程序设计与算法(三)C++面向对象程序设计 第十周 相关笔记
一、C++11 新特性(1)
1、
任何容器的初始化
= {1,12,4124,124}
2、
auto关键字
decltype(1) a = 5;
3、
#include<memory>
shared_ptr




#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node{ int x; node (int a){ x = a; } ~node(){ cout<<x<<" destructor"<<endl; } }; int main(){ shared_ptr<node> sp1 (new node(2)); shared_ptr<node> sp2; cout<<sp1->x<<endl; sp2 = sp1; sp1.reset(); sp2.reset(); cout<<"end main"<<endl; }

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node{ int x; node (int a){ x = a; } ~node(){ cout<<x<<" destructor"<<endl; } }; int main(){ shared_ptr<node> sp1 (new node(2)); cout<<sp1->x<<endl; sp1.reset(); cout<<"end main"<<endl; }
4、基于范围的for循环 (不用加范围了)

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ int a[] = {1,2,5,4,5,1,56,1}; for(auto &x:a)x*=10; for(auto x:a)cout<<x<<" "; cout<<endl; }
5、左值引用 右值引用

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class node{ int x; public: node (int a){ x = a; } }; int main(){ node && t= node(4); }
避免深拷贝
二、C++11 新特性(2)
1、
#include<unordered_map>
hash实现和map功能差不多

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<unordered_map> using namespace std; unordered_map<string,int> mp; int main(){ mp.insert(make_pair("Bruce",123)); mp.insert(make_pair("Leo",233)); mp.insert(make_pair("Jack",233)); mp["Jack"] = 212; auto iter = mp.find("Br"); if(iter!=mp.end()) cout<<iter->second<<endl; }
2、regex
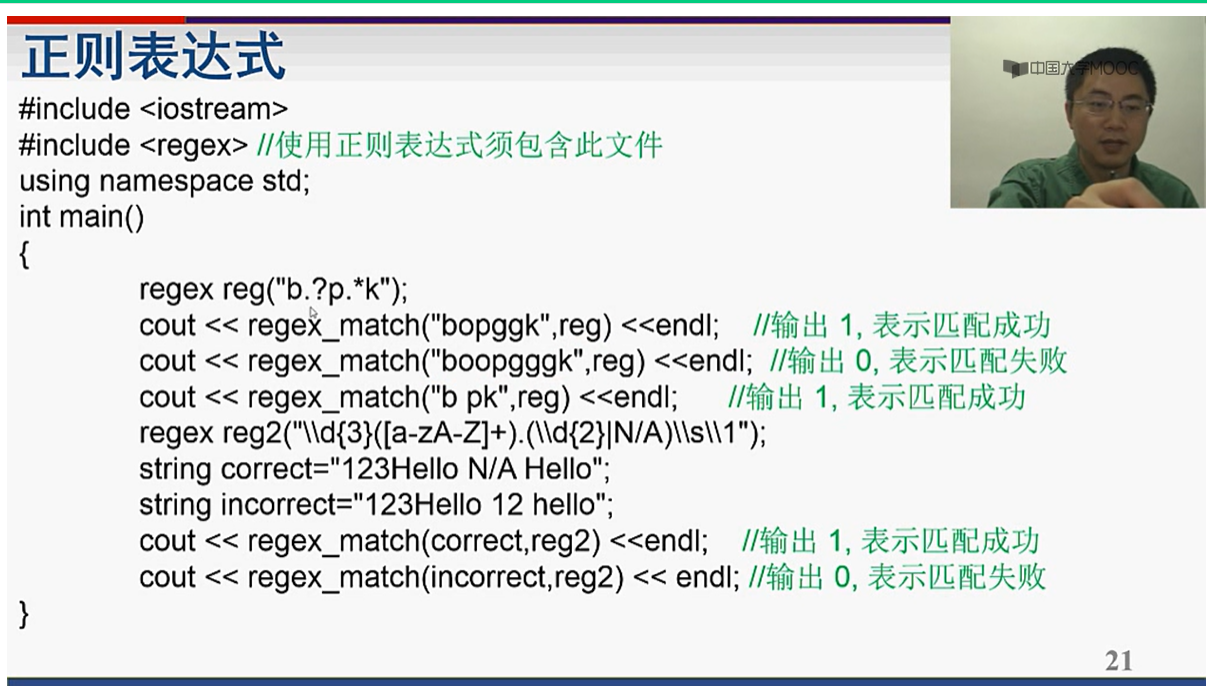
3、
lambda表达式 简化函数

1)

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<regex> using namespace std; int main(){ int z =0; cout<<[](int a,int b){return a+b;}(1,2)<<endl; auto ff = [&z](int a,int b){ z = a+b; return a-b; }; // ff(5,3); cout<<z<<" "<<ff(5,3); return 0; }
2)for_each 与 lambda

