ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock是一种基于AQS框架的应用实现,是JDK中的一种线程并发访问的同步手段,它的功能类似于synchronized是一种互斥锁,可以保证线程安全。
相对于 synchronized, ReentrantLock具备如下特点: 1、可中断 2、可以设置超时时间 3、可以设置为公平锁 4、支持多个条件变量 5、与 synchronized 一样,都支持可重入
synchronized和ReentrantLock的区别: 1、synchronized是JVM层次的锁实现,ReentrantLock是JDK层次的锁实现; 2、synchronized的锁状态是无法在代码中直接判断的,但是ReentrantLock可以通过ReentrantLock#isLocked判断; 3、synchronized是非公平锁,ReentrantLock是可以是公平也可以是非 公平的; 4、synchronized是不可以被中断的,ReentrantLock#lockInterruptibly方法是可以被中断的;在发生异常时synchronized会自动释放锁,而5、5、ReentrantLock需要开发者在finally块中显示释放锁; 6、ReentrantLock获取锁的形式有多种:如立即返回是否成功的tryLock(),以及等待指定时长的获取,更加灵活; 7、synchronized在特定的情况下对于已经在等待的线程是后来的线程先获得锁(回顾一下sychronized的唤醒策略),而ReentrantLock对于已经在等待的线程是先来的线程先获得锁;
ReentrantLock公平锁和非公平锁的性能谁更高?
非公平锁
ReentrantLock的使用
1、lock() 2、lockInterruptibly() 3、tryLock() 4、unlock()
Condition类来实现线程之间的协调。调用Condition.await() 方法使线程等待,其他线程调用Condition.signal() 或Condition.signalAll() 方法唤醒等待的线程。 注意:调用Condition的await()和signal()方法,都必须在lock保护之内。
lock加锁源码(查看笔记)
unlock解锁源码(查看笔记)
源码流程解析:
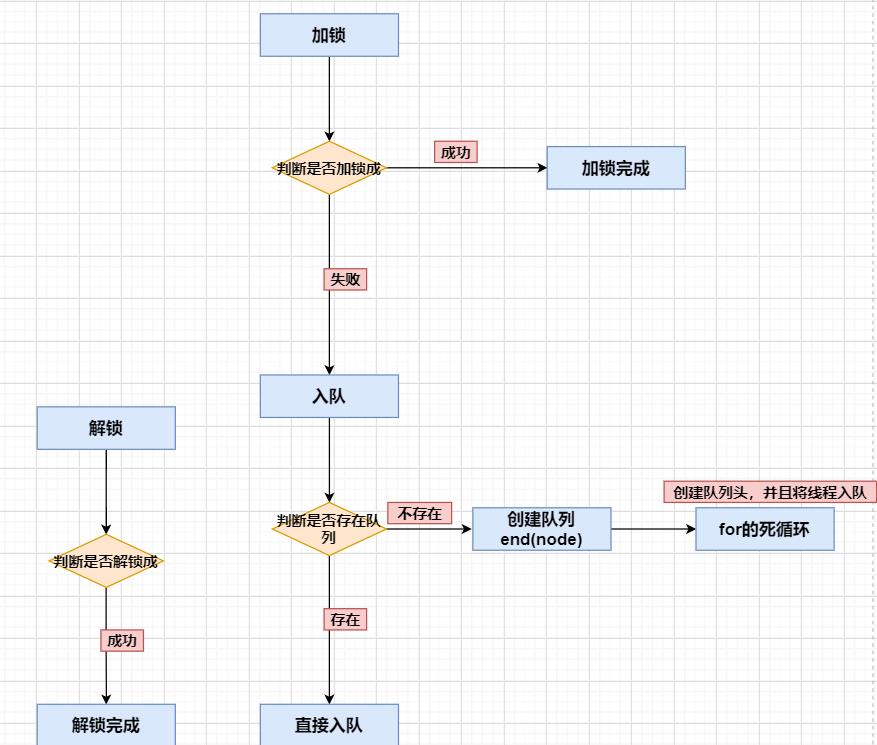
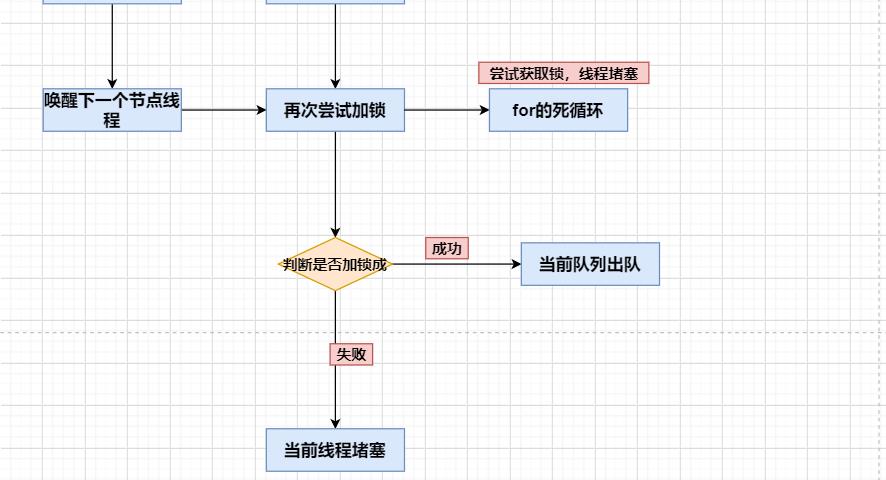
Condition接口详解
调用Condition#await方法会释放当前持有的锁,然后阻塞当前线程,同时向Condition队列尾部添加一个节点,所以调用Condition#await方法的时候必须持有锁。
调用Condition#signal方法会将Condition队列的首节点移动到阻塞队列尾部,然后唤醒因调用Condition#await方法而阻塞的线程(唤醒之后这个线程就可以去竞争锁了),所以调用Condition#signal方法的时
候必须持有锁,持有锁的线程唤醒被因调用Condition#await方法而阻塞的线程。
等待唤醒机制之await/signal测试 @Slf4j public class ConditionTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 开始处理任务"); condition.await(); log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 结束处理任务"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }).start(); new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 开始处理任务"); Thread.sleep(2000); condition.signal(); log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 结束处理任务"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }).start(); }
ReentrantLock的使用
同步执行,类似于synchronized ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //参数默认false,不公平锁 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //公平锁 //加锁 lock.lock(); try { //临界区 } finally { // 解锁 lock.unlock(); 测试 public class ReentrantLockDemo { private static int sum = 0; private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { Thread thread = new Thread(()->{ //加锁 lock.lock(); try { for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) { sum++; } } finally { // 解锁 lock.unlock(); } }); thread.start(); } Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println(sum); } 可重入 @Slf4j public class ReentrantLockDemo2 { public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static void main(String[] args) { method1(); } public static void method1() { lock.lock(); try { log.debug("execute method1"); method2(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void method2() { lock.lock(); try { log.debug("execute method2"); method3(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void method3() { lock.lock(); try { log.debug("execute method3"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } 可中断 @Slf4j public class ReentrantLockDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { log.debug("t1启动..."); try { lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { