离群值 Outliers
标准化
\[\begin{align*}
\pmb x&=\left(x^{(1)},x^{(2)},\dots,x^{(n)}\right)\\
\pmb\mu&=\frac1m\sum_{i=1}^m\pmb x_i\\
\pmb\sigma&=\sqrt{\delta+\frac1m\sum_{i=1}^m(\pmb x_i-\pmb\mu)^2}\\
\pmb x'&={\pmb x-\pmb\mu\over\pmb\sigma}
\end{align*}
\]
其中 \(\delta\) 为一个很小的正值。
标准化中的离群值
离群值对标准化的计算会有很大影响。
离群值是数据中那些远离主流数据的样本。可能由以下几个原因产生:
- 测量错误或输入错误;
- 数据损坏;
- 确实观察到了离群值。
但在大多数情况下,没有特定的检测离群值的手段。
移除离群值
使用标准差的方法
对于高斯分布的数据,标准差表明了数据分布的百分比:1 个标准差 68%;2 个标准差 96%;3 个标准差 99.7%。
如果选择 2 个标准差作为离群值阈值,则会去掉样本中所有差值大于 2 个标准差的样本。从分布上来看,去除了 4% 的离群值。
def standard_deviation(array: np.ndarray):
mean = array.sum() / array.size
std = ((array ** 2).sum() / array.size) ** 0.5
lower_bound, upper_bound = mean - std * 2, mean + std * 2
return array[(lower_bound < array) & (upper_bound > array)]
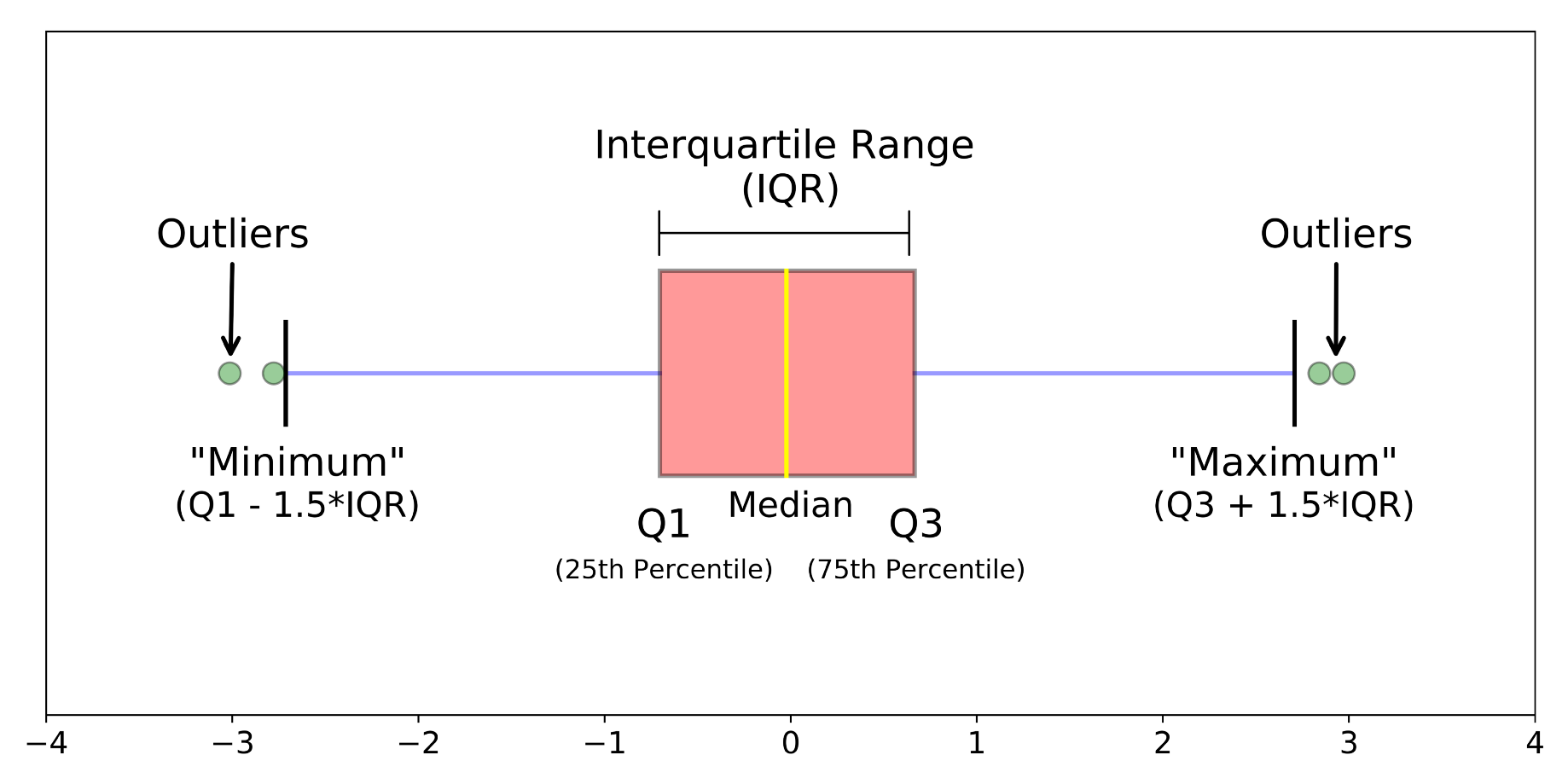
使用四分位距的方法
这一方法对应箱形图(box plot),将四分位点的 1.5 倍范围以外判定为离群值,当然也可以使用其他比例,但 1.5 比较常用。
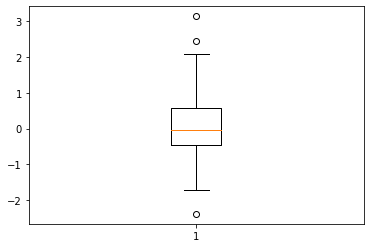
np.random.randn() 使用高斯分布,画出对应的箱形图为
x = np.random.randn(100)
plt.boxplot(x)
plt.show()
def interquartile_range(array: np.ndarray):
p25, p75 = np.percentile(array, 25), np.percentile(array, 75)
bound = (p75 - p25) * 1.5
lower_bound, upper_bound = p25 - bound, p75 - bound
return array[(lower_bound < array) & (upper_bound > array)]
相对应的,有一种变换方法比起标准化更能应对离群值,其方法为将数据减去中位数后缩小上下四分位点之差。
(x - np.median(x)) / (np.percentile(x, 75) - np.percentile(x, 25)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号