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<regex> using namespace std; int main(){ vector<int> v = {1,2,3,4}; for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),[](int &x){x*=2;}); for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),[](int &x){cout<<x<<" ";}); return 0; }
一、
二、C++11 新特性(2)
1、
#include<unordered_map>
hash实现和map功能差不多

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<unordered_map> using namespace std; unordered_map<string,int> mp; int main(){ mp.insert(make_pair("Bruce",123)); mp.insert(make_pair("Leo",233)); mp.insert(make_pair("Jack",233)); mp["Jack"] = 212; auto iter = mp.find("Br"); if(iter!=mp.end()) cout<<iter->second<<endl; }
2、regex

3、
lambda表达式 简化函数
1)

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<regex> using namespace std; int main(){ int z =0; cout<<[](int a,int b){return a+b;}(1,2)<<endl; auto ff = [&z](int a,int b){ z = a+b; return a-b; }; // ff(5,3); cout<<z<<" "<<ff(5,3); return 0; }
2)for_each 与 lambda
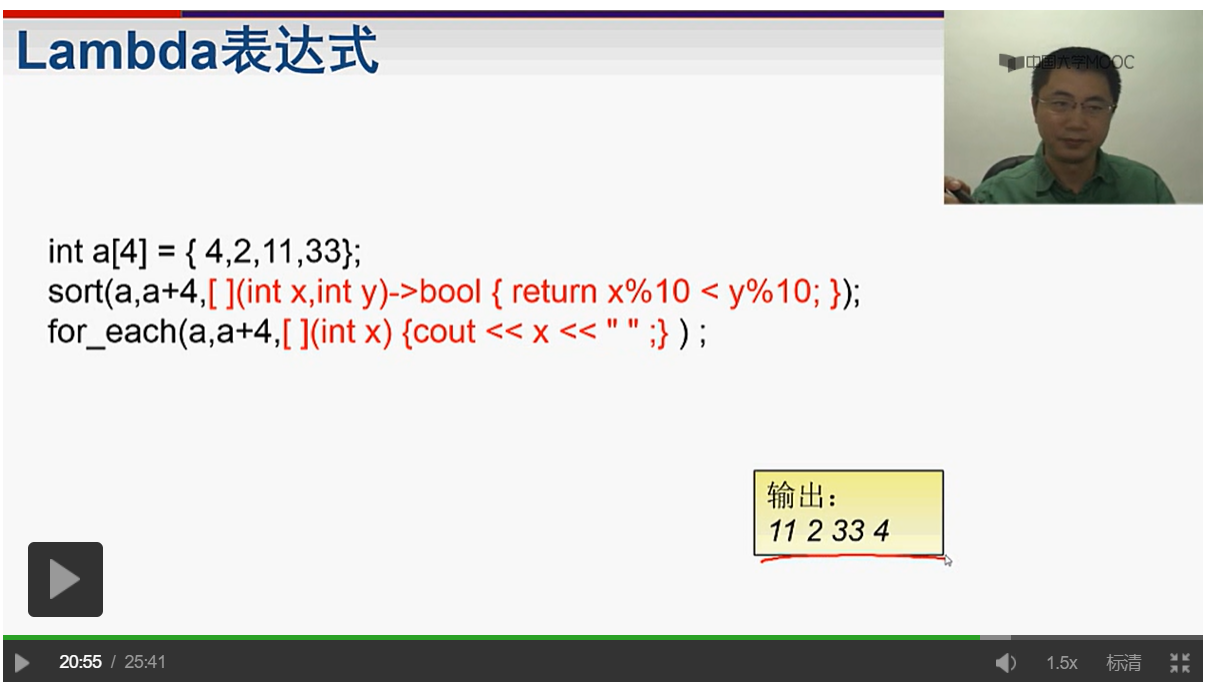



#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<regex> using namespace std; const int N = 1e5 + 10; int a[N]; int main(){ int n; cin>>n; for(int i = 1;i<=n;++i)cin>>a[i]; sort(a+1,a+1+n,[](int a,int b){return a<b;}); for_each(a+1,a+1+n,[](int a){cout<<a<<" ";}); return 0; }