log.debug("t1获得了锁"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); log.debug("t1等锁的过程中被中断"); } }, "t1"); lock.lock(); try { log.debug("main线程获得了锁"); t1.start(); //先让线程t1执行 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } t1.interrupt(); log.debug("线程t1执行中断"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } 锁超时 立即失败 @Slf4j public class ReentrantLockDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { log.debug("t1启动..."); // 注意: 即使是设置的公平锁,此方法也会立即返回获取锁成功或失败,公平策略不生效 if (!lock.tryLock()) { log.debug("t1获取锁失败,立即返回false"); return; } try { log.debug("t1获得了锁"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "t1"); lock.lock(); try { log.debug("main线程获得了锁"); t1.start(); //先让线程t1执行 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } 超时失败 @Slf4j public class ReentrantLockDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { log.debug("t1启动..."); //超时 try { if (!lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { log.debug("等待 1s 后获取锁失败,返回"); return; } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return; } try { log.debug("t1获得了锁"); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "t1"); lock.lock(); try { log.debug("main线程获得了锁"); t1.start(); //先让线程t1执行 try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } 公平锁 ReentrantLock 默认是不公平的 @Slf4j public class ReentrantLockDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //公平锁 for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) { new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running..."); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "t" + i).start(); } // 1s 之后去争抢锁 Thread.sleep(1000); for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) { new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running..."); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "强行插入" + i).start(); } } 思考:ReentrantLock公平锁和非公平锁的性能谁更高? 条件变量 java.util.concurrent类库中提供Condition类来实现线程之间的协调。调用Condition.await() 方法使线程等待,其他线程调用Condition.signal() 或 Condition.signalAll() 方法唤醒等待的线程。 注意:调用Condition的await()和signal()方法,都必须在lock保护之内。 @Slf4j public class ReentrantLockDemo6 { private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private static Condition cigCon = lock.newCondition(); private static Condition takeCon = lock.newCondition(); private static boolean hashcig = false; private static boolean hastakeout = false; //送烟 public void cigratee(){ lock.lock(); try { while(!hashcig){ try { log.debug("没有烟,歇一会"); cigCon.await(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("有烟了,干活"); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } //送外卖 public void takeout(){ lock.lock(); try { while(!hastakeout){ try { log.debug("没有饭,歇一会"); takeCon.await(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("有饭了,干活"); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ReentrantLockDemo6 test = new ReentrantLockDemo6(); new Thread(() ->{ test.cigratee(); }).start(); new Thread(() -> { test.takeout(); }).start(); new Thread(() ->{ lock.lock(); try { hashcig = true; //唤醒送烟的等待线程 cigCon.signal(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } },"t1").start(); new Thread(() ->{ lock.lock(); try { hastakeout = true; //唤醒送饭的等待线程 takeCon.signal(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } },"t2").start(); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号