Spring AI Alibaba 项目源码学习(八)-Flow Agent 分析
Flow Agent 分析
请关注微信公众号:阿呆-bot
概述
本文档分析 Spring AI Alibaba Agent Framework 中的 Flow Agent 系列,包括 FlowAgent 基类、SequentialAgent、ParallelAgent、LoopAgent 和 LlmRoutingAgent 的具体实现,重点分析其关键方法、功能职责和节点能力。
入口类说明
FlowAgent - Flow Agent 基类
FlowAgent 是所有 Flow Agent 的抽象基类,继承自 Agent,提供了多 Agent 编排的基础能力。
核心职责:
- 管理子 Agent 列表
- 提供 Graph 构建的抽象方法
- 委托给
FlowGraphBuilder构建图
关键代码:
public abstract class FlowAgent extends Agent {
protected List<String> interruptBefore;
protected List<Agent> subAgents;
protected FlowAgent(String name, String description, CompileConfig compileConfig, List<Agent> subAgents)
throws GraphStateException {
super(name, description);
this.compileConfig = compileConfig;
this.subAgents = subAgents;
}
@Override
protected StateGraph initGraph() throws GraphStateException {
// Use FlowGraphBuilder to construct the graph
FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config = FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig.builder()
.name(this.name())
.rootAgent(this)
.subAgents(this.subAgents());
// Delegate to specific graph builder based on agent type
return buildSpecificGraph(config);
}
@Override
public ScheduledAgentTask schedule(ScheduleConfig scheduleConfig) throws GraphStateException {
CompiledGraph compiledGraph = getAndCompileGraph();
return compiledGraph.schedule(scheduleConfig);
}
public StateGraph asStateGraph(){
return getGraph();
}
/**
* Abstract method for subclasses to specify their graph building strategy. This
* method should be implemented by concrete FlowAgent subclasses to define how their
* specific graph structure should be built.
* @param config the graph configuration
* @return the constructed StateGraph
* @throws GraphStateException if graph construction fails
*/
protected abstract StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config)
throws GraphStateException;
public CompileConfig compileConfig() {
return compileConfig;
}
public List<Agent> subAgents() {
return this.subAgents;
}
/**
* Creates a map with messages and input for String message
*/
private Map<String, Object> createInputMap(String message) {
return Map.of("messages", convertToMessages(message), "input", message);
}
}
关键方法:
buildSpecificGraph():抽象方法,子类实现具体的图构建策略subAgents():获取子 Agent 列表
SequentialAgent - 顺序执行 Agent
SequentialAgent 按顺序执行多个子 Agent,前一个 Agent 的输出作为下一个 Agent 的输入。
关键代码:
public class SequentialAgent extends FlowAgent {
protected SequentialAgent(SequentialAgentBuilder builder) throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.compileConfig, builder.subAgents);
}
public static SequentialAgentBuilder builder() {
return new SequentialAgentBuilder();
}
@Override
protected StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config) throws GraphStateException {
return FlowGraphBuilder.buildGraph(FlowAgentEnum.SEQUENTIAL.getType(), config);
}
/**
* Builder for creating SequentialAgent instances. Extends the common FlowAgentBuilder
* to provide type-safe building.
*/
public static class SequentialAgentBuilder extends FlowAgentBuilder<SequentialAgent, SequentialAgentBuilder> {
@Override
protected SequentialAgentBuilder self() {
return this;
}
@Override
protected void validate() {
super.validate();
// Add any SequentialAgent-specific validation here if needed
}
@Override
public SequentialAgent build() throws GraphStateException {
validate();
return new SequentialAgent(this);
}
}
}
执行模式:
- Agent1 → Agent2 → Agent3 → ... → END
- 每个 Agent 的输出作为下一个 Agent 的输入
ParallelAgent - 并行执行 Agent
ParallelAgent 并行执行多个子 Agent,然后合并结果。
关键代码:
public class ParallelAgent extends FlowAgent {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ParallelAgent.class);
private final MergeStrategy mergeStrategy;
private String mergeOutputKey;
private final Integer maxConcurrency;
protected ParallelAgent(ParallelAgentBuilder builder) throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.compileConfig, builder.subAgents);
this.mergeStrategy = builder.mergeStrategy != null ? builder.mergeStrategy : new DefaultMergeStrategy();
this.maxConcurrency = builder.maxConcurrency;
this.mergeOutputKey = builder.mergeOutputKey;
}
public static ParallelAgentBuilder builder() {
return new ParallelAgentBuilder();
}
@Override
protected StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config) throws GraphStateException {
// Add parallel-specific properties to config
config.customProperty("mergeStrategy", this.mergeStrategy);
config.customProperty("maxConcurrency", this.maxConcurrency);
return FlowGraphBuilder.buildGraph(FlowAgentEnum.PARALLEL.getType(), config);
}
/**
* Gets the merge strategy used by this ParallelAgent.
