JAVA---Collection和Map区别
==元素都是单值==
| 元素是否有序 | 元素是否可重复 | |
|---|---|---|
| List<T> | 有序(所有的元素都有索引位置) | 可以 |
| Set<T> | 无序(没有索引位置) | 不可以 |
1.1. List<T>
| 默认创建时没有给集合大小 | 数据结构 | 线程安全 | 效率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList<T>初次扩容10,之后按1.5倍扩容 | 动态数组 | 否 | 查/修改快 新增和删除慢 |
| LinkedList<T> | 双向链表 | 否 | 新增/删除快 查/修改慢 |
| Vector<T>初次扩容10,之后按2倍扩容,增量为0 | 动态数组 | 是 | 性能一般 |
| CopyonWriteArrayList<T>初次扩容10,之后每次+1 | 动态数组 | 是 | 性能最慢 |
1.2. Set<T>
| 默认创建时没有给集合大小 | 数据结构 | 线程安全 | 元素是否可以为null |
|---|---|---|---|
| HashSet初次扩容16达到阈值两倍扩容 | HashMap(数组+单向链表+红黑树) | 否 | 可以 |
| LinkedHashSet | HashMap | 否 | 可以 |
| TreeSet初次扩容16达到阈值两倍扩容 | 红黑树 TreeMap | 否 | 不可以 |
| CopyOnWriteArraySet | 动态数组 | 是 Lock | 可以 |
2. Map<K,V>
| 默认创建时没有给集合大小 | 数据结构 | 线程安全 | key/value是否可以为null |
|---|---|---|---|
| HashMap次扩容16达到阈值,两倍扩容 | 位桶(数组)+单向链表+红黑树 | 否 | k/v 都可以 |
| LinkedHashMap | 位桶+双向链表+红黑树 | 否 | k/v 都可以 |
| TreeMap初次扩容16达到阈值,两倍扩容 | 红黑树 | 否 | k不可以 v 可以 |
| HashTable初次扩容11达到阈值,两倍+1扩容 | jdk1.8位桶+单向链表+红黑树 | 是 | k/v 都不可以 |
|
ConcurrentHashmap初次扩容16, 达到阈值之后两倍扩容 |
jdk1.7 锁分段技术 segment jdk1.8 CAS 分段的数组+链表 |
是 | k/v 都不可以 |
CAS:
compare and swap 比较并交换 乐观锁 认为任何操作都不会出现问题 效率很快 查询的场景
多读少写 -----> Redis 缓存 (主从同步)
synchornized:
同步锁 悲观锁 互斥锁 可重入锁
![]()
数组:
存储相同类型的指定数组空间个元素数据。 length 基本+引用
新增: 手动扩容
删除: 后面元素循环移位
查询/修改: 效率最快 index
集合:
理论上存储不同类型的不定量元素数据。 实际开发中 还是存储相同类型的数据。 <T>
元素: 存储引用类型的数据。
<T>: 泛型的标志 类型的自动转换
A-Z: T E K V 参数化类型----> 传递
集合里面使用泛型:
集合元素数据有了限定。只能存储参数化的真实类型的数据。
集合分类:
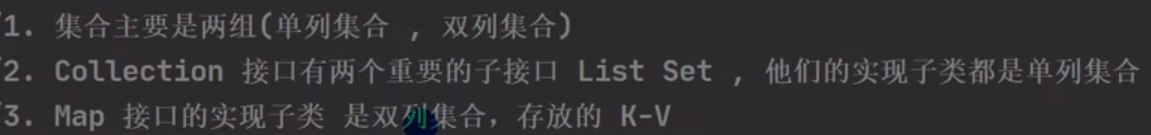
1. Collection<T>
1. 元素都是单值 2. 元素有序(索引位置)/是否可重复 不定
2. Map<K,V>
1. 元素是一组元素 键值对 key:value
2. key: 必须唯一 (不可重复) value: 可重复
1. Collection<T>
==元素都是单值==
| 元素是否有序 | 元素是否可重复 | |
|---|---|---|
| List<T> | 有序(所有的元素都有索引位置) | 可以 |
| Set<T> | 无序(没有索引位置) | 不可以 |
常用方法:
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
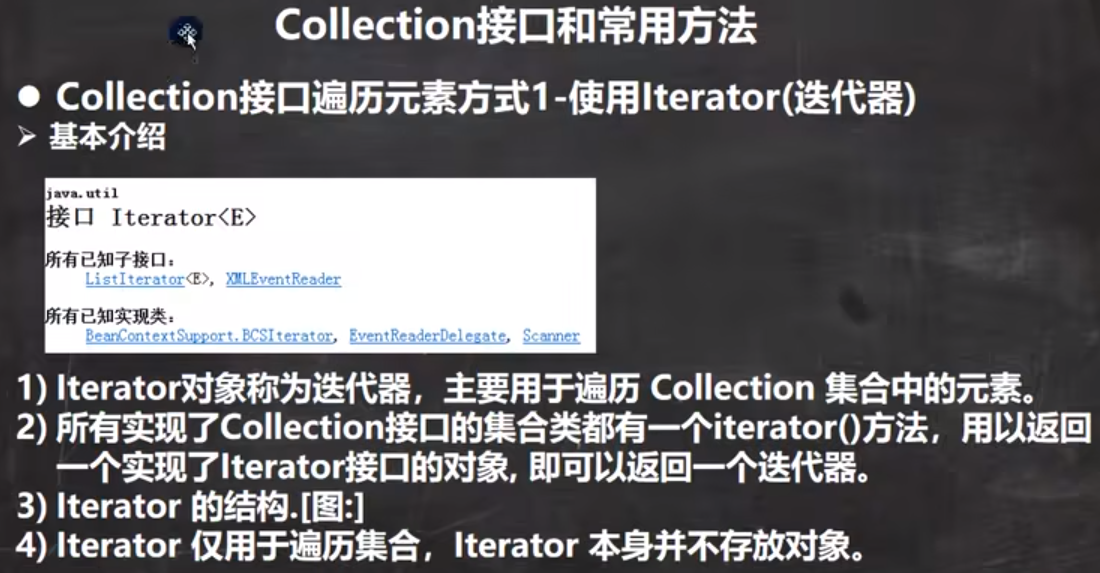
Iterable<T>: 提供了遍历集合元素的方式。
Iterator<T> iterator() 迭代 获得指定集合的迭代器对象。(将集合的 元素都放到了迭代器里面了)
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) 循环遍历集合元素
新增/==遍历(查询)==-----> 数据在数据库----> sql
新增元素:
boolean add(E e)
删除元素:
boolean remove(Object o)
default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) 删除满足条件的所有的元素
void clear() 清空集合所有的元素
查询/遍历元素:
Iterator<T> iterator()
1. boolean hasNext() 判断指针之后是否有更多的元素需要迭代
2. T next() 获得光标之后的数据
3. void remove() 删除元素数据
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)
判断:
boolean contains(Object o) 判断集合里面是否包含指定的元素
boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否是空
获得集合的元素个数:
int size()
集合转数组
Object[] toArray()
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a) 推荐使用
default Stream<E> parallelStream() 并行化
default Stream<E> stream() 串行化
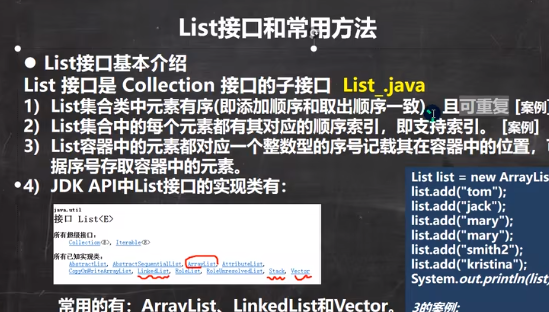
2. List<T>
