);
#endif
2 、链栈
 2.1 结构体定义
2.1 结构体定义
#define ElemType int
typedef struct StackNode
{
ElemType data;
struct StackNode *next;
}StackNode, *LinkStack;
2.2 功能代码实现
#include "LinkStack.h"
void InitStack(LinkStack *s)
{
*s = NULL;
}
void Push(LinkStack *s, ElemType x)
{
StackNode *t = (StackNode *)malloc(sizeof(StackNode));
assert(t != NULL);
t->data = x;
if (*s == NULL)
{
*s = t;
t->next = NULL;
}
else
{
t->next = *s;
*s = t;
}
}
void Show(LinkStack *s)
{
StackNode *p = *s;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
2.3 测试代码实现
#include "LinkStack.h"
void main()
{
LinkStack st;
InitStack(&st);
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
Push(&st, i);
}
Show(&st);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号