Locust入门及最佳实践
官方文档:https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/
基础demo
from locust import HttpUser, task
class HelloWorldUser(HttpUser):
@task
def hello_world(self):
self.client.get("/hello")
self.client.get("/world")
最佳实践
-
断言:
在 Locust 中,默认情况下,如果 HTTP 响应状态码是 2xx,请求会被标记为成功;否则会被标记为失败 -
SequentialTaskSet和TaskSet的区别:
TaskSet 是 Locust 的一个基本类,用于定义用户行为。
SequentialTaskSet 是 TaskSet 的子类,它会按照任务定义的顺序依次执行任务,每个任务执行完后才会执行下一个任务。 -
task:
方法上添加 @task 装饰器来定义用户任务。 -
定义负载形状:
- LoadTestShape自动化控制(使用该方式将无法通过WebUI手动控制)
用于定义负载形状,即用户数量和请求频率的变化规律。可以通过继承 LoadTestShape 类并重写 tick 方法来自定义负载形状。
tick 方法会在每个时间间隔内被调用,返回一个元组 (users, spawn_rate),表示当前的用户数量和每秒启动用户数。 - 使用 WebUI 手动调整
在压测过程中,随时点击右上角的 "+" 或 "-" 按钮 增加 / 减少用户数。
- LoadTestShape自动化控制(使用该方式将无法通过WebUI手动控制)
-
HttpUser:
用于定义 HTTP 用户类.每个 HttpUser 实例代表一个用户,它会执行定义的任务。- host: 指定请求的基础URL
- wait_time: 指定用户任务之间的等待时间
- tasks: 指定用户的任务列表
-
name:
对接口请求进行分组,接口参数可能是动态的,在用户统计信息中将这些 URL 组合在一起才有意义。 -
钩子函数:
- on_test_start: 测试开始时执行的函数
- on_test_stop: 测试结束时执行的函数
from locust import HttpUser, task, between, LoadTestShape, SequentialTaskSet, constant_throughput, events
@events.test_start.add_listener
def on_test_start(environment, **kwargs):
"""
测试开始时执行的函数,
"""
print("测试开始")
class UserBehavior(SequentialTaskSet):
"""用户行为"""
token = None
def on_start(self):
"""每个用户启动时执行的函数"""
print("用户启动")
@task
def login(self):
"""登录"""
with self.client.post("/login", name="登录", catch_response=True) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
self.token = response.json().get("token")
response.success()
else:
response.failure("status_code非200:" + response.text)
@task(3)
def create_product(self):
"""创建商品"""
if not self.token:
return # 如果没有token,不执行创建商品任务
body = {
"productName": "测试商品",
}
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.token}"
}
with self.client.post(url="/create_product", name="创建商品", json=body,headers=headers,
catch_response=True) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
response.success()
else:
response.failure("status_code非200:" + response.text)
@task