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<regex> using namespace std; int main(){ vector<int> v = {1,2,3,4}; for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),[](int &x){x*=2;}); for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),[](int &x){cout<<x<<" ";}); return 0; }
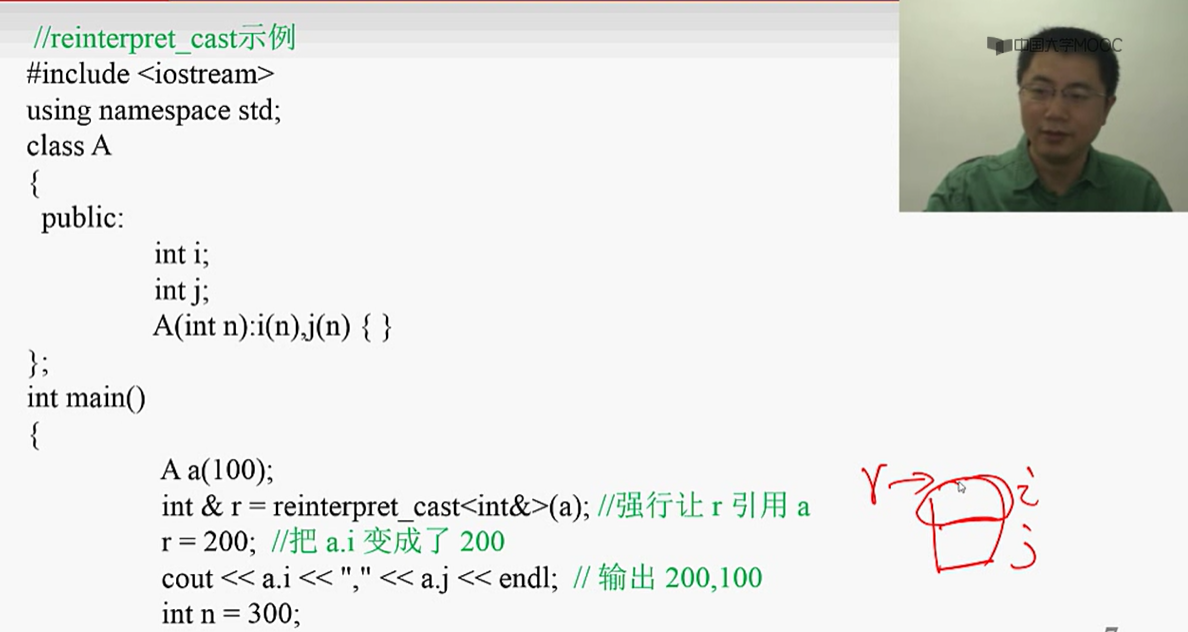
三、强制类型转换

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class node{ int x; public: node (int a){ x = a; } operator int (){ return x; } }; int main(){ int n; n = static_cast<int>(3.14); cout<<n<<endl; n = static_cast<int>(node(2)); cout<<n<<endl; }




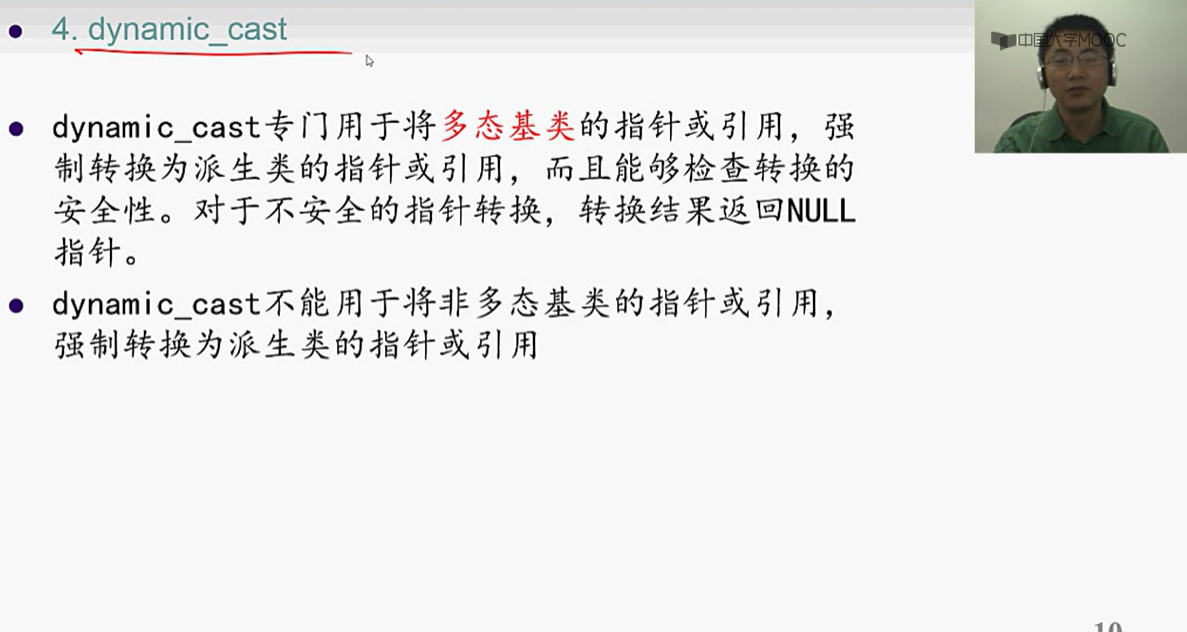
四、异常处理




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号