一. 什么是服务注册中心?
先来看看,微服务架构中各个服务的关系是怎样的?相信了解过微服务架构的人都知道康威法则:企业结构等同于系统设计。这句话其实很好的解答了我们刚才的问题。在企业结构下,各个部门需要交流配合。在微服务架构下,各个微服务也需要相同模式的配合。如果你需要另一个部门的人帮你做些事,你会怎么办呢?私交好的可能直接找那个部门的某个人,但是有个问题是和全公司所有人都建立私交难度很大,根本不可能。还会有人通过自己的领导和其他部门的领导协商,让部门领导来分配一个人来协助你,但是部门领导之间也是同级关系,部门交情不深可能也无法很好的协作。最好的方式其实是找到这两部门的共同大领导,大领导同意了啥事都好说。
上面例子的三种沟通方式对应到微服务中。方式1是微服务A的实例a直接找微服务B的实例b1,如果有一天实例b1请假了,就要去找b2,微服务B扩招了一个实例b3时实例a也要及时得到讯息。可以看到每个微服务实例都需要维护所有其他微服务实例,关系错综复杂根本不可能。方式2是实例a去找微服务B的LeaderB,让LeaderB分配一个实例b给自己。这种方式下微服务实例只需要维护其他微服务的Leader实例即可,但是在大项目下可能有上百上千个微服务,这种方式也不可取。方式3是实例a直接找所有微服务的大领导,让大领导命令微服务B来协作你,具体的协作方式比现实生活中更有面:把所有微服务B的实例都给你,你来自己挑。
这个大领导就是我们今天要说的服务注册中心。
二. 服务注册中心要解决什么问题?
上面我们提到服务注册中心是所有微服务的大领导,负责协调各个微服务的工作配合。
它的职责有以下几点:
1. 服务的上线下线(入职,离职)
2. 服务的心跳检测(有没有开小差)
3. 派发微服务列表(让你选择其他部门的一个人来协作)
三. 领导生病了怎么办?
有一天这个大领导发现,手下的微服务太多了,自己有点忙不过来,更重要的是自己一请假,所有微服务都迷茫了,这时候它就多请了几个人和自己一样当大领导。如果有服务上线只需要告诉其中一个大领导即可,这个大领导会定时同步给其他大领导,当然这里是有一定时间差的,对应CAP理论中就是实现了AP舍弃了C。当有服务器拉取服务列表的时候,也是直接从其中一个大领导处拉取即可,这样就算有一个大领导请假了,各微服务也能很好的运作。
职责4. 服务注册中心间同步
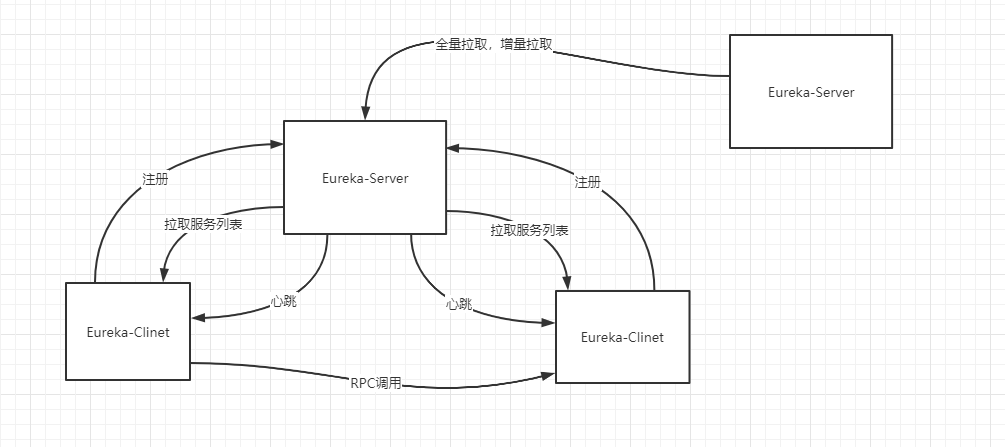
四. 领导也是要面试,也是要上班打卡的
Netfix中的服务注册发现组件叫Eureka,Eureka-server是服务注册中心。下边我们来将Eureka应用到SpringBoot项目中
面试:pom导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
上岗:单server配置
server: port: 8761 eureka: instance: hostname: localhost client: registerWithEureka: false fetchRegistry: false serviceUrl: defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
集群:双server配置
--- spring: profiles: peer1 eureka: instance: hostname: peer1 client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: https://peer2/eureka/ --- spring: profiles: peer2 eureka: instance: hostname: peer2 client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: https://peer1/eureka/
集群:三个以上server配置
eureka: client: serviceUrl: defaultZone: https://peer1/eureka/,http://peer2/eureka/,http://peer3/eureka/ --- spring: profiles: peer1 eureka: instance: hostname: peer1 --- spring: profiles: peer2 eureka: instance: hostname: peer2 --- spring: profiles: peer3 eureka: instance: hostname: peer3
启动Eureka还需要在SpringBoot启动类上加上注解@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaServer public class CloudEurekasApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(CloudEurekasApplication.class, args); } }
@EnableEurekaServer注解会导入EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration类
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class) public @interface EnableEurekaServer { }
EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration类会注册一个Marker类的bean
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration { @Bean public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() { return new Marker(); } class Marker { } }
根据名称来看Markder类是一个开关,我们应该首先想到可能是用作SpringBean的Condition注解中的。于是我们找一下Eureka-server包下的spring.factories文件
eureka-server/META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EurekaServerAutoConfiguration
看一下EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class) @ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class, InstanceRegistryProperties.class }) @PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties") public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer
在这个类里找到了我们想要的东西,只有存在Bean Marker时,才会导入EurekaServerAutoConfiguration,而EurekaServerAutoConfiguration又import了EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) public class EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration implements ServletContextAware, SmartLifecycle, Ordered