void add(int index, E element)
E get(int index)
ListIterator<E> listIterator()
E remove(int index)
E set(int index, E element)
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
| 数据结构 | 线程安全 | 效率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList<T> | 动态数组 | 否 | 查/修改 新增和删除慢 |
| LinkedList<T> | 双向链表 | 否 | 新增/删除快 查/修改慢 |
| Vector<T> | 动态数组 | 是 | 性能一般 |
| CopyonWriteArrayList<T> | 动态数组 | 是 | 性能最慢 |
链表结构:
单向链表:
元素数据element 下一个元素引用 next
双向链表:
上一个元素的引用 prev 元素数据element 下一个元素引用 next
==1. ArrayList<T>==
public class ArrayList<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable
RandomAccess: 标识接口 快速随机访问 表明这个类的查询很快。
ArrayList() 初始化10 (数组)
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
initialCapacity = 存储元素的最大个数/负载因子+1
使用方法
private static void testArrayList() {
//创建List集合对象
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
list.add(10);
list.add(11);// 0-size
list.add(20);
list.add(10);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.size());
//删除
// list.remove(new Integer(1));
//list.set(list.size() - 1, 300);
//遍历
// for (Integer integer : list) {
// System.out.println(integer);
// }
//
// System.out.println("----------------------");
// Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator();
// while (it.hasNext()) {
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
// System.out.println("----------------------");
// list.forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println("----------------------");
// for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// if(list.get(i).equals(10)){
// list.remove(i);
// i--;
// }
// }
//subList(start,end)
List<Integer> list1 = list.subList(0, 3);// view : 不能执行操作 看
//操作list1 任何操作都会作用到原集合上面
//list1.add(1000);
//list1.remove(0);
// list1.set(0, 1000);
//操作原集合 报异常
list = new ArrayList<>(list);
list.add(0, 1000);
System.out.println("list:" + list1);
System.out.println(list);
}
//服务于集合里面的快速失败的机制 fail-fast
//统计操作集合元素的次数(add/remove)
protected transient int modCount = 0;
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {//10
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);//真正扩容逻辑实现在grow
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {//10
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2. LinkedList<T>
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
Queue: 队列
双链表实现了List和Deque接口。 实现所有可选列表操作,并允许所有元素(包括null )。
3. Vector<T>
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);// 2倍的扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2. Set<T>
| 数据结构 | 线程安全 | 元素是否可以为null | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HashSet | HashMap(数组+单向链表+红黑树) | 否 | 可以 |
| LinkedHashSet | HashMap | 否 | 可以 |
| TreeSet | 红黑树 TreeMap | 否 | 不可以 |
