ThreadLocal
//ThreadLocal类提供的方法
1 public T get() {} //get()方法是用来获取ThreadLocal在当前线程中保存的变量副本 2 public void set(T value) {} //set()用来设置当前线程中变量的副本 3 public void remove() {} //remove()用来移除当前线程中变量的副本 4 protected T initialValue() {} //initialValue()是一个protected方法,一般是用来在使用时进行重写的,它是一个延迟加载方法
get方法的实现:

第一句是取得当前线程,然后通过getMap(t)方法获取到一个map,map的类型为ThreadLocalMap。然后接着下面获取到<key,value>键值对,注意这里获取键值对传进去的是 this,而不是当前线程t。
如果获取成功,则返回value值。
如果map为空,则调用setInitialValue方法返回value。
分析:
首先看一下getMap方法中做了什么:

在getMap中,是调用当期线程t,返回当前线程t中的一个成员变量threadLocals。
取Thread类中取看一下成员变量threadLocals是什么:

实际上就是一个ThreadLocalMap,这个类型是ThreadLocal类的一个内部类,继续取看ThreadLocalMap的实现:

可以看到ThreadLocalMap的Entry继承了WeakReference,并且使用ThreadLocal作为键值。然后再继续看setInitialValue方法的具体实现:

如果map不为空,就设置键值对,为空,再创建Map,看一下createMap的实现:

总结:
首先,在每个线程Thread内部有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的成员变量threadLocals,这个threadLocals就是用来存储实际的变量副本的,键值为当前ThreadLocal变量,value为变量副本(即T类型的变量)。
初始时,在Thread里面,threadLocals为空,当通过ThreadLocal变量调用get()方法或者set()方法,就会对Thread类中的threadLocals进行初始化,并且以当前ThreadLocal变量为键值,以ThreadLocal要保存的副本变量为value,存到threadLocals。
然后在当前线程里面,如果要使用副本变量,就可以通过get方法在threadLocals里面查找。
1)实际的通过ThreadLocal创建的副本是存储在每个线程自己的threadLocals中的;
2)为何threadLocals的类型ThreadLocalMap的键值为ThreadLocal对象,因为每个线程中可有多个threadLocal变量,就像上面代码中的longLocal和stringLocal;
3)在进行get之前,必须先set,否则会报空指针异常;
如果想在get之前不需要调用set就能正常访问的话,必须重写initialValue()方法。
简单示例:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static ThreadLocal<String> t1 = new ThreadLocal<>(); 4 5 /** 6 * 测试 7 * 第一个打印的是未设置值 8 * 第二个第三个分别获取的是 我的值 (也就证明了当没有向ThreadLocal中添加数据的时候,获取的是null) 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 if(t1.get() == null) { 12 System.out.println("未设置值"); 13 t1.set("我的值"); 14 } 15 System.out.println(t1.get()); 16 System.out.println(t1.get()); 17 } 18 }
测试线程变量的隔离性:
1 /** 2 * 工具类,定义公共的静态的ThreadLocal对象 3 */ 4 public class Tools { 5 6 public static ThreadLocal<String> t1 = new ThreadLocal<>(); 7 8 }
1 /** 2 * 线程A,当前线程运行时会设置值并获取值 3 */ 4 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 5 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 try { 9 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 10 Tools.t1.set("ThreadA" + (i+1)); 11 System.out.println("ThreadA get Value = " + Tools.t1.get()); 12 Thread.sleep(200); 13 } 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
1 /** 2 * 线程B,当前线程运行时会设置值并获取值 3 */ 4 public class ThreadB extends Thread { 5 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 try { 9 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 10 Tools.t1.set("ThreadB" + (i+1)); 11 System.out.println("ThreadB get Value = " + Tools.t1.get()); 12 Thread.sleep(200); 13 } 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 }
1 public class Run { 2 /** 3 * 测试线程变量的隔离性,每个线程获取的值都为自己设置的值 4 */ 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 try { 7 ThreadA a = new ThreadA(); 8 ThreadB b = new ThreadB(); 9 10 a.start(); 11 b.start(); 12 13 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 14 Tools.t1.set("Main" + (i+1)); 15 System.out.println("Main get Value=" + Tools.t1.get()); 16 Thread.sleep(200); 17 } 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 }
运行结果如下:

