1. 线程异步
线程在创建的之后,一般都是独立自主,并发的,线程间会进行资源的竞争,那么就会引来一个问题,如果多个线程在同一时间对同一资源进行访问,修改,会造成资源破坏的结果,如下例子:
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> int g_num = 0; void *pth_fun1(void *arg) { while(1) { printf("%d\n", g_num++); } } void *pth_fun2(void *arg) { while(1) { printf("%d\n", g_num++); } } int main(void) { pthread_t pth1, pth2; int res = pthread_create(&pth1, NULL, pth_fun1, NULL); if (res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return 0; } res = pthread_create(&pth2, NULL, pth_fun2, NULL); if (res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return 0; } pthread_join(pth1, NULL); pthread_join(pth2, NULL); printf("hello world!\n"); return 0; }
运行结果如下:
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ gcc 1.c -o main -lpthread
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ clear
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ gcc 1.c -o main -lpthread
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
0
2
3
4
5
1
7
8
9
^C
这个例子中,两个线程分别打印一个全局变量并且加1,理想是从0开始,每次加1, 结果却事与愿违原因就在于异步带来的问题,所以我们希望当一个线程在操作某个可能被其他线程访问的资源时,只允许该线程操作,只有该线程结束操作资源时,其它线程才可以访问,这也就是线程同步
2. 线程同步
并发和异步带来了线程间资源的竞争的无序性, 因此需要同步机制来消除这种缺陷,实现线程正确有序共享数据,我们常用的方法就是锁,如互斥锁,读写锁和条件变量
3. 互斥锁
互斥锁可以保护多线程的共享资源,同一时刻只允许一个线程对临界区进行访问
互斥锁的使用流程如下:
1) . 初始化一个互斥锁
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *attr)
-
-
- mutex:一个互斥锁指针
- attr:设置该互斥锁的属性,通常用NULL
- 返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
-
2). 线程进入临界区前进行加锁
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
-
-
- mutex: 已初始化过的互斥锁
- 返回值: 成功:0, 失败:errno
-
3). 线程退出临界区前进行解锁
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
-
-
- mutex:已经上过锁的互斥锁
- 返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
-
4). 在最后不用互斥锁时销毁
int pthread_mutex_destory(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
-
-
- mutex:已经初始化过的互斥锁
- 返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> int g_a = 100; int g_b = 200; pthread_mutex_t mutex; void *pth_fun1(void *arg) { while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 上锁 g_a -= 5; g_b += 5; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 } } void *pth_fun2(void *arg) { while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 上锁 printf("sum = %d\n", g_a + g_b); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 解锁 sleep(1); } } int main(void) { // 初始化一个互斥锁 int res = pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); if (res) { printf("create mutex error!\n"); return 0; } // 创建线程 pthread_t pth1, pth2; res = pthread_create(&pth1, NULL, pth_fun1, NULL); if (res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return 0; } res = pthread_create(&pth2, NULL, pth_fun2, NULL); if (res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return 0; } pthread_join(pth1, NULL); pthread_join(pth2, NULL); // 销毁线程 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); printf("hello world!\n"); return 0; }
运行结果如下:
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ gcc 1.c -o main -lpthread
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
sum = 300
sum = 300
sum = 300
sum = 300
sum = 300
sum = 300
sum = 300
sum = 300
^C
kunmzhao@build-245:~$
4. 读写锁
从上面我们可以看出,互斥锁只有两种状态,一个是上锁了,另一个就是没上锁,我们现在假设有10个线程,都要在同一时间访问某一个变量,每个线程要占用资源1秒,那么第十个线程就要等待10秒,这在多线程中是很不友好的。其实对某一个资源而言,只是访问该资源,而不是修改的时候,多个线程同时访问是不会破坏该资源的,因此我们引入读写锁。
读写锁分为读锁和写锁,一个线程在读取资源的时候,我们上读锁,而另一个线程也来读取资源的时候,发现上了读锁,但是仍然可以进入临界区,访问该资源。线程需要修改资源的时候需要上写锁,一旦某个线程上了写锁,他就跟互斥锁一样了,只能等待该线程解锁,其他线程的读锁和写锁才能再次访问
读写锁的使用:
1). 初始化读写锁
int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *attr)
rwlock:一个读写锁
attr:设置读写锁参数,常为NULL
返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
2). 上读锁
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock)
rwlock:已经初始化的读写锁
