设计模式之原型模式
prototype(原型模式)
一、原型模式简介
原型模式(Prototype Pattern)是用于创建重复的对象,同时又能保证性能。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
这种模式是实现了一个原型接口,该接口用于创建当前对象的克隆。当直接创建对象的代价比较大时,则采用这种模式。
例如,一个对象需要在一个高代价的数据库操作之后被创建。我们可以缓存该对象,在下一个请求时返回它的克隆,在需要的时候更新数据库,以此来减少数据库调用。
核心:
- 1、实现克隆操作,在 JAVA 继承 Cloneable,重写 clone()。
- 2、原型模式同样用于隔离类对象的使用者和具体类型(易变类)之间的耦合关系,它同样要求这些"易变类"拥有稳定的接口
-
3、短时间大量创建对象时,原型模式和普通new方式效率测试
- 4、克隆对象拥有原型对象相同的属性和值
二、原型模式优缺点比较
优点:
- 1、性能提高。
- 2、逃避构造函数的约束。
缺点:
- 1、配备克隆方法需要对类的功能进行通盘考虑,这对于全新的类不是很难,但对于已有的类不一定很容易,特别当一个类引用不支持串行化的间接对象,或者引用含有循环结构的时候
- 2、必须实现 Cloneable 接口
使用场景:
- 1、Spring中bean创建
- 2、类初始化需要消化非常多的资源,这个资源包括数据、硬件资源等
- 3、资源优化、性能和安全要求、一个对象多个修改者
注意事项:与通过对一个类进行实例化来构造新对象不同的是,原型模式是通过拷贝一个现有对象生成新对象的。浅拷贝实现 Cloneable,重写,深拷贝是通过实现 Serializable 读取二进制流。
三、实现UML类图
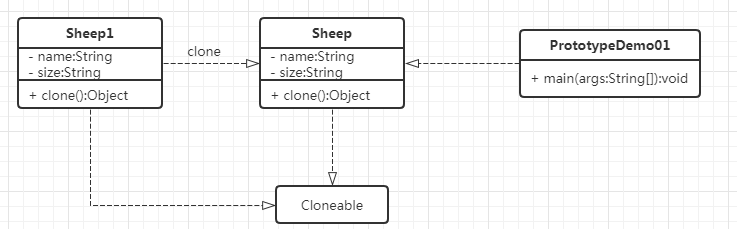
四、实现(浅拷贝)
步骤1:创建实体类,实现Cloneable接口并重写Clone()方法

import java.io.Serializable; /** * 原型模式 * 1.继承 Cloneable,重写 clone() * 2.浅克隆---Java Clone实现 * 3.深克隆---实现 Serializable 读取二进制流 * @author yw */ //1.实现Cloneable接口 public class Sheep implements Cloneable,Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String name; private Address address; public Sheep(String name, Address address) { this.name = name; this.address = address; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } //2.重写Clone方法 public Object Clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } import java.io.Serializable; public class Address implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String cuntry; private String loc; public Address(String cuntry, String loc) { this.cuntry = cuntry; this.loc = loc; } public String getCuntry() { return cuntry; } public void setCuntry(String cuntry) { this.cuntry = cuntry; } public String getLoc() { return loc; } public void setLoc(String loc) { this.loc = loc; } }
步骤2:使用调用者克隆(浅克隆)对象

/** * 浅拷贝 * @author yw */ public class PrototypeDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Address address = new Address("中国", "湖北"); Sheep sheep = new Sheep("多利", address); Sheep sheep1 = (Sheep)sheep.Clone(); System.out.println(sheep.getName()); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getCuntry()); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println(sheep1.getName()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getCuntry()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); address.setLoc("浙江"); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getLoc()); } }
步骤3:运行程序,观察结果
多利 中国 湖北 ------------------------------------------------- 多利 中国 湖北 ------------------------------------------------- 浙江 浙江
五、实现(深拷贝)
步骤1:创建实体类,实现Cloneable接口并重写Clone()方法 (类及引用对象均需要实现和重写)

package gof.com.yew.prototype; /** * 原型模式 *深克隆---克隆所有的属性 */ //1.实现Cloneable接口 public class Sheep1 implements Cloneable { private String name; private Address1 address; public Sheep1(String name, Address1 address) { this.name = name; this.address = address; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address1 getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address1 address) { this.address = address; } //2.重写Clone方法 public Object Clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Sheep1 sheep1 = (Sheep1)super.clone(); sheep1.address= (Address1)address.Clone(); return sheep1; } } class Address1 implements Cloneable { private String cuntry; private String loc; public Address1(String cuntry, String loc) { this.cuntry = cuntry; this.loc = loc; } public String getCuntry() { return cuntry; } public void setCuntry(String cuntry) { this.cuntry = cuntry; } public String getLoc() { return loc; } public void setLoc(String loc) { this.loc = loc; } //2.重写Clone方法 public Object Clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
步骤2:使用调用者克隆(深克隆)对象

/** * 深拷贝 * @author yw */ public class PrototypeDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Address1 address = new Address1("中国", "湖北"); Sheep1 sheep = new Sheep1("多利", address); Sheep1 sheep1 = (Sheep1)sheep.Clone(); System.out.println(sheep.getName()); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getCuntry()); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println(sheep1.getName()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getCuntry()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); address.setLoc("浙江"); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getLoc()); } }
步骤3:运行程序,观察结果
多利 中国 湖北 ------------------------------------------------- 多利 中国 湖北 ------------------------------------------------- 浙江 湖北
六、序列化和反序列化实现(深拷贝)
步骤1:创建实体类实现Serializable

public class Sheep2 implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String name; private Address address; public Sheep2(String name, Address address) { this.name = name; this.address = address; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } } public class Address implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String cuntry; private String loc; public Address(String cuntry, String loc) { this.cuntry = cuntry; this.loc = loc; } public String getCuntry() { return cuntry; } public void setCuntry(String cuntry) { this.cuntry = cuntry; } public String getLoc() { return loc; } public void setLoc(String loc) { this.loc = loc; } }
步骤2:使用调用者克隆(深克隆)对象

public class PrototypeDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Address address = new Address("中国", "湖北"); Sheep2 sheep = new Sheep2("多利", address); //使用系列化和反序列化实现深拷贝 ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); oos.writeObject(sheep); byte[] bs = bos.toByteArray(); ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bs); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); Sheep2 sheep1 = (Sheep2)ois.readObject(); System.out.println(sheep.getName()); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getCuntry()); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println(sheep1.getName()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getCuntry()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------"); address.setLoc("浙江"); System.out.println(sheep.getAddress().getLoc()); System.out.println(sheep1.getAddress().getLoc()); } }
步骤3:运行程序,观察结果
多利 中国 湖北 ------------------------------------------------- 多利 中国 湖北 ------------------------------------------------- 浙江 湖北
posted on 2020-03-28 20:48 VincentYew 阅读(171) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号