设计模式之代理模式
Proxy(代理模式)
一、代理模式简介
在代理模式(Proxy Pattern)中,一个类代表另一个类的功能。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式。
在代理模式中,我们创建具有现有对象的对象,以便向外界提供功能接口。
核心:
- 1、通过代理,控制对对象的访问。
- 2、可以详细控制访问某个(某类)对象的方法,在调用这个方法前做前置处理,调用这个方法后 做后置处理
二、代理模式优缺点比较
优点:
- 1、职责清晰。
- 2、高扩展、智能化。
缺点:
- 1、请求的处理速度变慢
- 2、实现代理模式需要额外的工作,有些代理模式的实现非常复杂
使用场景:
- 1、安全代理:屏蔽对真实角色的直接访问
- 2、远程代理:通过代理类处理远程方法调用(RMI)
- 3、延迟加载:先加载轻量级的代理对象,真正需要再加载真实对象
注意事项:1、和适配器模式的区别:适配器模式主要改变所考虑对象的接口,而代理模式不能改变所代理类的接口。 2、和装饰器模式的区别:装饰器模式为了增强功能,而代理模式是为了加以控制。
三、静态代理UML类图
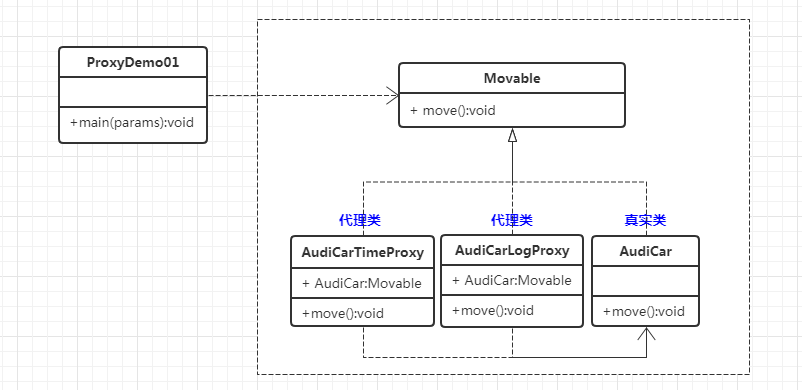
四、静态代理实现
步骤1:创建接口
public interface Movable { void move(); }
步骤2:创建实现接口的实体类
public class AudiCar implements Movable{ @Override public void move() { System.out.println("AudiCar is moving cacaca...................."); } }
步骤3:创建实现接口的代理类

public class AudiCarTimeProxy implements Movable { private Movable thing; public AudiCarTimeProxy(Movable thing) { this.thing = thing; } @Override public void move() { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("AudiCarTimeProxy move start "); try { Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("run exception"); } thing.move(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("AudiCarTimeProxy move end "); System.out.println("callback move 耗时为:"+(end-start)+"ms"); } } public class AudiCarLogProxy implements Movable { private Movable thing; public AudiCarLogProxy(Movable thing) { this.thing = thing; } @Override public void move() { System.out.println("AudiCarLogProxy move start"); thing.move(); System.out.println("AudiCarLogProxy move end"); } }
步骤4:调用者测试
public class StaticProxyDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { new AudiCarTimeProxy(new AudiCarLogProxy(new AudiCar())).move(); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------"); new AudiCarLogProxy(new AudiCarTimeProxy(new AudiCar())).move(); } }
步骤5:运行程序,观察结果
AudiCarTimeProxy move start AudiCarLogProxy move start AudiCar is moving cacaca..................... AudiCarLogProxy move end AudiCarTimeProxy move end callback move 耗时为:402ms -------------------------------------------------- AudiCarLogProxy move start AudiCarTimeProxy move start AudiCar is moving cacaca..................... AudiCarTimeProxy move end callback move 耗时为:661ms AudiCarLogProxy move end
五、动态代理UML类图
六、动态代理实现
步骤1:创建接口
public interface Movable { void move(); }
步骤2:创建实现接口的实体类
public class AudiCar implements Movable{ @Override public void move() { System.out.println("AudiCar is moving cacaca...................................."); } }
步骤3:创建处理类Handler对象
public class ProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler{ private Movable thing; public ProxyHandler(Movable thing) { this.thing = thing; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { method.invoke(thing, args); return null; } }
步骤4:调用者测试
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import gof.com.yew.proxy.staticproxy.AudiCar; import gof.com.yew.proxy.staticproxy.Movable; public class ProxyDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Movable audi = new AudiCar(); System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");//保存jdk动态代理生成的动态代理类class文件 ProxyHandler handler = new ProxyHandler(audi); Movable proxy = (Movable)Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), new Class[] {Movable.class}, handler); proxy.move(); } }
步骤5:运行程序,观察结果
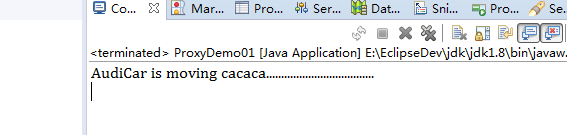
七、动态代理生成的类分析
package com.sun.proxy; import gof.com.yew.proxy.staticproxy.Movable; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException; public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Movable //动态代理类继承了Proxy并且实现了Movable接口 { private static Method m1; private static Method m3; private static Method m2; private static Method m0; public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler) throws { super(paramInvocationHandler); } public final boolean equals(Object paramObject) throws { try { return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] { paramObject })).booleanValue(); } catch (Error|RuntimeException localError) { throw localError; } catch (Throwable localThrowable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable); } } public final void move()//重写movable接口 throws { try { this.h.invoke(this, m3, null); return; } catch (Error|RuntimeException localError) { throw localError; } catch (Throwable localThrowable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable); } } public final String toString() throws { try { return (String)this.h.invoke(this, m2, null); } catch (Error|RuntimeException localError) { throw localError; } catch (Throwable localThrowable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable); } } public final int hashCode() throws { try { return ((Integer)this.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue(); } catch (Error|RuntimeException localError) { throw localError; } catch (Throwable localThrowable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable); } } static { try { m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") }); m3 = Class.forName("gof.com.yew.proxy.staticproxy.Movable").getMethod("move", new Class[0]); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]); return; } catch (NoSuchMethodException localNoSuchMethodException) { throw new NoSuchMethodError(localNoSuchMethodException.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException localClassNotFoundException) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError(localClassNotFoundException.getMessage()); } } }
posted on 2020-03-29 20:10 VincentYew 阅读(221) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号