spring-Security《一》
源码介绍:
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String var1) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
里面返回一个UserDetails,来看下UserDetails里面是什么
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword(); 密码
String getUsername(); 用户名
boolean isAccountNonExpired(); 账号是否被过期
boolean isAccountNonLocked();账号是否被锁定
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired(); 证书(密码)是否过期
boolean isEnabled();账号是否被启用
}
UserDetails也是个接口,那么他肯定有实现类
里面果然有个User去实现它

看下User是什么东东
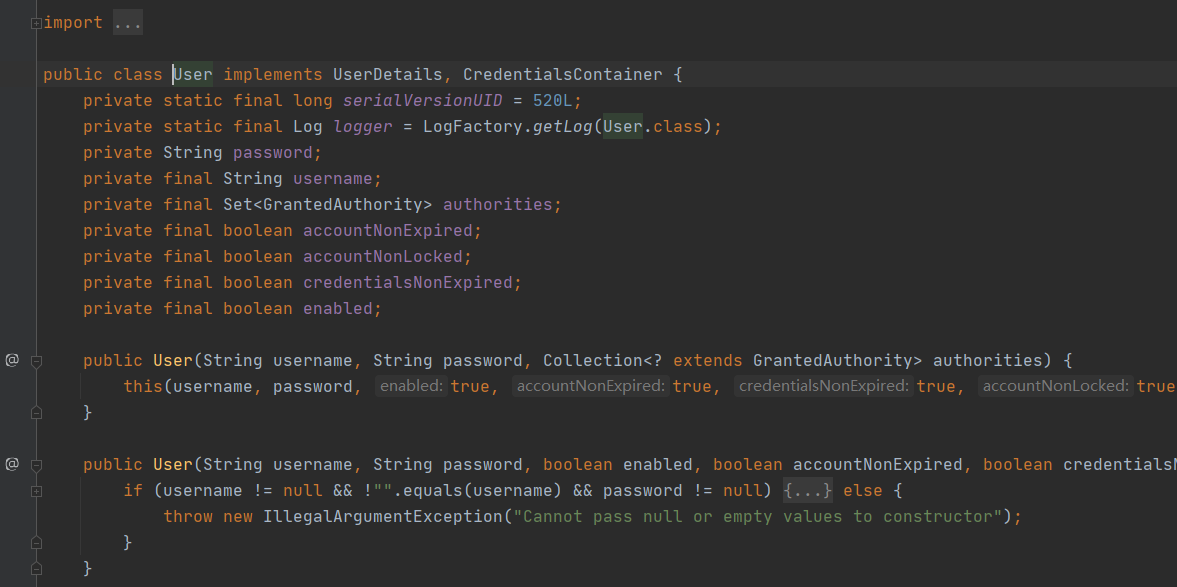
属性是与接口对应,有两个构造函数
用户名,密码,授权
public User(String username, String password, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this(username, password, true, true, true, true, authorities);
}
就是那一堆属性构造方法了
public User(String username, String password, boolean enabled, boolean accountNonExpired, boolean credentialsNonExpired, boolean accountNonLocked, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
if (username != null && !"".equals(username) && password != null) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.enabled = enabled;
this.accountNonExpired = accountNonExpired;
this.credentialsNonExpired = credentialsNonExpired;
this.accountNonLocked = accountNonLocked;
this.authorities = Collections.unmodifiableSet(sortAuthorities(authorities));
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot pass null or empty values to constructor");
}
}
上面介绍了下账户授权,密码呀入口,别着急一丢丢来,慢慢爬 那么问题来了,既然是安全框架,密码不可能是明文吧,那么是怎么加密的呢 于是我们蒙蔽的找啊找,嘿哦看到一个密码Password名称的类
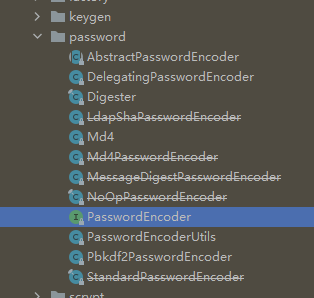
哎呦我操,你看看还真有,什么抽象的,策略的,加密的我都看不懂,就后面那俩Password的还认识下,点进去看看,上源码
public interface PasswordEncoder {
/**
* Encode the raw password. Generally, a good encoding algorithm applies a SHA-1 or
* greater hash combined with an 8-byte or greater randomly generated salt.
人话就是推荐SHA-1或者8位的hash加盐的密码
*/
String encode(CharSequence rawPassword);
/**
* Verify the encoded password obtained from storage matches the submitted raw
* password after it too is encoded. Returns true if the passwords match, false if
* they do not. The stored password itself is never decoded.
*
* @param rawPassword the raw password to encode and match
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password from storage to compare with
* @return true if the raw password, after encoding, matches the encoded password from
* storage
人话就是原密码与加密的匹配
*/
boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword);
/**
* Returns true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false. The default implementation always returns false.
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password to check
* @return true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false.
