九、linux 之 定时任务调度
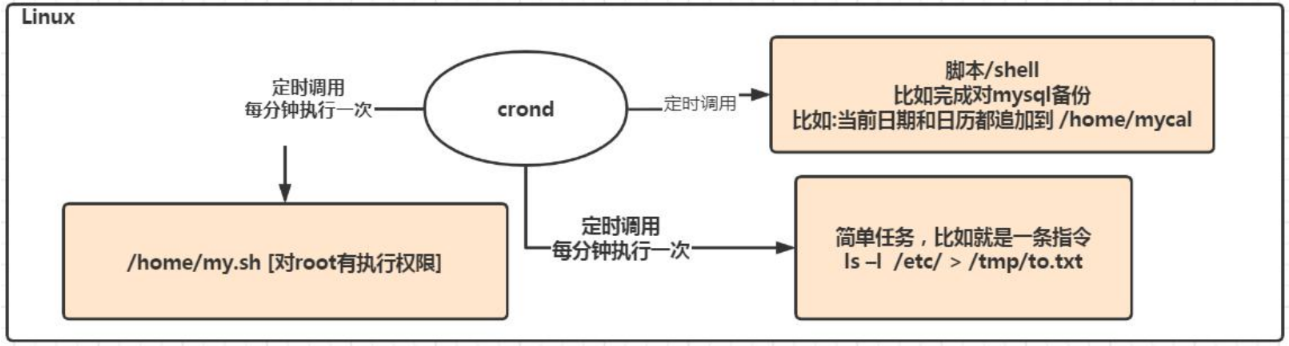
一、crond任务调度
1.1 crond任务调度的概述
任务调度:是指系统在某个时间执行的特定的命令或程序。
任务调度分类:
1. 系统工作:有些重要的工作必须周而复始地执行。如病毒扫描等
2. 个别用户工作:个别用户可能希望执行某些程序,比如对 mysql 数据库的备份。
1.2 基本用法
1.2.1 基本用法
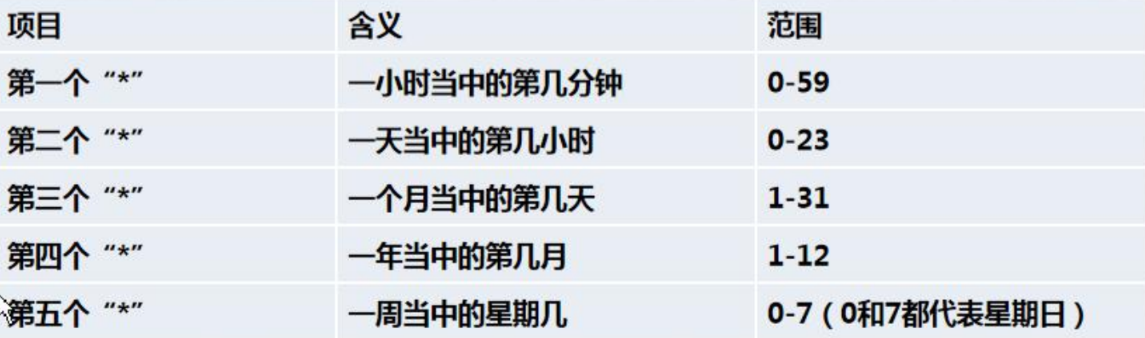
crontab [选项]
设置任务调度文件:/etc/crontab
例子: 每分钟执行查看一次/ect目录,把目录内容写进/tml/a.txt下
具体实现步骤:
1.crontab –e
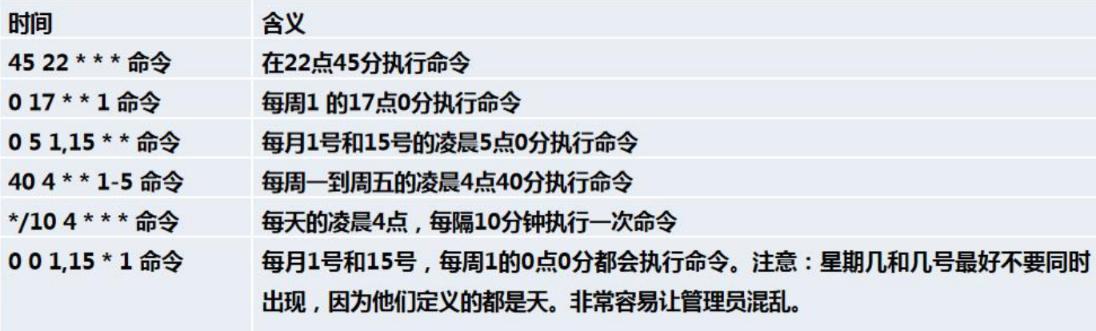
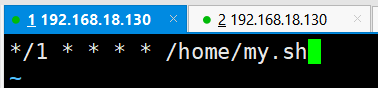
2.*/1 * * * * ls -l /etc >> /tmp/a.txt
意思说每小时的每分钟执行 ls –l /etc/ > /tmp/a.txt 命令
1.3 应用实例
1.3.1 案例一
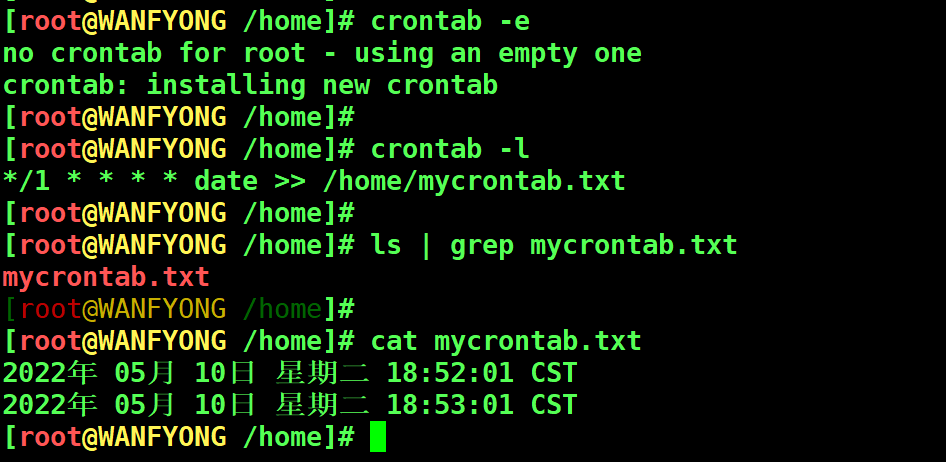
# 每隔 1 分钟,就将当前的日期信息,追加到 /home/mycrontab.txt 文件中 [root@WANFYONG /home]# crontab -e no crontab for root - using an empty one crontab: installing new crontab [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# crontab -l */1 * * * * date >> /home/mycrontab.txt [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# ls | grep mycrontab.txt mycrontab.txt [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# cat