spring编程式事务
事物的传播行为:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:事务不存在就创建一个(默认的事务隔离级别)。 PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS:有事务支持存在的事务,没有事务,以非事务运行。 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY:支持当前事务,当前事务不存在直接抛出异常(属于强制事务)。 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:创建一个新事务,如果存在则暂停当前事务。 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:不支持当前交易;而是始终以非事务方式执行。 PROPAGATION_NEVER:以不支持事物的方式运行,如果存在事务抛异常。 PROPAGATION_NESTED:如果当前事务存在,则在嵌套事务中执行,当前不存在就和PROPAGATION_REQUIRED一样 ISOLATION_DEFAULT:使用底层数据存储的默认隔离级别。所有其他级别对应于 JDBC 隔离级别(mysql默认的就是可重复读)
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED:表示可能发生脏读、不可重复读和幻读 ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED:表示防止脏读;可能发生不可重复读取和幻读 ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ:表示防止脏读和不可重复读;幻读可能发生(mysql8.0这个隔离级别已经解决了幻读的问题) ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE:表示防止脏读、不可重复读和幻读。
接下来介绍下声明式事务的几个关键类和源码流程图:
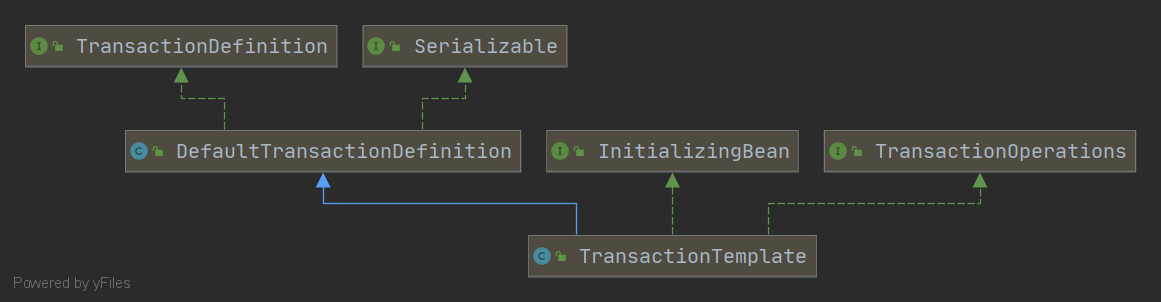
中心方法是 {@link execute},支持实现 {@link TransactionCallback}
接口的事务代码。此模板处理事务生命周期和可能的异常,
因此 TransactionCallback 实现和调用代码都不需要显式处理事务
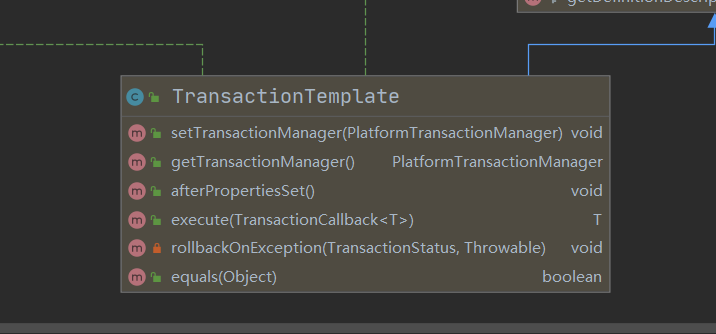
接下来看execute这个和新方法的参数:TransactionCallback
- /** 通常用于将对事务 不感知的数据访问服务的各种调用 组合成具有事务划分的更高级别的服务方法。
- 作为替代方案,考虑使用声明性事务划分
- */ @FunctionalInterface public interface TransactionCallback<T>
- { /** 在事务上下文中由 {@link TransactionTemplateexecute} 调用。
- 不需要关心事务本身,尽管它可以通过给定的状态对象检索和影响当前事务的状态,
- 例如设置只回滚。 <p>允许返回在事务中创建的结果对象,即域对象或域对象的集合。
- 回调抛出的 RuntimeException 被视为强制回滚的应用程序异常。
- 任何此类异常都将传播到模板的调用者,除非回滚出现问题,
- 在这种情况下将抛出 TransactionException。 @param status 关联交易状态
*/ @Nullable T doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status); }
TransactionCallback 看完他的结构看下他的实现类:
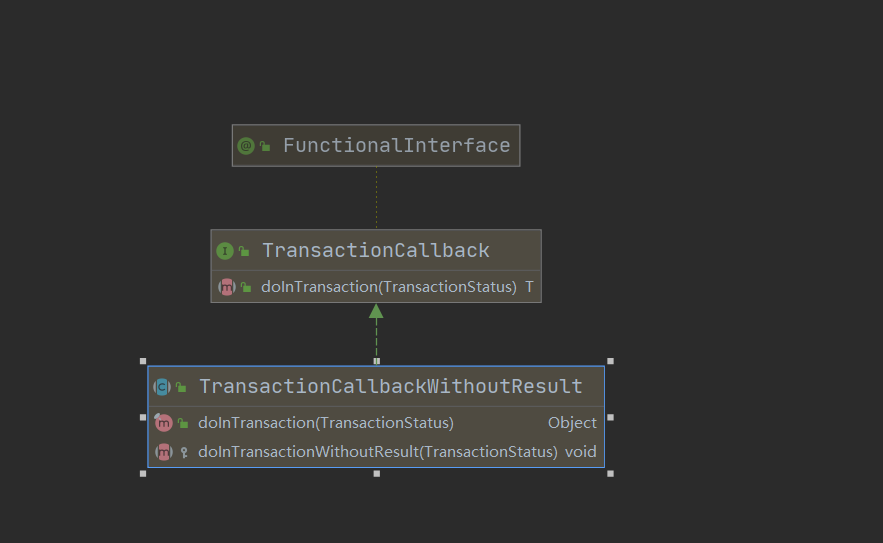
public abstract class TransactionCallbackWithoutResult implements TransactionCallback<Object> {
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
doInTransactionWithoutResult(status);
return null;
}
/**
* Gets called by {@code TransactionTemplate.execute} within a transactional
* context. Does not need to care about transactions itself, although it can retrieve
* and influence the status of the current transaction via the given status object,
* e.g. setting rollback-only.
* <p>A RuntimeException thrown by the callback is treated as application
* exception that enforces a rollback. An exception gets propagated to the
* caller of the template.
* <p>Note when using JTA: JTA transactions only work with transactional
* JNDI resources, so implementations need to use such resources if they
* want transaction support.
* @param status associated transaction status
* @see TransactionTemplate#execute
*/
protected abstract void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status);
}
从TransactionCallbackWithoutResult可以看出出原来的TransactionTemplate的execute的执行方法, 如果传入的是TransactionCallbackWithoutResult这个有返回值得方法, 那么在处理doInTransactionWithoutResult这方法(也是我们处理业务的地方)没有返回值,源码返回了个null
本文来自博客园,作者:余生请多指教ANT,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangbiaohistory/p/16170623.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号