离散数学——Mathematical Logic
Propositional Logic
A proposition is a declarative statement that is either true or false. More complex propositions can be built from elementary statements using logical connectives.
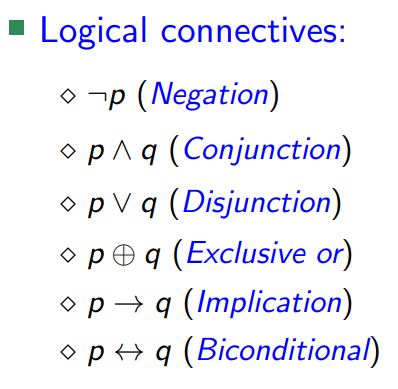

Two propositions are equivalent if they always have the same truth value.
The propositions p and q are called logically equivalent if p ↔ q is a tautology, denoted by p ≡ q or p ⇔ q.
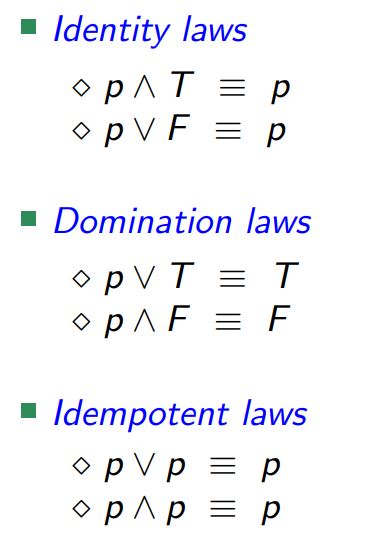
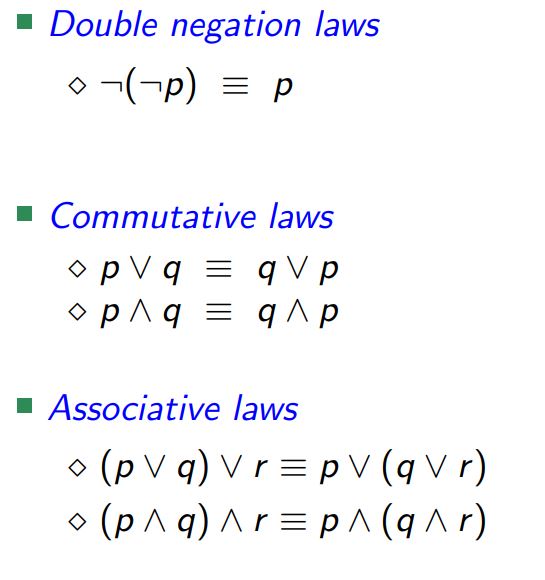

Predicate Logic

A predicate P(x) assigns a value T or F to each x depending on whether the property holds or not for x

Two types of quantified statements: universal and existential
The truth values of ∃x P(x) and ∀x P(x) depend on both the propositional function P(x) and the universe.

The order of nested quantifiers matters if quantifiers are of different type
The order of nested quantifiers does no matter if quantifiers are of the same type.
nested negation

Rules of Inference
For Propositional Logic




For Quantified Statements

Proving Method





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号