可以看到EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration继承了SmartLifecycle,SmartLifecycle又继承了Lifecycle。就是说Spring在启动的时候,会执行EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration中的start方法。我们来看看start方法做了哪些事。
@Override public void start() { new Thread(() -> { try { // TODO: is this class even needed now? // eureka初始化 eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized( EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext); log.info("Started Eureka Server"); // 发布Eureka注册事件 publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig())); EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true; // 发布Eureka启动事件 publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig())); } catch (Exception ex) { // Help! log.error("Could not initialize Eureka servlet context", ex); } }).start(); } public void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) { try { // 初始化环境变量 initEurekaEnvironment(); // 初始化上下文 initEurekaServerContext(); context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext); } catch (Throwable e) { log.error("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e); throw new RuntimeException("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e); } } protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception { // For backward compatibility JsonXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(), XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH); XmlXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(), XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH); if (isAws(this.applicationInfoManager.getInfo())) { this.awsBinder = new AwsBinderDelegate(this.eurekaServerConfig, this.eurekaClientConfig, this.registry, this.applicationInfoManager); this.awsBinder.start(); } EurekaServerContextHolder.initialize(this.serverContext); log.info("Initialized server context"); // Copy registry from neighboring eureka node,从内存中获取同步服务清单 int registryCount = this.registry.syncUp(); // this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount); // Register all monitoring statistics. EurekaMonitors.registerAllStats(); } @Override public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) { super.openForTraffic(applicationInfoManager, count == 0 ? this.defaultOpenForTrafficCount : count); } @Override public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) { // Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2. // 计算renew时间间隔 this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count; updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); logger.info("Got {} instances from neighboring DS node", count); logger.info("Renew threshold is: {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold); this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (count > 0) { this.peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup = false; } DataCenterInfo.Name selfName = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getDataCenterInfo().getName(); boolean isAws = Name.Amazon == selfName; if (isAws && serverConfig.shouldPrimeAwsReplicaConnections()) { logger.info("Priming AWS connections for all replicas.."); primeAwsReplicas(applicationInfoManager); } logger.info("Changing status to UP"); applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP); // 开启定时剔除器 super.postInit(); }
五. Eureka-Rest-API
InstanceResource



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号