| CopyOnWriteArraySet | CopyOnWriteArrayList | 是 Lock | 可以 |
1. HashSet<T>
HashSet()
构造一个新的空集合; 背景HashMap实例具有默认初始容量(16)和负载因子(0.75)。
HashSet(int initialCapacity) 16
private static void testHashSet() {
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>(16);
//完全无序
hashSet.add(1);
hashSet.add(100);
hashSet.add(10);
hashSet.add(16);
hashSet.add(1000);
hashSet.add(null);
System.out.println(hashSet);
//遍历方式 与Collection一样
hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------");
Iterator<Integer> it = hashSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
2. LinkedHashSet<T>
元素有序。 新增的顺序与遍历顺序是一致的。
3. TreeSet<T>
排序。元素都是有序的 按照自然顺序进行排列。升序排列
TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) 自定义外部比较器
private static void testUsersTreeSet() {
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: com.javasm.util.User cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
//元素类型肯定要实现Comparable
TreeSet<User> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
//效率慢
treeSet.add(new User(1, "admin", 30));
treeSet.add(new User(2, "admin", 18));
treeSet.add(new User(3, "张三", 20));
treeSet.add(new User(4, "李四", 18));
treeSet.add(new User(5, "王五", 22));
treeSet.add(new User(6, "admin", 17));
System.out.println(treeSet);
treeSet.forEach(System.out::println);
// System.out.println(treeSet.first())
}
3. Map<K,V>
key:value key: 唯一 value: 可重复的
| 数据结构 | 线程安全 | key/value是否可以为null | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HashMap | 位桶+单向链表+红黑树 | 否 | k/v 都可以 |
| LinkedHashMap | 位桶+单向链表+红黑树 | 否 | k/v 都可以 |
| TreeMap | 红黑树 | 否 | k不可以 v 可以 |
| HashTable | hash表 | 是 | k/v 都不可以 |
| ConcurrentHashmap | jdk1.7 锁分段技术 segment jdk1.8 CAS | 是 | k/v 都不可以 |
CAS:
compare and swap 比较并交换 乐观锁 认为任何操作都不会出现问题 效率很快 查询的场景
多读少写 -----> Redis 缓存 (主从同步)
synchornized:
同步锁 悲观锁 互斥锁 可重入锁
V put(K key, V value) 增
V remove(Object key) 删
default boolean remove(Object key, Object value)
default V replace(K key, V value) 改
default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue)
V get(Object key) 查
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue)
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 遍历 推荐
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) 推荐
Set<K> keySet()
==1. HashMap<K,V>==
HashMap()
构造一个空的 HashMap ,默认初始容量(16)和默认负载系数(0.75)。
HashMap(int initialCapacity)
构造一个空的 HashMap具有指定的初始容量和默认负载因子(0.75)。
使用方法
private static void testHashMap() {
//存储用户信息: Map的key几乎都是要String或者Integer 类似前端json的数据 key:value
HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>(16);
//map的key重复了 值会被覆盖的
hashMap.put("id", 1001);
hashMap.put("name", "张三");
hashMap.put("age", 20);
hashMap.put("balance", 20000.776);
System.out.println(hashMap);
//删除
//System.out.println(hashMap.remove("age"));