* @return the merge strategy
*/
public MergeStrategy mergeStrategy() {
return mergeStrategy;
}
public String mergeOutputKey() {
return mergeOutputKey;
}
/**
* Gets the maximum concurrency limit for this ParallelAgent.
* @return the max concurrency, or null if unlimited
*/
public Integer maxConcurrency() {
执行模式:
- 所有子 Agent 同时执行(Fan-Out)
- 执行完成后合并结果(Gather)
- 支持最大并发数限制
LoopAgent - 循环执行 Agent
LoopAgent 循环执行一个子 Agent,支持多种循环策略。
关键代码:
public class LoopAgent extends FlowAgent {
private final LoopStrategy loopStrategy;
public static final String LOOP_STRATEGY = "loopStrategy";
private LoopAgent(LoopAgentBuilder builder) throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.compileConfig, builder.subAgents);
this.loopStrategy = builder.loopStrategy;
}
@Override
protected StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config) throws GraphStateException {
config.customProperty(LOOP_STRATEGY, loopStrategy);
return FlowGraphBuilder.buildGraph(FlowAgentEnum.LOOP.getType(), config);
}
public static LoopAgentBuilder builder() {
return new LoopAgentBuilder();
}
public static class LoopAgentBuilder extends FlowAgentBuilder<LoopAgent, LoopAgentBuilder> {
private LoopStrategy loopStrategy = null;
@Override
protected LoopAgentBuilder self() {
return this;
}
public LoopAgentBuilder subAgent(Agent subAgent) {
this.subAgents = List.of(subAgent);
return self();
}
@Override
public LoopAgentBuilder subAgents(List<Agent> subAgents) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("LoopAgent must have only one subAgent, please use subAgent() method.");
}
public LoopAgentBuilder loopStrategy(LoopStrategy loopStrategy) {
this.loopStrategy = loopStrategy;
return self();
循环策略:
- CountLoopStrategy:固定次数循环
- ConditionLoopStrategy:条件循环(条件为 true 时终止)
- ArrayLoopStrategy:遍历数组元素
LlmRoutingAgent - LLM 路由 Agent
LlmRoutingAgent 使用 LLM 根据输入内容路由到不同的子 Agent。
关键代码:
public class LlmRoutingAgent extends FlowAgent {
private final ChatModel chatModel;
protected LlmRoutingAgent(LlmRoutingAgentBuilder builder) throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.compileConfig, builder.subAgents);
this.chatModel = builder.chatModel;
}
public static LlmRoutingAgentBuilder builder() {
return new LlmRoutingAgentBuilder();
}
@Override
protected StateGraph buildSpecificGraph(FlowGraphBuilder.FlowGraphConfig config) throws GraphStateException {
config.setChatModel(this.chatModel);
return FlowGraphBuilder.buildGraph(FlowAgentEnum.ROUTING.getType(), config);
}
/**
* Builder for creating LlmRoutingAgent instances. Extends the common FlowAgentBuilder
* and adds LLM-specific configuration.
*/
public static class LlmRoutingAgentBuilder extends FlowAgentBuilder<LlmRoutingAgent, LlmRoutingAgentBuilder> {
private ChatModel chatModel;
/**
* Sets the ChatModel for LLM-based routing decisions.