mycrontab.txt 2022年 05月 10日 星期二 18:52:01 CST 2022年 05月 10日 星期二 18:53:01 CST [root@WANFYONG /home]#
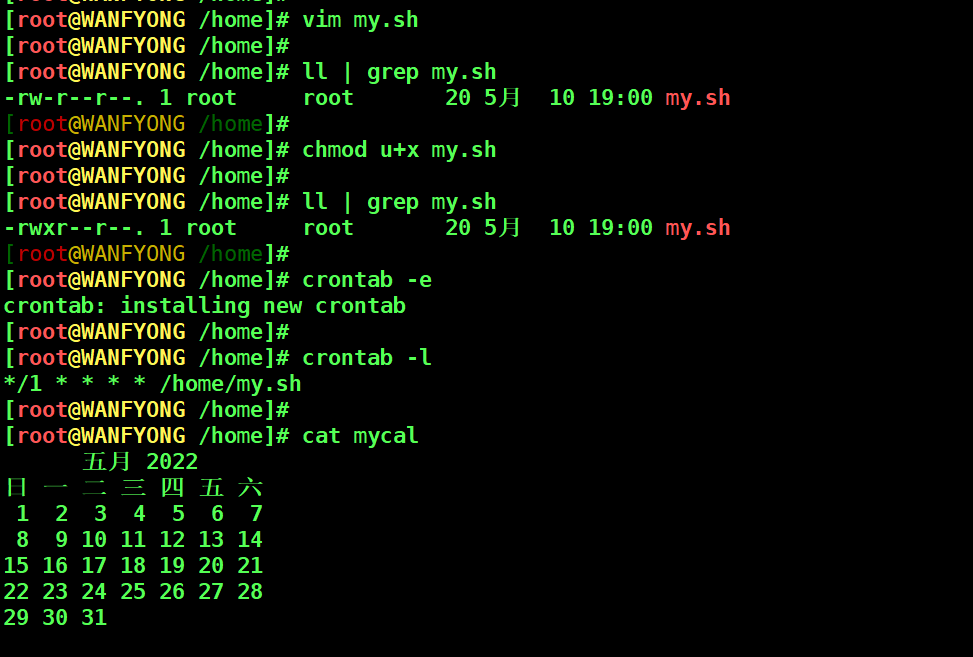
# 每隔 1 分钟, 将当前日期和日历都追加到 /home/mycal 文件中 [root@WANFYONG /home]# vim my.sh [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# ll | grep my.sh -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 20 5月 10 19:00 my.sh [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# chmod u+x my.sh [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# ll | grep my.sh -rwxr--r--. 1 root root 20 5月 10 19:00 my.sh [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# crontab -e ### --> 写入 */1 * * * * /home/my.sh crontab: installing new crontab [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# crontab -l */1 * * * * /home/my.sh [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# cat mycal 五月 2022 日 一 二 三 四 五 六 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
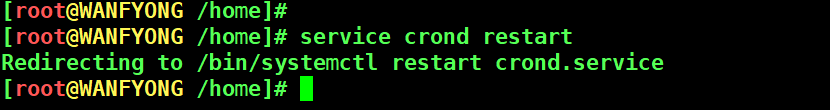