//System.out.println(hashMap.remove("age",20));
//修改
//System.out.println(hashMap.replace("age", 21));
//System.out.println(hashMap.replace("age", 20,21));
//查询
// System.out.println(hashMap.get("name1"));
//System.out.println(hashMap.get("name1").equals("aaa"));
// System.out.println(hashMap.getOrDefault("name1", ""));
System.out.println(hashMap);
}
private static void testHashMap1() {
HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>(16);
hashMap.put("id", 1001);
hashMap.put("name", "张三");
hashMap.put("age", 20);
hashMap.put("balance", 20000.776);
//遍历map集合元素
// hashMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
// System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
// });
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entrySet = hashMap.entrySet();
// 将map里面的每一组元素都封装成一个个的Entry对象 再将entry对象存储set集合
// Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Object>> iterator = entrySet.iterator();
// while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = iterator.next();
// System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
// }
// for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : entrySet) {
// System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
// }
Set<String> keySet = hashMap.keySet();//将map里面所有的key存储在set集合中
for (String key : keySet) {
System.out.println(key+":"+hashMap.get(key));
}
}
private static void testDemo() {
String str = "abcvdg121111aaavvcc";
//使用hashmap 每个字符出现的次数
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(16);
int length = str.length();
for (int index = 0; index < length; index++) {
String s = String.valueOf(str.charAt(index));//每个字符
/* if(!map.containsKey(s)){
map.put(s, 1);
}else{
map.put(s, map.get(s)+1);
}*/
//判断之前是否存储字符s
Integer count = map.get(s);
if (count == null) {
map.put(s, 1);
} else {
map.put(s, ++count);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
源码
1. HashMap解决hash冲突的方式
2. HashMap的扩容机制
//位桶(数组)+单向链表+红黑树
transient Node<K,V>[] table;//(位桶)数组 维护map集合里面部分元素 null
final float loadFactor;//负载因子 0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 初始化容量 16
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;//最大容量
//单向链表上 7个的时候 (map的size>64) 会自动将链表转换成树结构
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;//链表转树临界点
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;//树转链表的临界点
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
int threshold;// 阈yu值 临界点 再次扩容临界点 0 12
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; //0.75F
}
//单向链表
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;// key的hash
final K key;//key的值
V value;
Node<K,V> next;//下一组元素的引用
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
// 97 a 1
