Spring AI Alibaba 项目源码学习(三)-Graph 执行流程分析
Graph 执行流程分析
概述
本文档分析 spring-ai-alibaba-graph-core 模块中 Graph 的执行流程,包括执行器(Executor)、调度机制、Checkpoint 机制和状态管理。
入口类说明
GraphRunner - 执行入口
GraphRunner 是基于 Project Reactor 的响应式图执行引擎,是执行 Graph 的主要入口。
核心职责:
- 封装编译后的图和执行配置
- 提供响应式执行接口(返回 Flux)
- 委托给 MainGraphExecutor 执行实际流程
关键代码:
public class GraphRunner {
private final CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
private final RunnableConfig config;
private final AtomicReference<Object> resultValue = new AtomicReference<>();
// Handler for main execution flow - demonstrates encapsulation
private final MainGraphExecutor mainGraphExecutor;
public GraphRunner(CompiledGraph compiledGraph, RunnableConfig config) {
this.compiledGraph = compiledGraph;
this.config = config;
// Initialize the main execution handler - demonstrates encapsulation
this.mainGraphExecutor = new MainGraphExecutor();
}
public Flux<GraphResponse<NodeOutput>> run(OverAllState initialState) {
return Flux.defer(() -> {
try {
GraphRunnerContext context = new GraphRunnerContext(initialState, config, compiledGraph);
// Delegate to the main execution handler - demonstrates polymorphism
return mainGraphExecutor.execute(context, resultValue);
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Flux.error(e);
}
});
}
MainGraphExecutor - 主执行器
MainGraphExecutor 是主执行流程处理器,继承自 BaseGraphExecutor,负责协调整个图的执行。
核心职责:
- 处理开始节点和结束节点
- 管理迭代次数和中断逻辑
- 协调节点执行和边路由
- 处理 Checkpoint 和恢复
关键代码:
public class MainGraphExecutor extends BaseGraphExecutor {
private final NodeExecutor nodeExecutor;
public MainGraphExecutor() {
this.nodeExecutor = new NodeExecutor(this);
}
/**
* Implementation of the execute method. This demonstrates polymorphism as it provides
* a specific implementation for main execution flow.
* @param context the graph runner context
* @param resultValue the atomic reference to store the result value
* @return Flux of GraphResponse with execution result
*/
@Override
public Flux<GraphResponse<NodeOutput>> execute(GraphRunnerContext context, AtomicReference<Object> resultValue) {
try {
if (context.shouldStop() || context.isMaxIterationsReached()) {
return handleCompletion(context, resultValue);
}
final var returnFromEmbed = context.getReturnFromEmbedAndReset();
if (returnFromEmbed.isPresent()) {
var interruption = returnFromEmbed.get().value(new TypeRef<InterruptionMetadata>() {
});
if (interruption.isPresent()) {
return Flux.just(GraphResponse.done(interruption.get()));
}
return Flux.just(GraphResponse.done(context.buildCurrentNodeOutput()));
}
if (context.getCurrentNodeId() != null && context.getConfig().isInterrupted(context.getCurrentNodeId())) {
context.getConfig().withNodeResumed(context.getCurrentNodeId());
return Flux.just(GraphResponse.done(GraphResponse.done(context.getCurrentStateData())));
}
if (context.isStartNode()) {
return handleStartNode(context);
}
if (context.isEndNode()) {
return handleEndNode(context, resultValue);
}
final var resumeFrom = context.getResumeFromAndReset();
if (resumeFrom.isPresent()) {
if (context.getCompiledGraph().compileConfig.interruptBeforeEdge()
&& java.util.Objects.equals(context.getNextNodeId(), INTERRUPT_AFTER)) {
var nextNodeCommand = context.nextNodeId(resumeFrom.get(), context.getCurrentStateData());
context.setNextNodeId(nextNodeCommand.gotoNode());
context.setCurrentNodeId(null);
}
}
if (context.shouldInterrupt()) {
try {
InterruptionMetadata metadata = InterruptionMetadata
.builder(context.getCurrentNodeId(), context.cloneState(context.getCurrentStateData()))
.build();
return Flux.just(GraphResponse.done(metadata));
NodeExecutor - 节点执行器
NodeExecutor 负责执行单个节点,处理节点动作的执行和结果处理。
核心职责:
- 执行节点动作(NodeAction)
- 处理中断逻辑(InterruptableAction)
- 处理流式输出(StreamingOutput)
- 更新状态并确定下一个节点
关键代码:
public class NodeExecutor extends BaseGraphExecutor {
private final MainGraphExecutor mainGraphExecutor;
public NodeExecutor(MainGraphExecutor mainGraphExecutor) {
this.mainGraphExecutor = mainGraphExecutor;
}
/**
* Implementation of the execute method. This demonstrates polymorphism as it provides
* a specific implementation for node execution.
* @param context the graph runner context
* @param resultValue the atomic reference to store the result value
* @return Flux of GraphResponse with execution result
*/
@Override
public Flux<GraphResponse<NodeOutput>> execute(GraphRunnerContext context, AtomicReference<Object> resultValue) {
return executeNode(context, resultValue);
}
/**
* Executes a node and handles its result.