返回值:成功0,失败:errno
3) 上写锁
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock)
rwlock:已经初始化的读写锁
返回值:成功0,失败:errno
4) 解锁
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock)
rwlock:已经上锁的读写锁
返回值:成功0,失败:errno
5)销毁读写锁
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t * rwlock)
rwlock:已经初始化的互斥锁
返回值:成功0,失败:errno
下面用一个demon来展示读写锁和互斥锁的运行速度比拼
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <sys/time.h> int g_a = 100; // 分别定义一个互斥锁和读写锁 pthread_mutex_t g_mutex; pthread_rwlock_t g_rwlock; // 线程1 void *pth_fun1(void *arg) { for(int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex); // 上锁 int temp = g_a; // 只读全局变量 pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex); // 解锁 } pthread_exit(0); } // 线程2 void *pth_fun2(void *arg) { for(int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex); // 上锁 int temp = g_a; // 只读全局变量 pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex); // 解锁 } pthread_exit(0); } // 线程3 void *pth_fun3(void *arg) { for(int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&g_rwlock); // 上锁 int temp = g_a; // 只读全局变量 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&g_rwlock); // 解锁 } pthread_exit(0); } // 线程4 void *pth_fun4(void *arg) { for(int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&g_rwlock); // 上锁 int temp = g_a; // 只读全局变量 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&g_rwlock); // 解锁 } pthread_exit(0); } // 互斥锁函数 void mutex_fun() { pthread_t pth1,pth2; struct timeval start, end; pthread_mutex_init(&g_mutex, NULL); // 初始化一个互斥锁 gettimeofday(&start, NULL); int res = pthread_create(&pth1, NULL, pth_fun1, NULL); if(res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return ; } res = pthread_create(&pth2, NULL, pth_fun2, NULL); if(res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return ; } pthread_join(pth1, NULL); pthread_join(pth2, NULL); gettimeofday(&end, NULL); long long total = (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) * 1000000 + (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec);// 微秒 long total_msec = total / 1000; // 毫秒 printf("mutex takes %ld msec\n", total_msec); pthread_mutex_destroy(&g_mutex); return; } // 读写锁函数 void rwlock_fun() { pthread_t pth1,pth2; struct timeval start, end; pthread_rwlock_init(&g_rwlock, NULL); gettimeofday(&start, NULL); int res = pthread_create(&pth1, NULL, pth_fun3, NULL); if(res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return ; } res = pthread_create(&pth2, NULL, pth_fun4, NULL); if(res) { printf("create pthread error!\n"); return ; } pthread_join(pth1, NULL); pthread_join(pth2, NULL); gettimeofday(&end, NULL); long long total = (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) * 1000000 + (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec);// 微秒 long total_msec = total / 1000; // 毫秒 printf("rwlock takes %ld msec\n", total_msec); pthread_rwlock_destroy(&g_rwlock); return; } int main(void) { mutex_fun(); rwlock_fun(); printf("hello world!\n"); return 0; }
运行结果如下:
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1608 msec
rwlock takes 2679 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1753 msec
rwlock takes 2039 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1433 msec
rwlock takes 2877 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1646 msec
rwlock takes 2275 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1607 msec
rwlock takes 2124 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1350 msec
rwlock takes 2001 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1591 msec
rwlock takes 2448 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$ ./main
mutex takes 1370 msec
rwlock takes 2973 msec
hello world!
