Codeforces Round #739 (Div. 3) 题解
文章目录
A. Dislike of Threes
-
题意
请你找到第 k k k个满足不能被 3 3 3整除且个位不为 3 3 3的数。 -
解题思路
预处理处前 1000 1000 1000个,直接输出即可。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:A_Dislike_of_Threes
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-18 22:35
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t,k;
int dp[N];
void init(){
int cnt = 1;
for(int i = 1;; ++ i){
if(i % 3 == 0 || i % 10 == 3)continue;
dp[cnt++] = i;
if(cnt == 1001)break;
}
}
void solve(){
cout << dp[k] << endl;
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
init();
while(t -- ){
cin >> k;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B. Who’s Opposite?
-
题意
给你一个环如图:
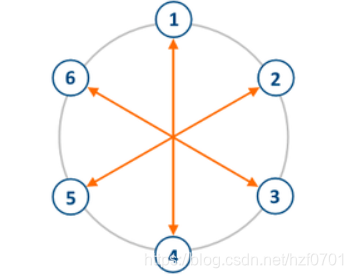
给出 a a a和其对应的 b b b。问 c c c对应的编号是哪个? -
解题思路
不难发现,圈的编号上限或者说圈的大小为 n = ∣ a − b ∣ × 2 n=|a-b|\times 2 n=∣a−b∣×2。通过这个我们就可以求得圈的大小,至此,如果要符合要求,说明 a ≤ n b ≤ n c ≤ n a\leq n \ b\leq n\ c\leq n a≤n b≤n c≤n,满足条件我们确定 d d d即可通过 ∣ c − d ∣ × 2 = n |c-d|\times 2=n ∣c−d∣×2=n来求解。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:B_Who_s_Opposite_
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-18 22:39
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t,a,b,c,d;
void solve(){
int n = (b - a) * 2;
if(n % 2 || a > n || b > n || c > n){
cout << - 1 << endl;
}
else{
n /= 2;
//abs(c - d) * 2 = n,
int d = c - n > 0 ? c - n : c + n;
cout << d << endl;
}
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if(a > b)swap(a,b);
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C. Infinity Table
-
题意
有这样一个数字矩阵,构造形式如图。问值为 k k k的数在第几行第几列。
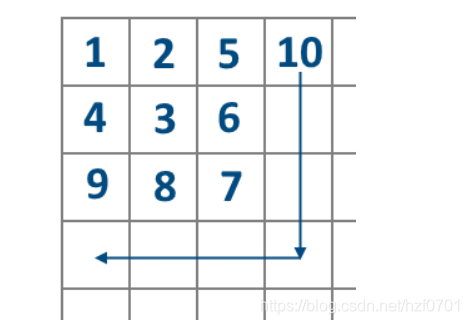
-
解题思路
规律题。我们可以将其以层数看待,第一层为 1 1 1,第二层为 2 , 3 , 4 2,3,4 2,3,4,第三层 … \dots …,我们发现,第 i i i层的数量为 2 × ( i − 1 ) + 1 2\times(i -1) +1 2×(i−1)+1。那么第 i i i层的坐标又有什么规律呢?我们发现在第 1 1 1到 i i i个数列坐标为 i i i,横坐标为其第几个数决定。那么在第 i + 1 i+1 i+1到第 2 × ( i − 1 ) + 1 2\times(i-1)+1 2×(i−1)+1个数,其横坐标为 i i i,列坐标则为 2 × i − k 2\times i - k 2×i−k。
至此,我们只要确定在第几层即可。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:C_Infinity_Table
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-18 22:56
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t,k;
void solve(){
int x = 1;
while(k > 2 * (x - 1) + 1){
k -= 2 * (x - 1) + 1;
x ++;
}
if(k <= x){
cout << k << " " << x << endl;
}
else{
cout << x << " " << 2 * x - k << endl;
}
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
cin >> k;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D. Make a Power of Two
-
题意
给你一个整数 n n n,每次你能进行一个操作,操作类型为:- 删除该整数的任意一位。
- 在末尾添加任意一位。
问凑成 2 2 2的次幂的最小操作次数是多少?