* @param context the graph runner context
* @param resultValue the atomic reference to store the result value
* @return Flux of GraphResponse with node execution result
*/
private Flux<GraphResponse<NodeOutput>> executeNode(GraphRunnerContext context,
AtomicReference<Object> resultValue) {
try {
context.setCurrentNodeId(context.getNextNodeId());
String currentNodeId = context.getCurrentNodeId();
AsyncNodeActionWithConfig action = context.getNodeAction(currentNodeId);
if (action == null) {
return Flux.just(GraphResponse.error(RunnableErrors.missingNode.exception(currentNodeId)));
}
if (action instanceof InterruptableAction) {
context.getConfig().metadata(RunnableConfig.STATE_UPDATE_METADATA_KEY).ifPresent(updateFromFeedback -> {
if (updateFromFeedback instanceof Map<?, ?>) {
context.mergeIntoCurrentState((Map<String, Object>) updateFromFeedback);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
});
Optional<InterruptionMetadata> interruptMetadata = ((InterruptableAction) action)
.interrupt(currentNodeId, context.cloneState(context.getCurrentStateData()), context.getConfig());
if (interruptMetadata.isPresent()) {
GraphRunnerContext - 执行上下文
GraphRunnerContext 管理图执行过程中的状态和上下文信息。
核心职责:
- 管理当前节点和下一个节点
- 管理迭代次数
- 处理 Checkpoint 和恢复
- 管理状态更新
关键代码:
public class GraphRunnerContext {
public static final String INTERRUPT_AFTER = "__INTERRUPTED__";
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GraphRunner.class);
final CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
final AtomicInteger iteration = new AtomicInteger(0);
OverAllState overallState;
RunnableConfig config;
String currentNodeId;
String nextNodeId;
String resumeFrom;
ReturnFromEmbed returnFromEmbed;
public GraphRunnerContext(OverAllState initialState, RunnableConfig config, CompiledGraph compiledGraph)
throws Exception {
this.compiledGraph = compiledGraph;
this.config = config;
if (config.metadata(RunnableConfig.HUMAN_FEEDBACK_METADATA_KEY).isPresent()) {
initializeFromResume(initialState, config);
} else {
initializeFromStart(initialState, config);
}
}
private void initializeFromResume(OverAllState initialState, RunnableConfig config) {
log.trace("RESUME REQUEST");
var saver = compiledGraph.compileConfig.checkpointSaver()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalStateException("Resume request without a configured checkpoint saver!"));
var checkpoint = saver.get(config)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalStateException("Resume request without a valid checkpoint!"));
