2024.2.8
通过阅读CatWhojava代码。
package dada; public class CatchWho { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
最后运行结果
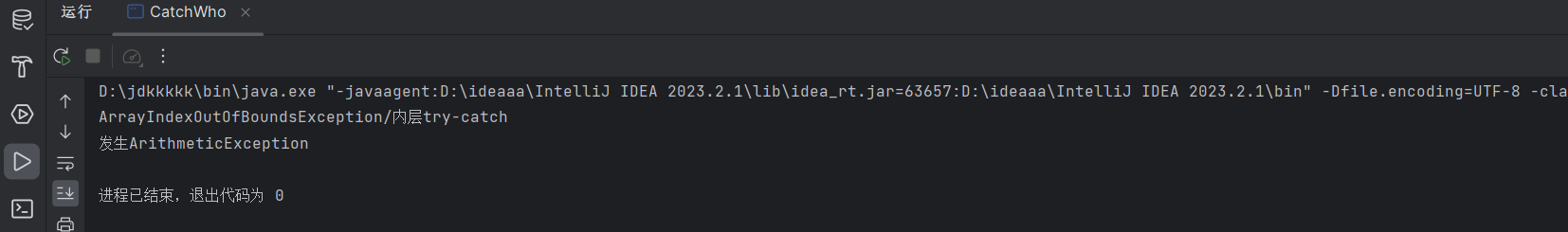
通过CatchWho2.java
package dada; public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
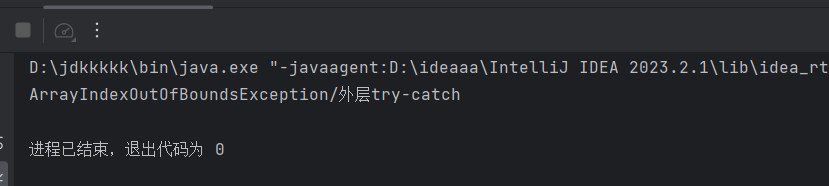
这段代码演示了嵌套的 try-catch 块以及异常处理的流程。
首先,在外层的 try-catch 块中:
1. 尝试抛出一个 `ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException` 异常,在内层的 catch 块之前。
2. 然后,由于 `ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException` 与内层 catch 块中指定的 `ArithmeticException` 异常类型不匹配,所以不会执行内层 catch 块中的代码,而是跳过该 catch 块。
3. 继续执行外层的 catch 块。
需要注意的是,当遇到异常的时候,程序会寻找与抛出的异常类型匹配的 catch 块来处理异常。如果找不到匹配的 catch 块,则异常会被传递给上一级的调用者或者虚拟机处理。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号