工厂模式之抽象工厂
Abstract Factory(抽象工厂)
一、抽象工厂模式简介
抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory)是围绕一个超级工厂创建其他工厂。该超级工厂又称为其他工厂的工厂。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
在抽象工厂模式中,接口是负责创建一个相关对象的工厂,不需要显式指定它们的类。每个生成的工厂都能按照工厂模式提供对象。
二、抽象工厂模式优缺点比较
优点:当一个产品族中的多个对象被设计成一起工作时,它能保证客户端始终只使用同一个产品族中的对象。
缺点:产品族扩展非常困难,要增加一个系列的某一产品,既要在抽象的 Creator 里加代码,又要在具体的里面加代码。
使用场景: 1、QQ 换皮肤,一整套一起换。 2、生成不同操作系统的程序。
注意事项:用来生产不同产品族的全部产品,不可以增加产品,可以增加产品族
三、实现UML类图
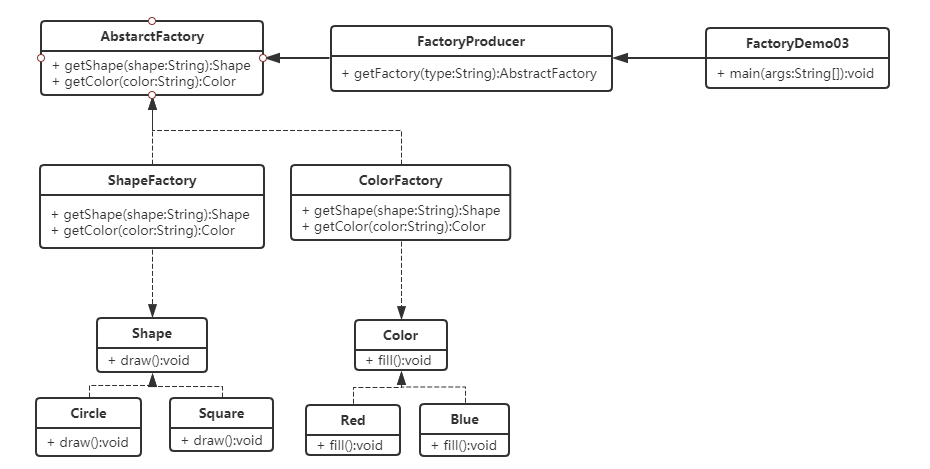
四、实现
步骤1:创建接口
public interface Color { public void fill(); } public interface Shape{ public void draw(); }
步骤2:创建实现接口的实体类
class Red implements Color{ @Override public void fill() { System.out.println("Callback Red::fill method"); } } class Blue implements Color{ @Override public void fill() { System.out.println("Callback Blue::fill method"); } } class Circle implements Shape{ @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Callback Circle::draw() method"); } } class Square implements Shape{ @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Callback Square::draw() method"); } }
步骤3:创建抽象工厂方法接口
/** *增加产品无能为力,可增加产品族 * @author yw */ public interface AbstractFactory { Shape getShape(String shape); Color getColor(String color); }
步骤4:创建实现抽象工厂方法接口的实体工厂方法
public class ShapeFactory implements AbstractFactory { @Override public Shape getShape(String shape) { Shape src = null; if("Cicle".equals(shape)) { src = new Circle(); }else if("Square".equals(shape)) { src = new Square(); } return src; } @Override public Color getColor(String color) { return null; } } public class ColorFactory implements AbstractFactory { @Override public Shape getShape(String shape) { return null; } @Override public Color getColor(String color) { Color c = null; if("Red".equals(color)) { c = new Red(); }else if("Blue".equals(color)) { c = new Blue(); } return c; } }
步骤5:创建一个工厂创造器/生成器类,通过传递形状或颜色信息来获取工厂
public class FactoryProducer { public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String type) { if("shape".equals(type)) { return new ShapeFactory(); }else if("color".equals(type)) { return new ColorFactory(); } return null; } }
步骤6:调用者调用
public class FactoryDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { AbstractFactory factory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("shape"); factory.getShape("Cicle").draw(); factory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("color"); factory.getColor("Red").fill(); } }
步骤7:运行程序,观察结果
Callback Circle::draw() method
Callback Red::fill method
posted on 2020-03-26 22:49 VincentYew 阅读(211) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号