人话就是对加密的密码再次编码
*/
default boolean upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) {
return false;
}
}
看一下他的实现类,真他妈离谱他妈给离谱开门了,离谱到家了,怎么那么多,老子看哪个,问问用过的老司机吧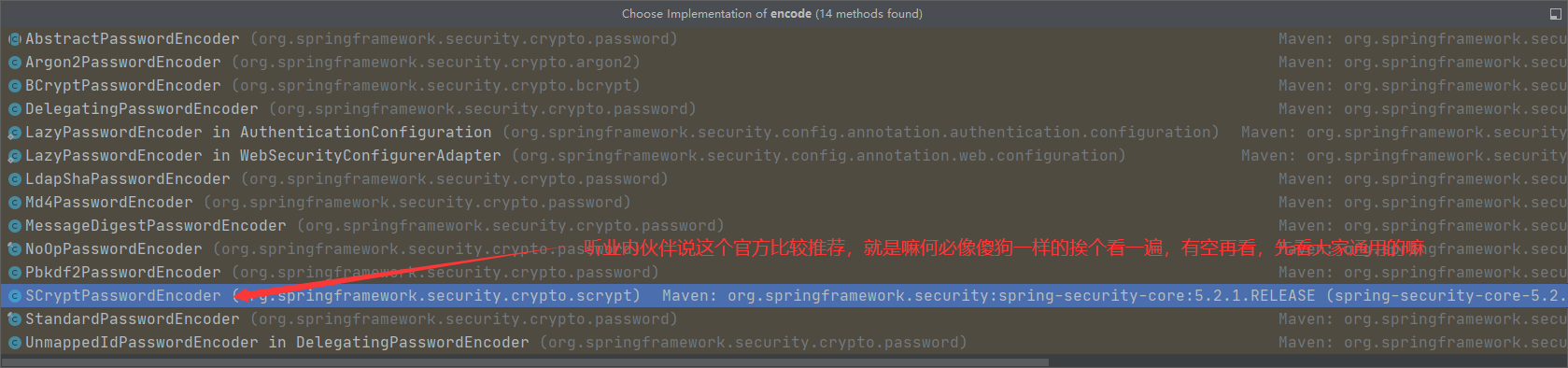
点击去kankan
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return digest(rawPassword, saltGenerator.generateKey());
}
好家伙按位运算加盐加特殊字符¥拼接了,
private String digest(CharSequence rawPassword, byte[] salt) {
byte[] derived = SCrypt.generate(Utf8.encode(rawPassword), salt, cpuCost, memoryCost, parallelization, keyLength);
String params = Long
.toString(((int) (Math.log(cpuCost) / Math.log(2)) << 16L) | memoryCost << 8 | parallelization, 16);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder((salt.length + derived.length) * 2);
sb.append("$").append(params).append('$');
sb.append(encodePart(salt)).append('$');
sb.append(encodePart(derived));
return sb.toString();
}
//熟悉的呻吟bsae64编码
private byte[] decodePart(String part) {
return Base64.getDecoder().decode(Utf8.encode(part));
}
private String encodePart(byte[] part) {
return Utf8.decode(Base64.getEncoder().encode(part));
}
测试一下:
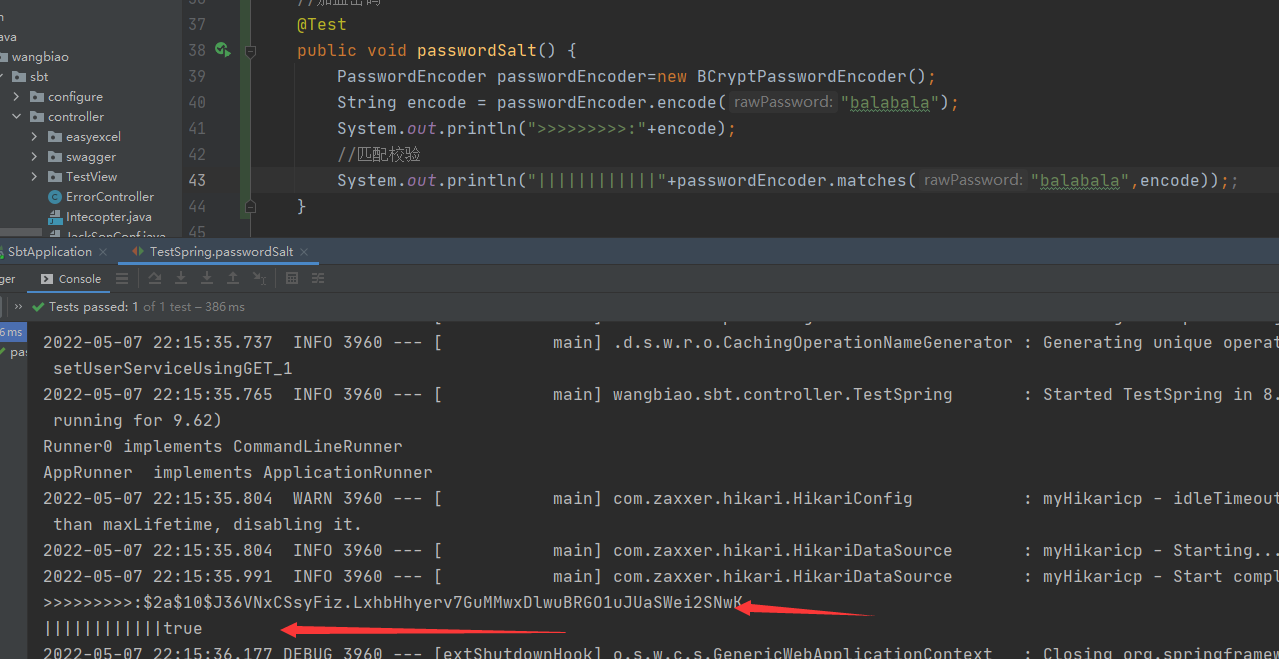
随机盐saltGenerator.generateKey()这里已经生成了,就算密码一样,盐不一样结果也不一样
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return digest(rawPassword, saltGenerator.generateKey());
}
本文来自博客园,作者:余生请多指教ANT,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangbiaohistory/p/16244273.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号