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;//获得扩容之后数组的长度
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//解决key值重复(解决hash冲突的方式)
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// hash一致 元素数据不同
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
2. TreeMap<K,V>
略 元素会按照自然顺序进行排列 要求TreeMap的key的类型必须要提供排序规则。
4. 排序
了解。
java.lang.Comparable<T> ----> compareTo()(内部比较器)
java.util.Comparator<T> ---->compare() 推荐(外部比较器)
1. List集合
实现Comparable
private static void demo2() {
//存储的自定义类对象
List<UserInfo> userInfoList = new ArrayList<>(10);
Collections.addAll(userInfoList,
new UserInfo(1, "jim1", 20),
new UserInfo(10, "jim2", 20),
new UserInfo(7, "jim3", 18),
new UserInfo(3, "jim4", 17)
);
userInfoList.forEach(System.out::println);
//按照年龄升序排列 年龄相等 按照id进行降序排列
Collections.sort(userInfoList);
System.out.println("------------------------");
userInfoList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Setter
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
//高内聚 低耦合(层与层)
public class UserInfo implements Comparable<UserInfo> {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public int compareTo(UserInfo userInfo) {
int result = this.age.compareTo(userInfo.age);//0 -1 1
if (result == 0) {
result = userInfo.id.compareTo(this.id);
}
return result;
}
}
使用Comparator
private static void demo2() {
//存储的自定义类对象
List<UserInfo> userInfoList = new ArrayList<>(10);
Collections.addAll(userInfoList,
new UserInfo(1, "jim1", 20),
new UserInfo(10, "jim2", 20),
new UserInfo(7, "jim3", 18),
new UserInfo(3, "jim4", 17)
);
userInfoList.forEach(System.out::println);
//按照年龄升序排列 年龄相等 按照id进行降序排列
// Collections.sort(userInfoList);
//外部比较器
// userInfoList.sort(new Comparator<UserInfo>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(UserInfo user1, UserInfo user2) {
// int result = user1.getAge().compareTo(user2.getAge());
// if (result == 0) {
// result = user2.getId().compareTo(user1.getId());
// }
// return result;
// }
// });
// userInfoList.sort((user1, user2) -> {
// int result = user1.getAge().compareTo(user2.getAge());
// if (result == 0) {
// result = user2.getId().compareTo(user1.getId());
// }
// return result;
// });
userInfoList.sort(Comparator.comparing(UserInfo::getAge).reversed());
System.out.println("------------------------");
userInfoList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
2. Set集合
HashSet/LinkedHashSet TreeSet
private static void demo1() {
//HashSet/LinkedHashSet 完全无序 无法直接排序
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(16);
Collections.addAll(set, 20, 1, 0, 100, 9, 8);
System.out.println(set);
//获得set集合元素的最值
Integer max = Collections.max(set);
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(Collections.min(set));
//set转换List?
