计算程序运行总花费时间 模板(C/C++(boost)/Java/Python)( 精确到毫秒)
C语言版本
#include<stdio.h>
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
clock_t start,end;
start= clock();
//to do
end = clock();
printf("本程序运行时间总花费:\t\t%f\tms", (float)(end - start)*1000.0/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
return 0;
}
C++版本
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<time.h>
int main()
{
clock_t start,end;
start= clock();
//to do
end = clock();
cout<<"本程序运行时间总花费:\t"<<(end - start)*1000.0/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"\tms"<<endl;
return 0;
}
boost 库 (C++ 编写)
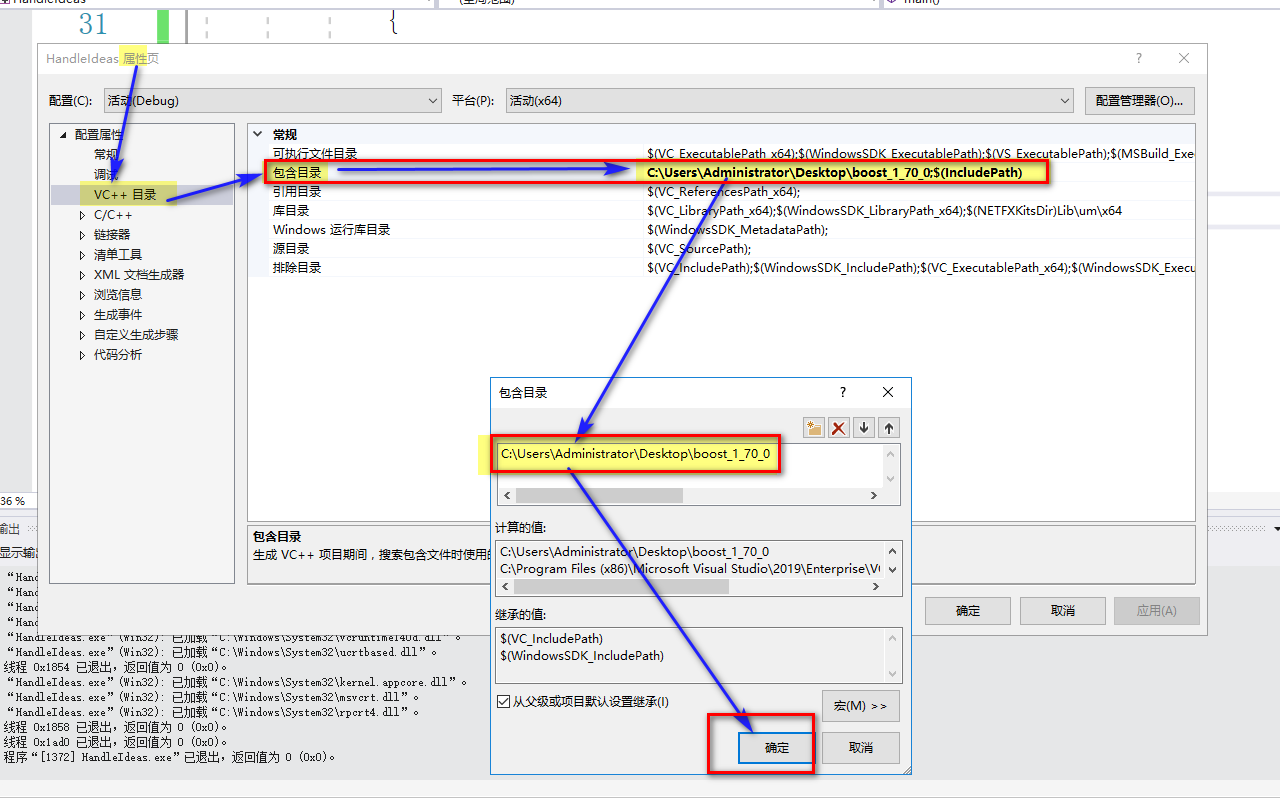
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<boost/timer.hpp>
#include<boost/progress.hpp>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
int main()
{
progress_timer t;// 开始计时
int j = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
j++;
}
//***************************************************************//
vector<string> v(1000);
//progress_display是一个能够显示程序进度的工具
//progress_display可以在控制台程序中显示程序的执行进度,
//如果程序执行很耗费时间,那么它能够提供一个良好的等待界面。
progress_display pd(v.size());
for(auto&x:v)
{
cout << x;
++pd;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 600; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < 600; j++)
{
}
}
}
cout <<"本程序花费总时间为:\t:"<< t.elapsed() << endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/loongsking/article/details/80136004
https://blog.csdn.net/jiang_xinxing/article/details/60757662
java版本
public class Driver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取系统剩余的内存空间
long begin1 = Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory();
//获取系统的当前时间
long start01 = System.currentTimeMillis();
//to do
//获取系统剩余的内存空间
long end2 = Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory();
//获取系统的当前时间 单位是毫秒
long finish02 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("本程序占用内存:" + (begin1 - end2));
System.out.println("本程序占用时间:" + (finish02 - start01));
}
}
Python版本
# python 的标准库手册推荐在任何情况下尽量使用time.clock().
# 只计算了程序运行CPU的时间,返回值是浮点数
import time
start = time.clock()
# to do
end = time.clock()
# 单位是秒
# print('Running time: %s Seconds' % (end - start))
print("本程序运行花费总是时间:\t", (end - start) * 1000)
posted on 2019-04-28 00:18 Indian_Mysore 阅读(258) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号