-
解题思路
由于 2 2 2次幂特别少,我们只需要预处理处 60 60 60以内次幂的数即可。然后我们考虑 n n n这个数变成这些需要多少操作次数,由于操作的限制性,针对单个 2 2 2次幂数,我们凑成它相当于在寻找最长公共字串,然后删除多余的部分再添上少去的部分即可。
根据以上分析,我们只需要遍历完所有的数然后取最小值即可,注意,这里用字符串处理更方便。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:D_new
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-19 00:03
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
string a[N];
int t,minn;
string n;
void init(){
//预处理处2的次幂。
ll temp = 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= 60; ++ i){
a[i] = to_string(temp);
temp *= 2;
}
}
void solve(){
int ans = INF;
for(int i = 0; i <= 60; ++ i){
int cnt = 0;
int l1 = 0,l2 = 0;
while(l1 < a[i].size() && l2 < n.size()){
if(a[i][l1] != n[l2]){
l2 ++;
cnt ++;
}
else{
l1 ++,l2 ++;
}
}
if(l1 != a[i].size()){
cnt += (a[i].size() - l1);
}
if(l2 != n.size()){
cnt += (n.size() - l2);
}
ans = min(ans,cnt);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
init();
while(t -- ){
cin >> n;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E. Polycarp and String Transformation
-
题意
给你一个字符串 s s s,构造一个字符串 t t t通过以下操作直到 s s s为空。- t = s + t t = s + t t=s+t。
- 选择一个字符 c c c,删除 s s s中的所有字符 c c c。
-
解题思路
不难发现,生成的字符串 t t t最后一个字符一定是最后删除的,同理,当我们从后往前遍历的时候,第一次遇到的字符则是当前被删除的字符,以至于后面的都没有出现过。所以我们可以通过这个确定删除字符的顺序列表。我们设 k k k是删除某个字母的步骤的编号, c k ck ck该字母在字符串s的初始值中出现的次数,那么这个字母在 t t t中恰好出现了 d k = k ∗ c k dk = k * ck dk=k∗ck,则可得 c k = d k / k ck = dk / k ck=dk/k。所以我们能得到每个字符在原字符串中出现的次数,从而得到总和,即原字符串的长度,那么对于 t t t中,如果存在答案,那么前缀则是字符串 s s s。
根据以上分析,我们可以确定 s s s和删除字符的顺序列表。那么我们还需要验证答案的合理性,所以我们需要模拟构造,判断是否可以得到字符串 t t t。
至此题解。 -
AC代码
/**
*@filename:E_Polycarp_and_String_Transformation
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-19 15:26
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<string,string> pss;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t;
string s;
int cnt[26];//统计字母出现次数。
pss work(string s){
string order = "";
//从后往前遍历,得到删除的逆顺序。
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
for(auto c : s){
if(!cnt[c - 'a']){
order += c;
}
cnt[c - 'a'] ++;
}
int len = 0,n = order.size();//为原来的字符串长度。
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i){
//依次出现了m - i次。
len += cnt[order[i] - 'a'] / (n - i);
}
reverse(order.begin(),order.end());//将顺序回正。
//由于这里我们发转了,所以我们需要从后取到前。
return {string(s.rbegin(),s.rbegin() + len), order};
}
bool check(pss ans){
string result = ans.first;
for(auto c : ans.second){
string temp ;
//将c删除。
for(auto d : ans.first){
if(d != c){
temp += d;
}
}
result += temp;
ans.first = temp;
}
return s == result;
}
void solve(){
pss ans = work(s);
//验证正确性。
if(check(ans)){
cout << ans.first << " " << ans.second << endl;
}
else{
cout << -1 << endl;
}
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
cin >> s;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
F1,F2. Nearest Beautiful Number
-
题意
给你一个整数 n n n,你需要找到一个最小的整数 x x x,使得 x ≥ n x\geq n x≥n且 x x x是 k k k漂亮的。如果 x x x是 k k k漂亮的说明 x x x中出现的不同数字不超过 k k k个。 -
解题思路
- 针对easy版本,我们很好处理,先构造出 1 1 1漂亮的最小整数,然后单独的针对 k = 2 k=2 k=2,我们可以暴力枚举出现的两个整数 a , b a,b a,b,然后贪心的修改,获取得到的最小值,此贪心修改的意思是根据高位到地位决定的,即如果出现了大于,说明已经符合了,这个时候低位就要尽量填最小的即可。
- 针对hard版本,我们按easy处理肯定不行。但我们肯定还是按照贪心的原则,但这次我们可以直接在
n
n
n上做修改,找到不包含
k
k
k个不同数字
n
n
n的最大前缀,当超过了的时候,我们就需要进行修改,即从不合法位置开始增加
1
1
1,然后让后面的位置全变为
0
0
0,这样是有效的,因为不合法位置终将要被处理,这即是我们贪心的选择。注意,这增加
1
1
1的过程中可能会产生进位,所以这里需要特殊处理。
作为维护处理不同数字的数量,我们采用set来进行维护。
-
F1AC代码
/**
*@filename:F1_Nearest_Beautiful_Number_easy_version_
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-19 00:58
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t,k;
string s1;
void solve(){
//先构造1beautiful的。
string s2(s1.size(),s1[0]);
if(s2 < s1){
s2 = string(s1.size(),s1[0] + 1);
}
//判断是否为2beautiful。
if(k == 2){
//枚举两个数构造。
for(char a = '0'; a <= '9'; ++ a){
for(char b = '0'; b <= '9'; ++ b){
bool flag = true;//判断是否构造成功。
for(int i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++ i){
if(s1[i] < b){
//小于最大值了。此时可以构造。
string temp = s1;
//构造一位大于的,其余全填最小的a。
if(temp[i] < a)temp[i] = a;
else temp[i] = b;
for(int j = i + 1; j < s1.size(); ++ j){
temp[j] = a;
}
//更新最小值。
if(temp < s2){
s2 = temp;
}
}
if(s1[i] != a && s1[i] != b){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
//这个说明s1就全由a,b这个组成的
cout << s1 << endl;
return;
}
}
}
}
cout << s2 << endl;
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
cin >> s1 >> k;
solve();
}
return 0;
}
- F2AC代码
/**
*@filename:F2_Nearest_Beautiful_Number_hard_version
*@author: pursuit
*@created: 2021-08-19 14:24
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(a) cout << "debug : " << (#a)<< " = " << a << endl
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int P = 1e9 + 7;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int t,k;
string s1;
void solve(){
while(true){
set<char> s;//检索当前构造的数有多少个不同的数。
for(int i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++ i)s.insert(s1[i]);
if(s.size() <= k){
//符合题目要求。
cout << s1 << endl;
break;
}
s.clear();
int idx = 0;
while(true){
//构造。
s.insert(s1[idx]);
if(s.size() > k){
//说明这里出现了分歧错误。我们需要提高这里的值。
while(s1[idx] == '9'){
//这里进位相当于是进位了,我们找到最开始进位的那个即可。
idx --;
}
s1[idx] ++;//增加一位再判断。
for(int i = idx + 1; i < s1.size(); ++ i){
s1[i] = '0';
}
break;
}
idx ++;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> t;
while(t -- ){
cin >> s1 >> k;
solve();
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号