kunmzhao@build-245:~$
5. 条件变量
当我们希望一个线程在某个条件下才能执行,比如一个缓存区,其中一个线程不断读取,一个不断写入,当缓存区满了,则写线程就应该暂停,同理,缓存区空了,读线程就应该停止,我们引入条件变量来同步线程
条件变量使用步骤:
1)初始化一个条件变量
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *attr)
cond:一个条件变量
attr:设置条件变量,常设置为NULL
返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
2) 等待条件变量
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t * cond, pthread_mutex_t * mutex)
cond:已初始化的条件变量
mutex:已上锁的互斥锁
返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
3) 唤醒等待变量
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond)
cond:已经初始化的条件变量
返回值:成功:0, 失败:errno
注意点:
1. 条件变量必须和互斥锁配合使用
2. pthread_cond_wait()调用的时候必须已经上锁,因为第二个形参就是该互斥锁,因为该函数会解锁,同时条件变量会作为阻塞,等待唤醒的到来,醒来后会再次加锁
3. pthread_cond_signal()调用的时候,最后后面就是要解锁
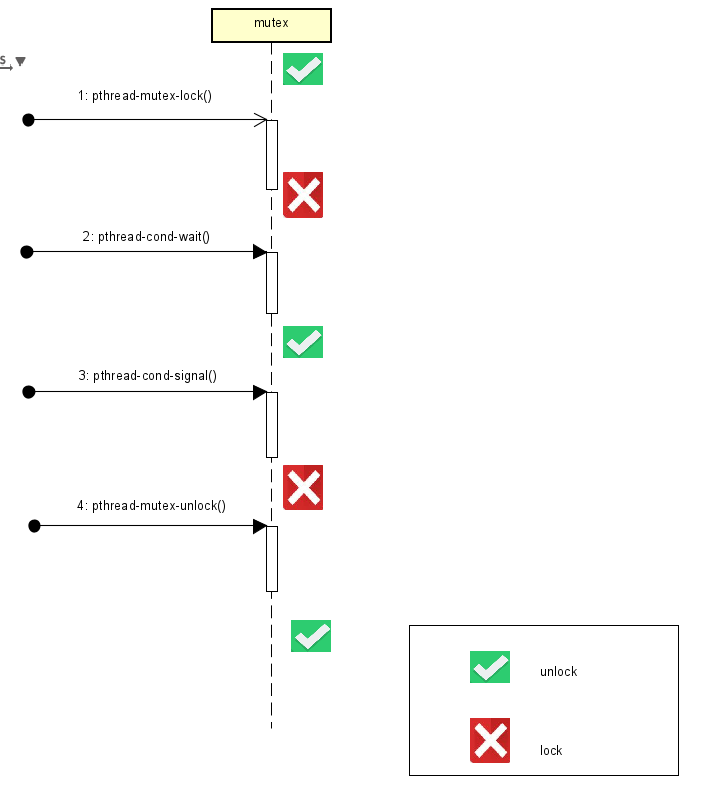
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> char g_buff[100] = {0}; int g_buff_size = 0; pthread_mutex_t g_mutex; pthread_cond_t g_cond; // put char in g_buff void *pth_put(void *arg) { for(int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { if (g_buff == NULL) return NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex); if (g_buff_size == 100) { printf("put:g_buff is full!\n"); pthread_cond_wait(&g_cond, &g_mutex); //printf("put :pthread received signal\n"); } g_buff[g_buff_size] = 'A'; g_buff_size++; if (g_buff_size == 1) { //printf("put:g_buff is not empty!\n"); pthread_cond_signal(&g_cond); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex); } } // get char from g_buff void *pth_get(void *arg) { for(int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { if(g_buff == NULL) return NULL; pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex); if(g_buff_size == 0) { printf("get:g_buff is empty!\n"); pthread_cond_wait(&g_cond, &g_mutex); //printf("get :pthread received signal\n"); } g_buff[g_buff_size - 1] = 0; g_buff_size--; if (g_buff_size == 00) { //printf("get:g_buff is not full!\n"); pthread_cond_signal(&g_cond); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex); } } int main(void) { pthread_t pth1, pth2; pthread_mutex_init(&g_mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&g_cond, NULL); pthread_create(&pth1, NULL, pth_get, NULL); pthread_create(&pth2, NULL, pth_put, NULL); pthread_join(pth1, NULL); pthread_join(pth2, NULL); pthread_mutex_destroy(&g_mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&g_cond); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { printf("%d ", g_buff[i]); } return 0; }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号