def logout(self):
"""退出登录"""
if not self.token:
return # 如果没有token,不执行退出登录任务
with self.client.post("/logout", name="退出登录", catch_response=True) as response:
if response.status_code == 200:
self.token = None # 登出后清空token
response.success()
else:
response.failure("status_code非200:" + response.text)
class TimeLimitLoadShape(LoadTestShape):
"""10分钟后自动退出的负载形状"""
def tick(self):
# 获取当前压测运行时间(秒)
run_time = self.get_run_time()
# 10分钟 = 600秒,超过则退出
if run_time > 600:
return None # 返回None表示终止测试
# 压测期间保持100用户(可根据需求调整用户数和增长策略)
return (100, 10) # (目标用户数, 每秒启动用户数)
class LiveAuctionUser(HttpUser):
tasks = [UserBehavior]
wait_time = constant_throughput(2) # 每个用户每秒最多执行2次循环

负载压测实践
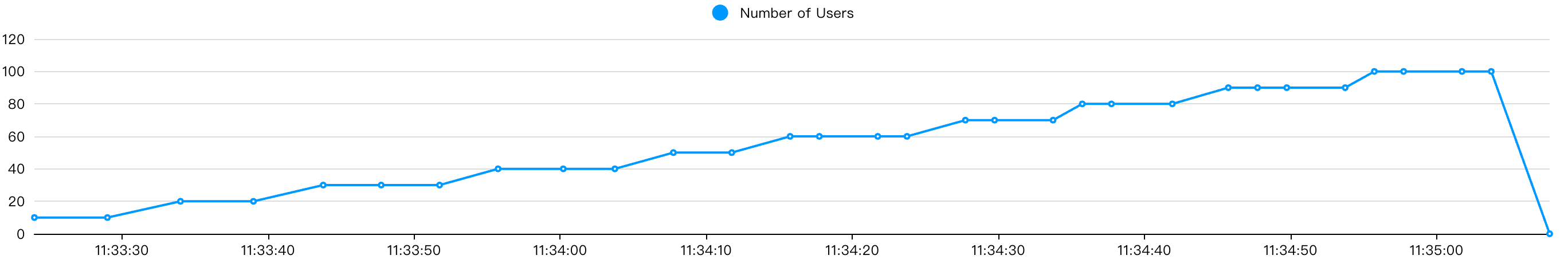
class StepLoadShape(LoadTestShape):
"""
阶梯压测形状:
- 每 step_duration 秒增加 step_users 个用户
- 直到达到 max_users 为止
"""
step_time = 10 # 每个阶梯持续时间(秒)
step_users = 10 # 每个阶梯增加的用户数
spawn_rate = 10 # 每秒启动的用户数
max_users = 100 # 最大用户数
def tick(self):
# 计算当前所处的阶梯数
run_time = self.get_run_time()
current_step = int(run_time / self.step_time) + 1
# 计算当前应有的用户数
users = current_step * self.step_users
# 检查是否达到最大用户数
if users > self.max_users:
return None # 停止压测
return (users, self.spawn_rate)
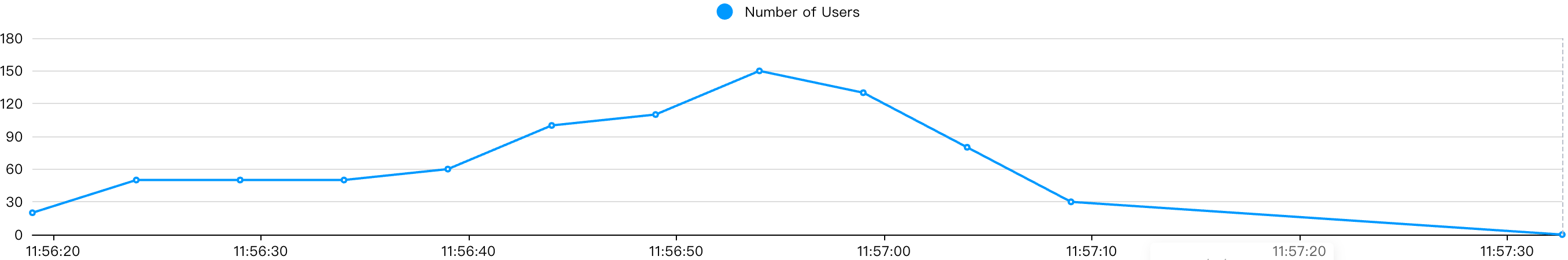
class StagedLoadShape(LoadTestShape):
"""
分阶段阶梯压测:
1. 预热阶段
2. 稳定阶段
3. 加压阶段
4. 收尾阶段
"""
stages = [
{"duration": 10, "users": 50, "spawn_rate": 10}, # 预热阶段
{"duration": 20, "users": 50, "spawn_rate": 10}, # 稳定阶段
{"duration": 30, "users": 100, "spawn_rate": 10}, # 加压阶段1
{"duration": 40, "users": 150, "spawn_rate": 10}, # 加压阶段2
{"duration": 45, "users": 100, "spawn_rate": 20}, # 减压阶段1
{"duration": 50, "users": 50, "spawn_rate": 20}, # 减压阶段2
{"duration": 55, "users": 0, "spawn_rate": 20}, # 减压阶段3
]
def tick(self):
run_time = self.get_run_time()
# 查找当前所处的阶段
for stage in self.stages:
if run_time < stage["duration"]:
tick_data = (stage["users"], stage["spawn_rate"])
return tick_data
# 所有阶段完成后停止
return None
高阶使用
- 分布式测试
- 数据参数化
- TaskSet嵌套




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号