System Design - Twitter - New version
CREATED 2021年12月03日22:12:04
System Design - Twitter
Functional requirements
Post tweet (including text, image, video) / Delete
Get Timeline / Newsfeed (a. Home b. User) (Aggregating tweets in reverse chronological order)
Follow / Unfollow user
Like / Dislike / Comment
Mark tweets as favorites
Extended requirements
Retweet / forward
Search
HashTag / Rank Trending Topics
Non-Functional requirements
highly available(Without the guarantee that the latest news will be returned).
Acceptable latency of the system is 200ms for timeline generation.
Consistency (Eventual Consistency)
Fault tolerance
Estimations
DAU
A read-heavy system (compared to write)
200 Million users
100 Million tweets => 1200 QPS write
Total view: 200M DAU ((2 + 5) 20 tweets) = 28B/day => 324K QPS read
Storage
Tweets 140 characters maximum per tweet (280 bytes), metadata 30 bytes : 100M * (280 + 30) bytes = 31 GB / day
Images 100 M x 20% x 200 Bytes/image = 4TB / day
Videos 100 M x 10% x 2 MB/video = 20TB / day
Total new media every day: 24 TB.
Bandwidth
35 GB/s
Basic APIs
1 postTweet(TweetContent content)
E.g. post_tweet(api_dev_key, tweet_text, location, imageId, videoId or media_ids)
2 GetTimeline(pagination)
E.g. get_tweets(api_dev_key, max_number_to_return, next_page_token)
3 follow(userId)
Basic Flows
Post Tweet
User posts a tweet to [Tweets Server]. The [Tweets Server] will write the data to [Tweets Cache] as well as [Tweets DB].
[Tweets Server] next will do a [Fan Out On Write] operation to add this tweet to all his/her follower's timeline by [Tweets Feed Servers] as well as to [Tweets Feed Cache]. (Pushing Mode with time complexity - Read O(1) Write O(N))
If this user is a hot user/celebrity, [Tweets Server] next will do a [Fan Out On Read] operation to store this post in this celebrity's timelne own cache.
Also [Tweets Server] will call [Notification Server] if he/she has special follower(s).
Read Timeline / Read Tweets feed
User makes request to [Tweets Feed Servers] and get all his/her tweets feed for the latest update.
[Tweets Feed Servers] will fetch data(urls json) from [Tweets Feed Cache] and [User Cache], [Tweets Cache].
The tweets are mixed from non-celebrity and celebrity together in the runtime of user's request.
Construct the page by fetching images and videos from CDN by giving specific urls. And finally it is shown to the users in mobile terminals.
Infra
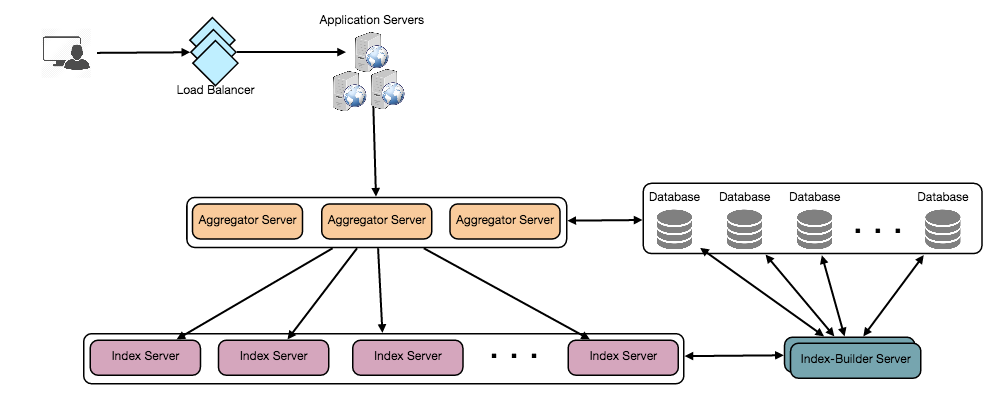
DB Schema
UserDB
userId (Primary Key) | Name | Description | PhotoId | Email | DateOfBirth | CreationDate | Tweets[] | favoriteTweets[]
TweetDB
TweetId (Primary Key) | userId | Text | ImageIds[] | VideoId[] | Location | Timestamp | Hashtag | (originTweetId in Re-tweet)
Follow DB (if SQL)
(userId1, userId2) (Primary Key)
Tweet Favorite DB (if SQL)
FavoriteId (Primary Key) | TweetId | userId | timestamp
(TweetId , userId)(Primary Key) | Timestamp
Storage DB
ImageId (Primary Key) | image_url
VideoId (Primary Key) | video_url
FanOut Service
Non-celebrity / Fan Out On Write
Save tweet to DB/Cache
Fetch all the followers that follow user A
Inject this tweet into all the followers' queues/in-memory timelines
Finally, all the followers can see this tweet in their timelines.
Not suitable for inactive users.
Celebrity / Fan Out On Read
Generated during read time / On-demand mode
Mixed with the tweets from celebrity in the runtime of user's request
For inactive users, this mode works better.
Sharding
1 Sharding based on creation date/time
Cons:
Traffic load will not be distributed. All new tweets will be going to one server and the remaining ones will be sitting idle.
2 Sharding based on userId
Cons:
Hot user
Unbalanced data (some users can end up storing a lot of tweets. Not uniform distribution.)
Read Timeline needs to query multiple servers
3 Sharding based on tweetId
Pros:
Balanced data distributed
Cons:
Read Timeline needs to query multiple servers
4 Combined timestamp into tweetID. Epoch time + auto-incrementing
31 bits for epoch seconds + 17 bits for auto incrementing sequence number
Pros:
Reduce the latency for reading
Cons:
Read Timeline still needs to query multiple servers
Cache
-
improve read performance and reduce database pressure
-
least recently used (LRU)
-
try to cache 20% tweets which have 80% traffic of reading (size of cache) in the past 3 days
-
Due to limit of number of connections. It should be split into multiple servers.
-
celebrities timeline should be in the cache.
-
key : userId, value: tweets (double linked list due to descending order)
Replication and Fault Tolerance
We can have multiple secondary database servers for each DB partition. Secondary servers will be used for read traffic only. All writes will first go to the primary server and then will be propagated to secondary servers.
Whenever the primary server goes down, we can failover to a secondary server.
Monitor/Metrics
Number of tweets per second/hour/day...
Latency of refreshing timeline
Server Internal errors 500
Reference
[1] https://github.com/donnemartin/system-design-primer/tree/master/solutions/system_design/twitter
[2] https://medium.com/@narengowda/system-design-for-twitter-e737284afc95
[3] https://www.educative.io/courses/grokking-the-system-design-interview/xV9mMjj74gE
[4] https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Sf4y1e7wc?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号