# service crond restart [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# service crond restart Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart crond.service
二、at定时任务
2.1 基本介绍
1. at 命令是一次性定时计划任务,at 的守护进程 atd 会以后台模式运行,检查作业队列来运行。
2. 默认情况下,atd 守护进程每 60 秒检查作业队列,有作业时,会检查作业运行时间,如果时间与当前时间匹配,则 运行此作业。
3. at 命令是一次性定时计划任务,执行完一个任务后不再执行此任务了
4. 在使用 at 命令的时候,一定要保证 atd 进程的启动 , 可以使用相关指令来查看 ps -ef | grep atd //可以检测 atd 是否在运行
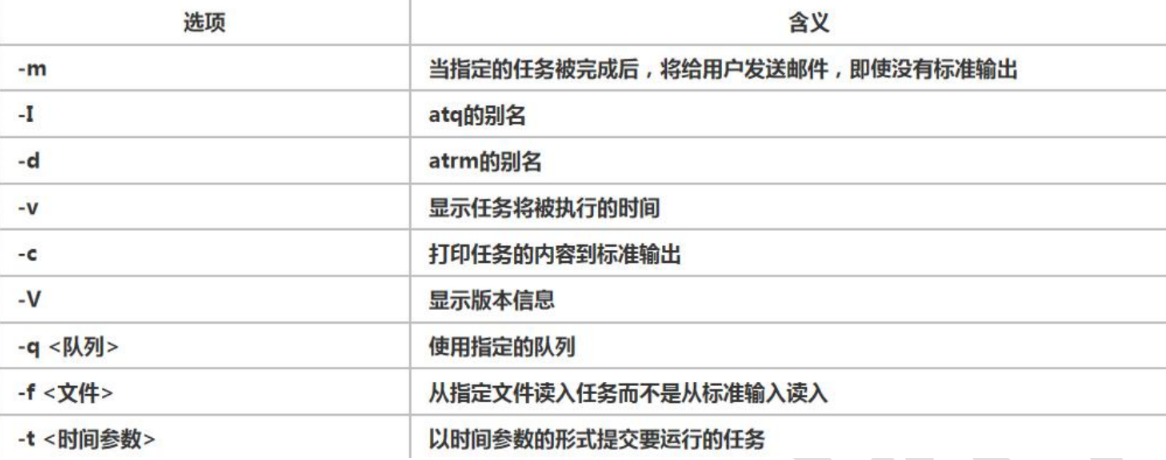
# at [选项] [时间] # Ctrl + D 结束 at 命令的输入, 输出两次
1. 接受在当天的 hh:mm(小时:分钟)式的时间指定。假如该时间已过去,那么就放在第二天执行。 例如:04:00
2. 使用 midnight(深夜),noon(中午),teatime(饮茶时间,一般是下午 4 点)等比较模糊的词语来指定时间。
3. 采用 12 小时计时制,即在时间后面加上 AM(上午)或 PM(下午)来说明是上午还是下午。 例如:12pm
4. 指定命令执行的具体日期,指定格式为 month day(月 日)或 mm/dd/yy(月/日/年)或 dd.mm.yy(日.月.年),指 定的日期必须跟在指定时间的后面。 例如:04:00 2021-03-1
5. 使用相对计时法。指定格式为:now + count time-units ,now 就是当前时间,time-units 是时间单位,这里能够是 minutes (分钟)、hours(小时)、days(天)、weeks(星期)。count 是时间的数量,几天,几小时。 例如:now + 5 minutes
6. 直接使用 today(今天)、tomorrow(明天)来指定完成命令的时间。