* @param chatModel the chat model to use for routing
* @return this builder instance for method chaining
*/
public LlmRoutingAgentBuilder model(ChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatModel = chatModel;
return this;
}
@Override
protected LlmRoutingAgentBuilder self() {
return this;
}
@Override
protected void validate() {
super.validate();
if (chatModel == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ChatModel must be provided for LLM routing agent");
}
}
@Override
public LlmRoutingAgent build() throws GraphStateException {
validate();
return new LlmRoutingAgent(this);
}
}
}
路由机制:
- 使用 LLM 分析输入内容
- 根据分析结果选择目标 Agent
- 支持动态路由决策
节点能力
ConditionEvaluator - 条件评估器
ConditionEvaluator 用于评估条件,支持条件路由。
功能:
- 评估状态中的条件表达式
- 返回布尔值用于路由决策
- 支持复杂条件逻辑
RoutingEdgeAction - 路由边动作
RoutingEdgeAction 用于实现路由逻辑,根据条件选择目标节点。
功能:
- 根据状态评估路由条件
- 返回目标节点 ID
- 支持 LLM 路由和条件路由
TransparentNode - 透明节点
TransparentNode 是一个透明节点,直接传递状态,不进行任何处理。
功能:
- 用于图结构的占位
- 保持状态不变
- 简化图结构
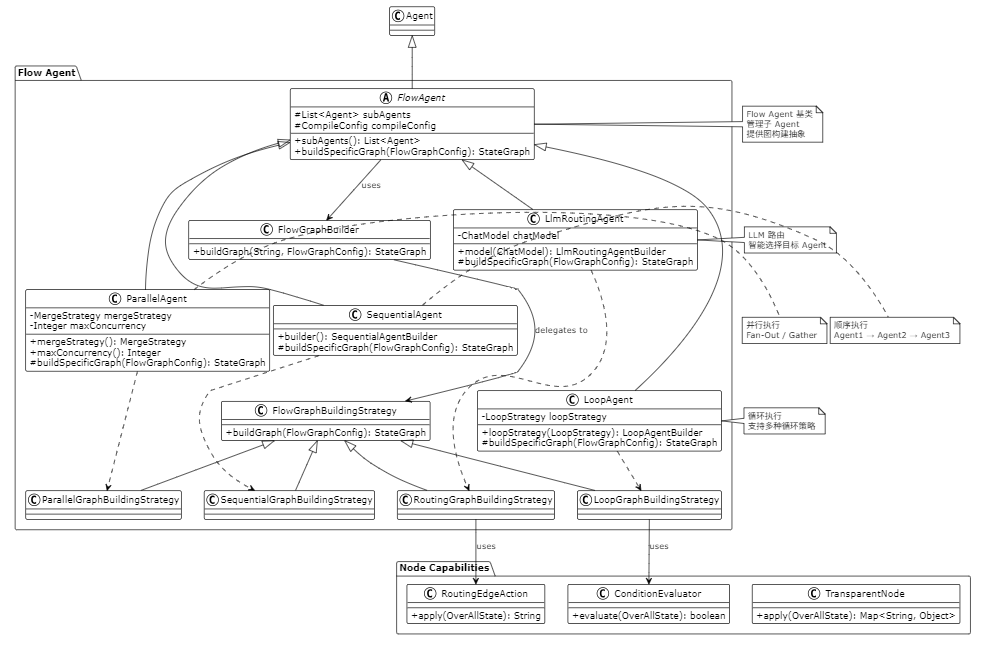
关键类关系
以下 PlantUML 类图展示了 Flow Agent 的类关系:
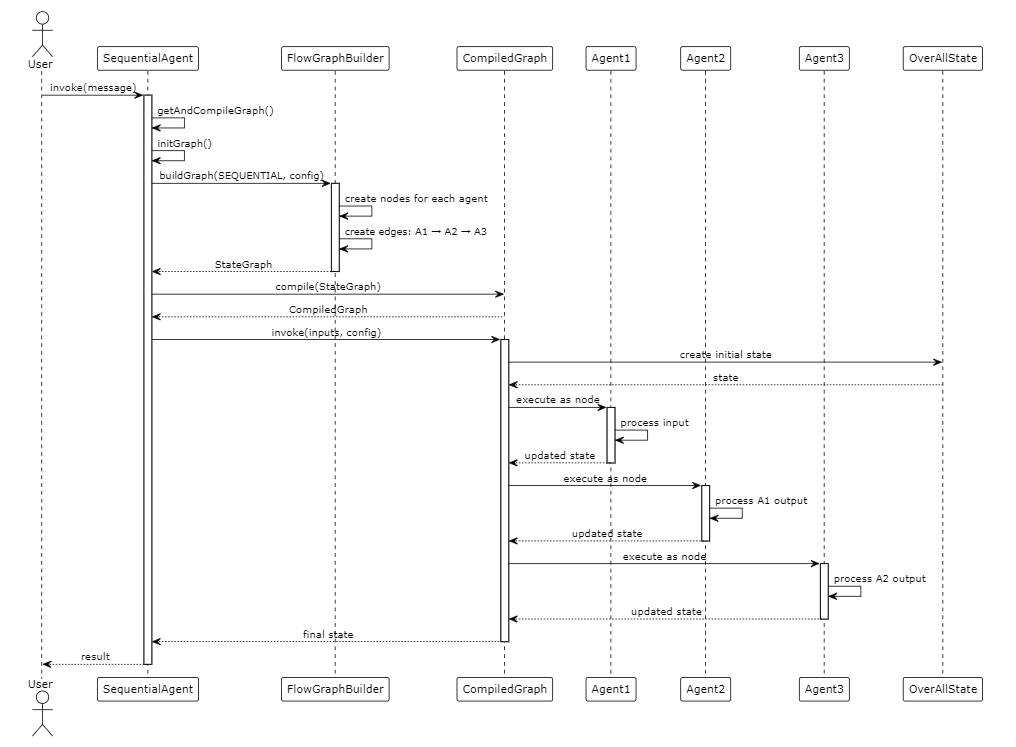
关键流程