//List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(set);
//jdk1.8+ Stream---> 操作集合元素(类似于一个更加强大的Iterator)
List<Integer> collect = set.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);//[0, 1, 8, 9, 20, 100]
}
TreeSet
private static void demo3() {
TreeSet<UserInfo> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(UserInfo::getAge));
Collections.addAll(treeSet,
new UserInfo(1, "jim", 20),
new UserInfo(10, "jim", 20),
new UserInfo(7, "jim", 18),
new UserInfo(3, "jim", 17)
);
treeSet.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3. Map集合
key值排序 类似Set map集合key: String Long Integer
5. Collections
操作集合元素工具类。
static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... elements) ; 将元素存储集合中
static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list) 排序
static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)
//将线程不安全的集合对象 转换成线程安全的集合对象
static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list)
static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m)
static void shuffle(List<?> list) 打乱集合元素顺序(类似于洗牌)
static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>>
T max(Collection<? extends T> coll)
static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp)
==6. 集合嵌套==
public static void main(String[] args) {
//根据省份查询所有的城市信息====> 根据key获得value Map
Map<String, List<String>> provinceMap = new HashMap<>(16);
List<String> cityList = new ArrayList<>(10);
cityList.add("郑州1");
cityList.add("郑州2");
cityList.add("郑州3");
cityList.add("郑州4");
cityList.add("郑州5");
provinceMap.put("he", cityList);
cityList = new ArrayList<>(10);
cityList.add("济南1");
cityList.add("济南2");
cityList.add("济南3");
cityList.add("济南4");
cityList.add("济南5");
provinceMap.put("sd", cityList);
//获得he省份下所有的城市信息
List<String> list = provinceMap.get("sd");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
List<Map<String, Object>> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
//用户类: 属性:值 key:value
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("username","admin");
map.put("id",10001);
map.put("roleName","管理员");
Map<String,Object> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("username","test");
map1.put("id",10001);
map1.put("roleName","test");
list1.add(map);
list1.add(map1);
list1.forEach(System.out::println);
}
==7. Stream==
jdk1.8+ 新特性 核心功能: 聚合数据 操作集合元素。
串行 vs 并行
串行: 线下完成 一个任务结束就是另外一个任务的开始。
并行: 多个任务同时执行的。
获得Stream对象的方式:
private static void demo2() {
//1. 集合里面的stream----> Collection
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
Stream<Integer> stream1 = list.parallelStream();
//2. Stream接口的方法
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3);
//3. Arrays---> 基本数据类型Stream----> unboxed
IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(new int[]{1, 2, 3});
Stream<Integer> boxed = intStream.boxed();
//4. Random
//获得1000-10000 5个随机的数字
Random random = new Random();
IntStream intStream1 = random.ints(5, 1000, 10001);