再次测试线程变量的隔离性:
1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 /** 4 * 工具类,定义公共的静态的ThreadLocal对象 5 */ 6 public class Tools { 7 8 public static ThreadLocal<Date> t1 = new ThreadLocal<>(); 9 10 }
1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 /** 4 * 线程A,当前线程运行时会先判断是否设置过值,如果没有设置,则设置一个值 5 * 如果设置过了,则直接获取值 6 */ 7 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 try { 11 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 12 if(Tools.t1.get() == null) { 13 Tools.t1.set(new Date()); 14 } 15 System.out.println("ThreadA get Value = " + Tools.t1.get().getTime()); 16 Thread.sleep(200); 17 } 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 }
1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 /** 4 * 线程B,当前线程运行时会先判断是否设置过值,如果没有设置,则设置一个值 5 * 如果设置过了,则直接获取值 6 */ 7 public class ThreadB extends Thread { 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 try { 11 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 12 if(Tools.t1.get() == null) { 13 Tools.t1.set(new Date()); 14 } 15 System.out.println("ThreadB get Value = " + Tools.t1.get().getTime()); 16 Thread.sleep(200); 17 } 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 }
1 public class Run { 2 /** 3 * 再次测试线程变量的隔离性,每个线程获取的值都为自己设置的值 4 */ 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 try { 7 ThreadA a = new ThreadA(); 8 a.start(); 9 Thread.sleep(1000); 10 ThreadB b = new ThreadB(); 11 b.start(); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 } 16 }
ThreadLocal设置默认值,避免第一次获取值为null:
1 /** 2 * 设置ThreadLocal中第一次默认值 3 */ 4 public class ThreadLocalExt extends ThreadLocal<String> { 5 @Override 6 protected String initialValue() { 7 return "我是ThreadLocal的默认值"; 8 } 9 }
1 public class Run { 2 3 public static ThreadLocalExt t1 = new ThreadLocalExt(); 4 /** 5 * 测试设置ThreadLocal默认值 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 if(t1.get() == null) { 10 System.out.println("未设置值"); 11 t1.set("我的值"); 12 } 13 System.out.println(t1.get()); 14 System.out.println(t1.get()); 15 } 16 }
运行结果如下:

父子线程分别获取自己的值:
1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 /** 4 * 设置ThreadLocal中第一次默认值 5 */ 6 public class ThreadLocalExt extends ThreadLocal<Date> { 7 8 @Override 9 protected Date initialValue() { 10 return new Date(); 11 } 12 }
1 /** 2 * 工具类,定义公共的静态的ThreadLocal对象 3 */ 4 public class Tools { 5 6 public static ThreadLocalExt t1 = new ThreadLocalExt(); 7 8 }
1 /** 2 * 线程A 3 */ 4 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 5 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 try { 9 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 10 System.out.println("ThreadA线程中取值为:" + Tools.t1.get()); 11 Thread.sleep(100); 12 } 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 }
1 public class Run { 2 /** 3 * 从输出结果看出,父线程和子线程分别获取自己的值 4 * 当main线程运行时获取的是线程当时new的Date 5 * 当ThreadA运行时获取的就是ThreadA线程当时new的Date 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 try { 9 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 10 System.out.println("Main线程中取值为:" + Tools.t1.get()); 11 Thread.sleep(100); 12 } 13 Thread.sleep(5000); 14 ThreadA a = new ThreadA(); 15 a.start(); 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 } 20 }
运行结果如下:
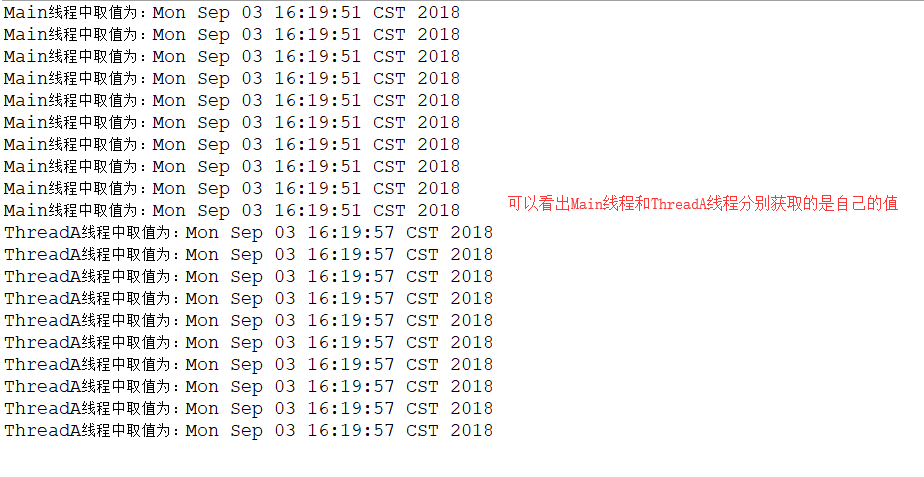
继承InheritableThreadLocal类,实现子线程从父线程中获取值:
1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 /** 4 * 实现InheritableThreadLocal类,实现从父线程获取值 5 */ 6 public class InheritableThreadLocalExt extends InheritableThreadLocal<Date> { 7 8 @Override 9 protected Date initialValue() { 10 return new Date(); 11 } 12 }
1 /** 2 * 工具类,定义公共的静态的ThreadLocal对象 3 */ 4 public class Tools { 5 6 public static InheritableThreadLocalExt t1 = new InheritableThreadLocalExt(); 7 8 }
1 /** 2 * 线程A 3 */ 4 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 try { 8 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 9 System.out.println("ThreadA线程中取值为:" + Tools.t1.get()); 10 Thread.sleep(100); 11 } 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 } 16 }
1 public class Run { 2 /** 3 * 测试InheritableThreadLocalExt,从父线程中取值 4 * 从输出结果可以看出,main线程运行时获取了默认的new Date() 5 * 当子线程ThreadA在运行时,则获取的时同一个Date对象 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 try { 9 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 10 System.out.println("Main线程中取值为:" + Tools.t1.get()); 11 Thread.sleep(100); 12 } 13 Thread.sleep(5000); 14 ThreadA a = new ThreadA(); 15 a.start(); 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 } 20 }
运行结果如下:
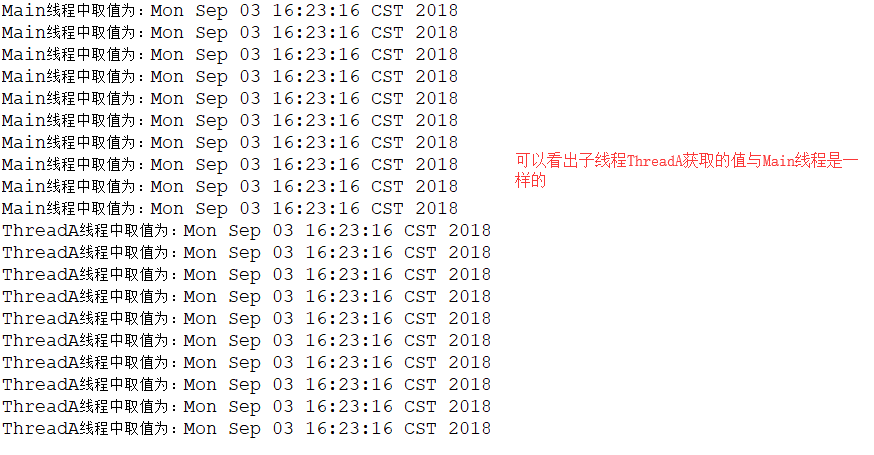
继承InheritableThreadLocal类,重写childValue()方法,修改子线程获取的默认值:
1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 /** 4 * 继承InheritableThreadLocal类,实现childValue()方法,修改子线程获取的默认值 5 */ 6 public class InheritableThreadLocalExt extends InheritableThreadLocal<Object> { 7 8 @Override 9 protected Object initialValue() { 10 return new Date().getTime(); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 protected Object childValue(Object parentValue) { 15 return parentValue + "我是子线程加的值"; 16 } 17 }
1 /** 2 * 工具类,定义公共的静态的ThreadLocal对象 3 */ 4 public class Tools { 5 6 public static InheritableThreadLocalExt t1 = new InheritableThreadLocalExt(); 7 8 }
1 /** 2 * 线程A 3 */ 4 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 try { 8 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 9 System.out.println("ThreadA线程中取值为:" + Tools.t1.get()); 10 Thread.sleep(100); 11 } 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 } 16 }
1 public class Run { 2 /** 3 * 通过继承InheritableThreadLocal实现子线程从父线程中获取值 4 * 此时如果需要修改子线程的值,则通过重写childValue方法来设置子线程的值 5 * 6 * 注:如果子线程在取得值的同时,主线程将InheritableThreadLocal中的值进行更改, 7 * 那么子线程取得的值还是旧的值 8 */ 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 try { 11 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 12 System.out.println("Main线程中取值为:" + Tools.t1.get()); 13 Thread.sleep(100); 14 } 15 Thread.sleep(5000); 16 ThreadA a = new ThreadA(); 17 a.start(); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 }
运行结果如下:
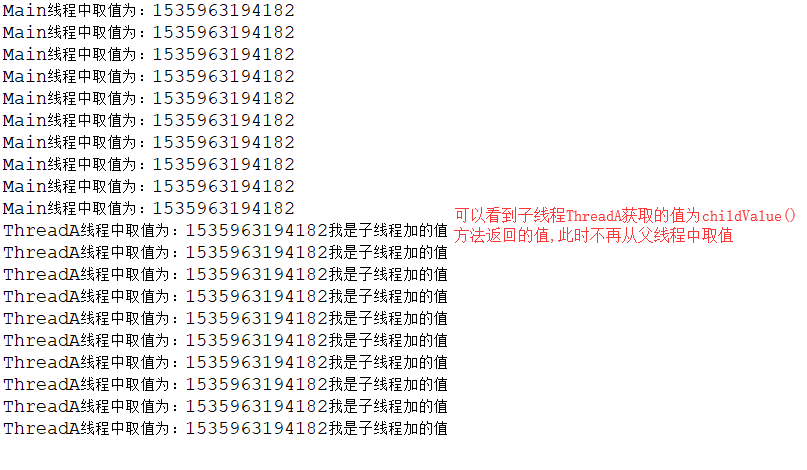




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号