执行流程时序图
以下 PlantUML 时序图展示了 Graph 的完整执行流程:
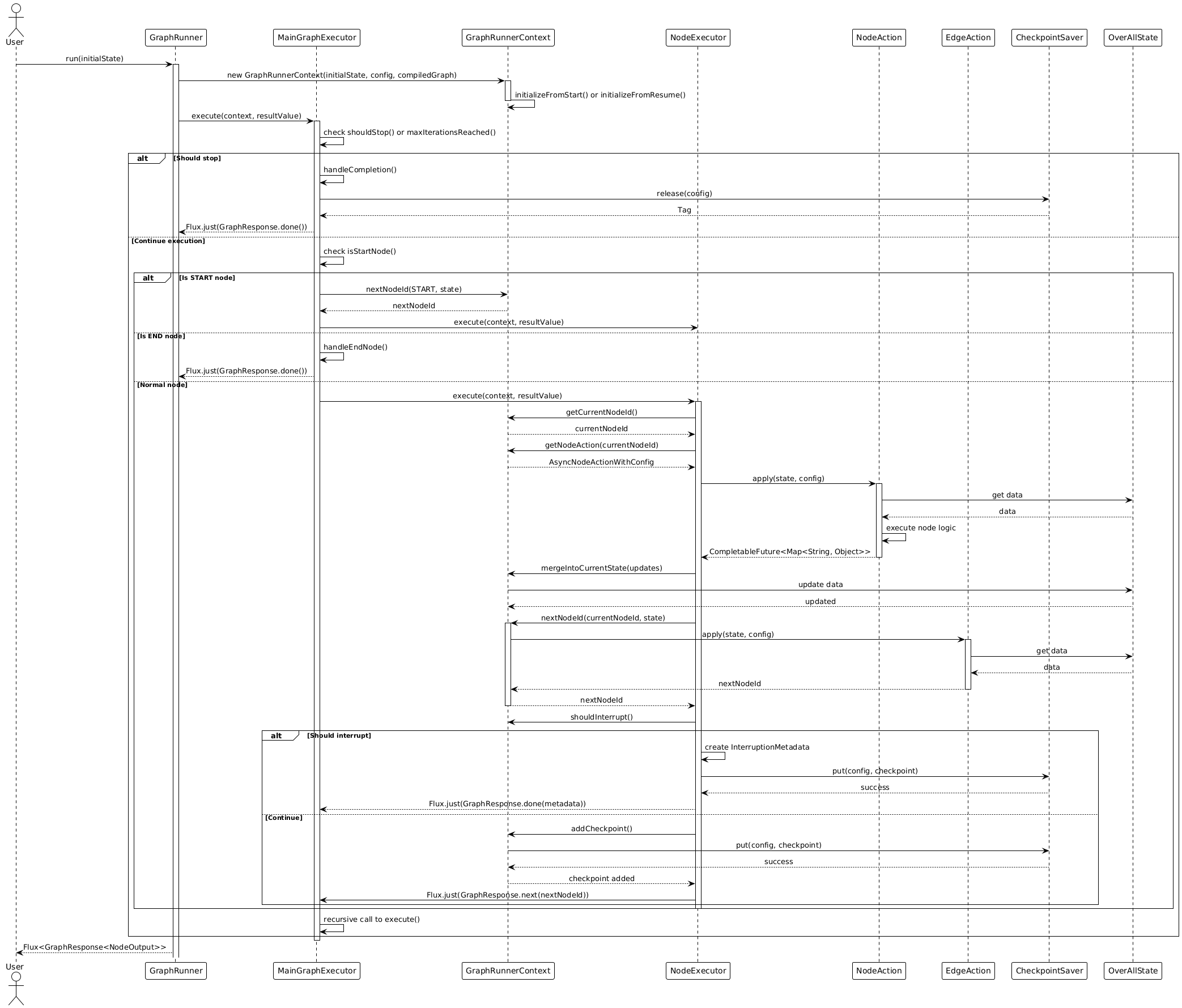
Checkpoint 机制
BaseCheckpointSaver - Checkpoint 保存器接口
BaseCheckpointSaver 定义了 Checkpoint 保存和恢复的接口。
关键代码:
public interface BaseCheckpointSaver {
String THREAD_ID_DEFAULT = "$default";
record Tag(String threadId, Collection<Checkpoint> checkpoints) {
public Tag(String threadId, Collection<Checkpoint> checkpoints) {
this.threadId = threadId;
this.checkpoints = ofNullable(checkpoints).map(List::copyOf).orElseGet(List::of);
}
}
default Tag release(RunnableConfig config) throws Exception {
return null;
}
Collection<Checkpoint> list(RunnableConfig config);
Optional<Checkpoint> get(RunnableConfig config);
RunnableConfig put(RunnableConfig config, Checkpoint checkpoint) throws Exception;
boolean clear(RunnableConfig config);
default Optional<Checkpoint> getLast(LinkedList<Checkpoint> checkpoints, RunnableConfig config) {
return (checkpoints == null || checkpoints.isEmpty()) ? Optional.empty() : ofNullable(checkpoints.peek());
}
default LinkedList<Checkpoint> getLinkedList(List<Checkpoint> checkpoints) {
return Objects.nonNull(checkpoints) ? new LinkedList<>(checkpoints) : new LinkedList<>();
}
}
Checkpoint 流程
- 保存 Checkpoint:在执行节点后,通过
GraphRunnerContext.addCheckpoint()保存当前状态 - 恢复 Checkpoint:通过
RunnableConfig中的 checkpoint ID 恢复执行 - 释放 Checkpoint:执行完成后释放 Checkpoint 资源
状态管理
OverAllState 更新机制
状态更新通过 KeyStrategy 控制:
- ReplaceStrategy:替换策略,新值完全替换旧值
- AppendStrategy:追加策略,新值追加到列表
- Reducer:归约策略,使用自定义函数合并值
状态更新流程:
- 节点执行返回
Map<String, Object>更新 GraphRunnerContext根据 KeyStrategy 合并更新- 更新后的状态传递给下一个节点
实现关键点说明
1. 响应式编程
使用 Project Reactor 的 Flux 实现响应式执行:
- 支持流式输出
- 支持背压控制
- 支持异步执行
2. 模板方法模式
BaseGraphExecutor 定义执行框架,子类实现具体逻辑:
MainGraphExecutor:主执行流程NodeExecutor:节点执行流程
3. 上下文模式
GraphRunnerContext 封装执行上下文:
- 管理当前执行状态
- 提供状态访问接口
- 处理 Checkpoint 和恢复
4. 中断和恢复机制
支持执行中断和恢复:
InterruptableAction:可中断的动作InterruptionMetadata:中断元数据- Checkpoint 保存和恢复
5. 迭代控制
通过 maxIterations 控制最大迭代次数,防止无限循环。
总结说明
核心执行流程
- 初始化:创建
GraphRunnerContext,初始化状态 - 开始执行:从 START 节点开始
- 节点执行:执行当前节点,更新状态
- 边路由:根据 EdgeAction 确定下一个节点
- Checkpoint:保存执行状态(可选)
- 迭代:重复步骤 3-5,直到到达 END 节点
- 完成:返回最终结果
关键设计特点
- 响应式:基于 Reactor 的响应式执行
- 可中断:支持执行中断和恢复
- 状态管理:灵活的状态更新策略
- 可观测:支持监控和追踪
- 容错性:错误处理和恢复机制
执行器层次结构
BaseGraphExecutor (抽象基类)
├── MainGraphExecutor (主执行器)
└── NodeExecutor (节点执行器)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号