}
常用的方法
filter() 过滤下来符合条件集合元素
private static void demo3() {
List<UserInfo> userInfoList = new ArrayList<>(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
userInfoList.add(new UserInfo(i, "张三" + i, +(1 + i)));
}
//过滤下来年龄>30用户对象
// List<UserInfo> userInfoList1 = new ArrayList<>(30);
// for (UserInfo userInfo : userInfoList) {
// if (userInfo.getAge() > 30) {
// userInfoList1.add(userInfo);
// }
// }
// userInfoList1.forEach(System.out::println);
//避免出现流中断: 链式调用方法
List<UserInfo> collect = userInfoList.parallelStream().filter(userInfo -> userInfo.getAge() > 30).collect(Collectors.toList());//中断
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
}
flatMap() 多对一 将多个Stream转换成1个Stream
<R> Stream<R> flatMap(Function<? super T,? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper)
private static void demo5() {
//集合转数组 toArray
//数组转集合 Arrays.asList()
List<Integer> list1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(10, 2, 30);
List<Integer> list3 = Arrays.asList(11, 21, 3, 7, 8);
//将list1 2 3 集合里面的 数据 去重 升序 转换到一个集合中
// Stream.of(list1, list2, list3).flatMap(new Function<List<Integer>, Stream<?>>() {
// @Override
// public Stream<?> apply(List<Integer> integers) {
// return null;
// }
// });
List<Integer> collect = Stream.of(list1, list2, list3).flatMap(List::parallelStream).distinct().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
map() 一对一 (每个元素都要参与运算) 一直使用的是同一个Stream对象
peek() 窥视 产生一个新的Stream对象
private static void demo6() {
List<UserInfo> userInfoList = new ArrayList<>(10);
Collections.addAll(userInfoList,
new UserInfo(1, "jim1", 20),
new UserInfo(10, "jim2", 20),
new UserInfo(7, "jim3", 18),
new UserInfo(3, "jim4", 17)
);
//将用户的名称全部在换大写
// for (UserInfo userInfo : userInfoList) {
// userInfo.setName(userInfo.getName().toUpperCase());
// userInfo.setAge(userInfo.getAge()+1);
// }
// userInfoList.forEach(System.out::println);
// userInfoList.parallelStream().map(new Function<UserInfo, UserInfo>() {
// @Override
// public UserInfo apply(UserInfo userInfo) {
// return null;
// }
// });
// userInfoList.parallelStream().peek(new Consumer<UserInfo>() {
// @Override
// public void accept(UserInfo userInfo) {
// userInfo.setName(userInfo.getName().toUpperCase());
// }
// });
// List<UserInfo> collect = userInfoList.parallelStream().map(user -> {
// user.setName(user.getName().toUpperCase());
// return user;
// }).collect(Collectors.toList());
// List<UserInfo> collect = userInfoList.parallelStream().peek(user -> user.setName(user.getName().toUpperCase())).collect(Collectors.toList());
// collect.forEach(System.out::println);
//获得所有用户name
// userInfoList.parallelStream().map(new Function<UserInfo, String>() {
// @Override
// public String apply(UserInfo userInfo) {
// return null;
// }
// });
// List<String> collect = userInfoList.parallelStream().map(userInfo ->userInfo.getName().toUpperCase()).collect(Collectors.toList());
