Python 流程控制(if/for/while)
Python if条件语句
Python条件语句是通过一条或多条语句的执行结果(True或者False)来决定执行的代码块。
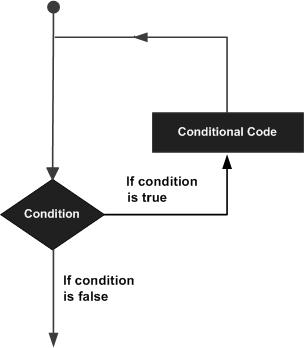
可以通过下图来简单了解条件语句的执行过程:

Python程序语言指定任何非0和非空(null)值为true,0 或者 null为false。
Python 编程中 if 语句用于控制程序的执行,基本形式为:
if 判断条件1:
执行语句1……
elif 判断条件2:
执行语句2……
elif 判断条件3:
执行语句3……
else:
执行语句4……
实例如下:
num = 5 if num == 3: # 判断num的值 print 'boss' elif num == 2: print 'user' elif num == 1: print 'worker' elif num < 0: # 值小于零时输出 print 'error' else: print 'roadman' # 条件均不成立时输出
由于 python 并不支持 switch 语句,所以多个条件判断,只能用 elif 来实现,如果判断需要多个条件需同时判断时,可以使用 or (或),表示两个条件有一个成立时判断条件成功;使用 and (与)时,表示只有两个条件同时成立的情况下,判断条件才成功。
num = 9 if num >= 0 and num <= 10: # 判断值是否在0~10之间 print 'hello' >>> hello # 输出结果 num = 10 if num < 0 or num > 10: # 判断值是否在小于0或大于10 print 'hello' else: print 'undefine' >>> undefine # 输出结果 num = 8 # 判断值是否在0~5或者10~15之间 if (num >= 0 and num <= 5) or (num >= 10 and num <= 15): print 'hello' else: print 'undefine' >>> undefine # 输出结果
当if有多个条件时可使用括号来区分判断的先后顺序,括号中的判断优先执行,此外 and 和 or 的优先级低于>(大于)、<(小于)等判断符号,即大于和小于在没有括号的情况下会比与或要优先判断。
Python 循环语句
编程语言提供了各种控制结构,允许更复杂的执行路径。
循环语句允许我们执行一个语句或语句组多次,下面是在大多数编程语言中的循环语句的一般形式:
Python提供了for循环和while循环:
| 循环类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| while 循环 | 在给定的判断条件为 true 时执行循环体,否则退出循环体。 |
| for 循环 | 重复执行语句 |
| 嵌套循环 | 你可以在while循环体中嵌套for循环 |
循环控制语句
循环控制语句可以更改语句执行的顺序。Python支持以下循环控制语句:
| 控制语句 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| break 语句 | 在语句块执行过程中终止循环,并且跳出整个循环 |
| continue 语句 | 在语句块执行过程中终止当前循环,跳出该次循环,执行下一次循环。 |
| pass 语句 | pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性。 |
Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串,最重要的是python中可迭代对象。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s)
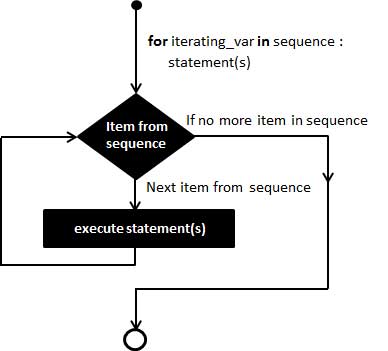
流程图:
for letter in 'Python': # 第一个实例 print '当前字母 :', letter fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango'] for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例 print '当前字母 :', fruit
Python While循环语句
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。其基本形式为:
while 判断条件: 执行语句……
执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当判断条件假false时,循环结束。
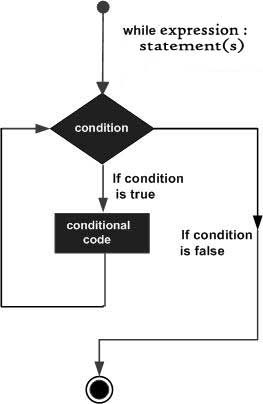
执行流程图如下:
实例:
count = 0 while (count < 9): print 'The count is:', count count = count + 1
while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环,continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外"判断条件"还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
# continue 和 break 用法 i = 1 while i < 10: i += 1 if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出 continue print i # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10 i = 1 while 1: # 循环条件为1必定成立 print i # 输出1~10 i += 1 if i > 10: # 当i大于10时跳出循环 break
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
count = 0 while count < 5: print count, " is less than 5" count = count + 1 else: print count, " is not less than 5" 以上实例输出结果为: 0 is less than 5 1 is less than 5 2 is less than 5 3 is less than 5 4 is less than 5 5 is not less than 5






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号