以下 PlantUML 时序图展示了 SequentialAgent 的执行流程:
实现关键点说明
1. 策略模式
Flow Agent 使用策略模式构建图:
FlowGraphBuildingStrategy定义图构建策略接口- 每种 Flow Agent 对应一个具体的策略实现
FlowGraphBuilder根据类型选择策略
2. Builder 模式
所有 Flow Agent 都使用 Builder 模式:
FlowAgentBuilder提供通用构建能力- 每个具体 Agent 有自己的 Builder 类
- 支持链式调用和参数验证
3. 节点转换
子 Agent 通过 asNode() 方法转换为 Graph 节点:
BaseAgent.asNode()将 Agent 转换为SubGraphNode- 支持 Agent 嵌套和组合
- 保持状态传递和隔离
4. 条件路由
支持条件路由能力:
ConditionEvaluator评估条件表达式RoutingEdgeAction实现路由逻辑- 支持复杂条件判断
5. 并行执行
ParallelAgent 实现真正的并行执行:
- 使用 Graph 的并行节点能力
- 支持最大并发数限制
- 提供结果合并策略
6. 循环策略
LoopAgent 支持多种循环策略:
CountLoopStrategy:固定次数ConditionLoopStrategy:条件循环ArrayLoopStrategy:数组遍历- 可扩展自定义策略
总结说明
核心设计理念
- 编排模式:提供顺序、并行、循环、路由四种编排模式
- 策略模式:通过策略模式实现灵活的图构建
- 节点能力:支持条件评估、路由选择等节点能力
- 可组合性:支持 Agent 嵌套和组合
关键优势
- 灵活性:支持多种编排模式,满足不同场景需求
- 可扩展性:通过策略模式支持自定义编排逻辑
- 性能:并行执行提高处理效率
- 智能路由:LLM 路由实现智能 Agent 选择
使用场景
- SequentialAgent:需要顺序处理的多步骤任务
- ParallelAgent:可以并行处理的独立任务
- LoopAgent:需要循环处理的任务(如批量处理)
- LlmRoutingAgent:需要根据内容智能选择处理方式的场景
Flow Agent 系列为多 Agent 编排提供了完整的解决方案,使开发者能够灵活构建复杂的 Agent 工作流。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号