// System.out.println(collect);
}
reduce() 聚合 多个元素参与运算 得到一个最终的结果 sum/avg/max/min
private static void demo7() {
List<UserInfo> userInfoList = new ArrayList<>(10);
Collections.addAll(userInfoList,
new UserInfo(1, "jim1", 20),
new UserInfo(10, "jim2", 20),
new UserInfo(7, "jim3", 18),
new UserInfo(3, "jim4", 17)
);
//求年龄最大的
// userInfoList.parallelStream().reduce(new BinaryOperator<UserInfo>() {
// @Override
// public UserInfo apply(UserInfo userInfo, UserInfo userInfo2) {
// return null;
// }
// });
//Optional null判断 避免出现NPE
Optional<UserInfo> optionalInfo = userInfoList.parallelStream().reduce((user1, user2) -> {
if (user1.getAge().compareTo(user2.getAge()) > 0) {
return user1;
}
return user2;
});
UserInfo userInfo = optionalInfo.get();
System.out.println(userInfo);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(79, 90, 80);
// Integer result = list.parallelStream().reduce(Integer::sum).get();
// System.out.println(result);
// System.out.println(result / list.size());
// Integer result = list.parallelStream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
// System.out.println(result);
}
8. Stream案例
@Setter
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Node {// Child
private Integer id;//节点的id
private String name;//节点名称
private Integer pid;//父级节点
private List<Node> childNodeList;//当前节点的子级节点
}
public class StreamDemo2 {
//初始化家族数据
static List<Node> family;
static {
family = new ArrayList<>(10);
//节点的pid为0的时候 证明1级节点
//1级
family.add(new Node(1, "爷爷", 0, null));
family.add(new Node(2, "二爷", 0, null));
family.add(new Node(3, "三爷", 0, null));
//2级
family.add(new Node(4, "爷爷-son1", 1, null));
family.add(new Node(5, "爷爷-son2", 1, null));
family.add(new Node(6, "爷爷-son3", 1, null));
family.add(new Node(7, "二爷-son1", 2, null));
family.add(new Node(8, "二爷-son2", 2, null));
family.add(new Node(9, "三爷-son1", 3, null));
//3级
family.add(new Node(10, "爷爷-son1-son1", 4, null));
family.add(new Node(11, "二爷-son1-son1", 7, null));
family.add(new Node(12, "三爷-son1-son1", 9, null));
family.add(new Node(13, "三爷-son1-son2", 9, null));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Stream的相关功能 展示层级关系
List<Node> nodeList = family.parallelStream()
.filter(node -> node.getPid().equals(0))
.peek(parentNode -> parentNode.setChildNodeList(selectChildNode(parentNode)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
nodeList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//递归
private static List<Node> selectChildNode(Node parentNode) {
return family.parallelStream()
.filter(node -> node.getPid().equals(parentNode.getId()))
.peek(child -> child.setChildNodeList(selectChildNode(child)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
![]()
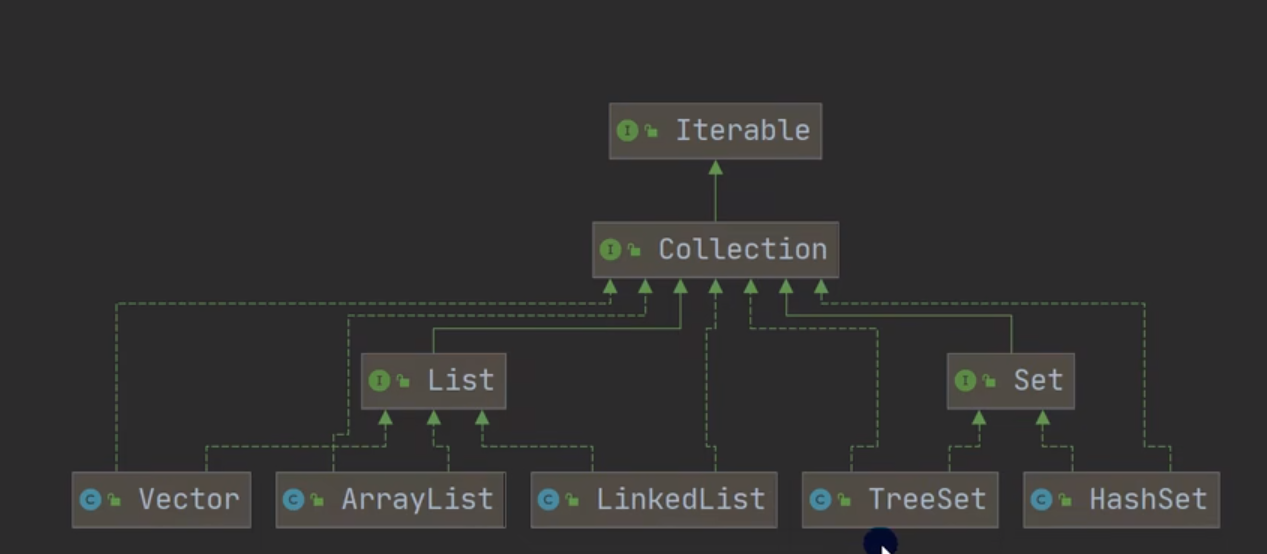
实线继承,虚线实现 Collection体系
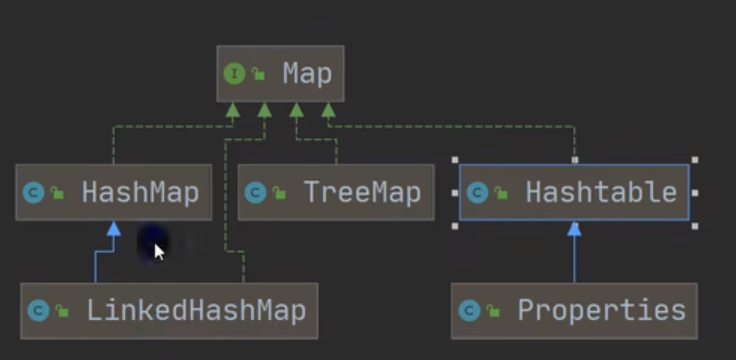
Map体系








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号