# atq 查看 # atrm [编号] 删除编号的任务 [root@WANFYONG /home]# atq 2 Thu May 12 17:00:00 2022 a root [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# atrm 2 [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# atq [root@WANFYONG /home]#
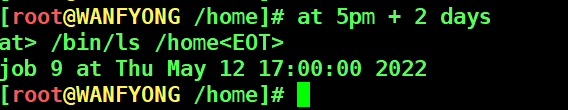
# 1. 2 天后的下午 5 点执行 /bin/ls /home [root@WANFYONG /home]# at 5pm + 2 days at> /bin/ls /home<EOT> job 5 at Thu May 12 17:00:00 2022 [root@WANFYONG /home]#
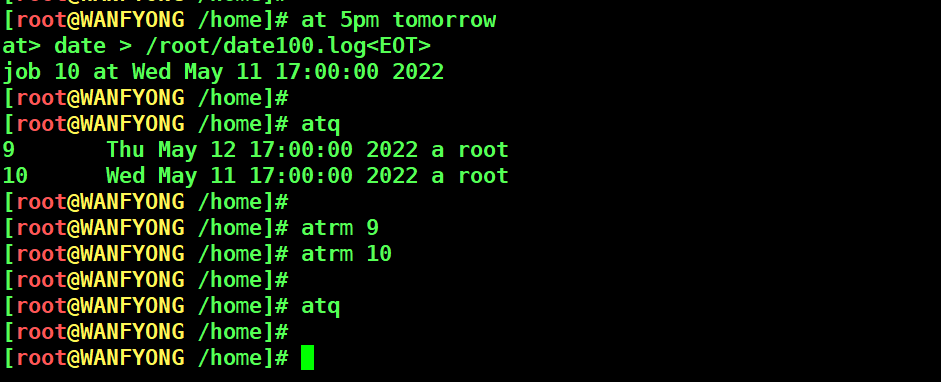
# 2. 明天 17 点钟,输出时间到指定文件内 比如 /root/date100.log [root@WANFYONG /home]# at 5pm tomorrow at> date > /root/date100.log<EOT> job 10 at Wed May 11 17:00:00 2022 [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# atq 9 Thu May 12 17:00:00 2022 a root 10 Wed May 11 17:00:00 2022 a root [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# atrm 9 [root@WANFYONG /home]# atrm 10 [root@WANFYONG /home]# [root@WANFYONG /home]# atq [root@WANFYONG /home]#





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号