第三周作业:卷积神经网络
net = torch.nn.Sequential( Reshape(), nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(84, 10)) #对网络进行测试 X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32) for layer in net: X = layer(X) print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape: \t',X.shape)
一:深度学习计算:
1.参数访问:net[ ].state_dict( )
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,8), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(8, 1)) print(net[2].state_dict())
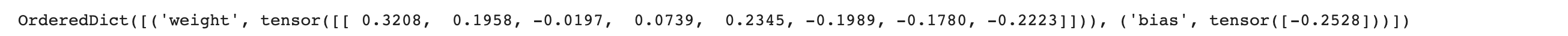
2.一次性访问所有参数: named_parameters()
print(*[(name, param.shape) for name, param in net[0].named_parameters()]) print(*[(name, param.shape) for name, param in net.named_parameters()])

3.内置初始化:
def init_normal(m): if type(m) == nn.Linear: #生成一个均值为0方差为1的权重 nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0, std=0.01) nn.init.zeros_(m.bias) net.apply(init_normal) net[0].weight.data[0], net[0].bias.data[0]
使用apply函数给net所有Linear层初始化
4.读写文件
存储张量:
#存储张量 x = torch.arange(4) torch.save(x, 'x-file' #读回内存 x2 = torch.load('x-file') x2
加载和保存模型参数:
class MLP(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.hidden = nn.Linear(20, 256) self.output = nn.Linear(256, 10) def forward(self, x): return self.output(F.relu(self.hidden(x))) net = MLP() X = torch.randn(size=(2, 20)) Y = net(X) #将模型保存到mlp.params文件夹中 torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'mlp.params') #模型恢复 clone = MLP() clone.load_state_dict(torch.load('mlp.params')) clone.eval()
二:卷积神经网络:
1.两个特性:
平移不变性:不管检测对象出现在图像中的哪个位置,神经网络的前面几层应该对相同的图像区域具有相似的反应
局部性(locality):神经网络的前面几层应该只探索输入图像中的局部区域,而不过度在意图像中相隔较远区域的关系。
2.目标边缘检测:
(1)构造一个6*8像素的黑白图像,中间为黑(0),其余为白(1)
X = torch.ones((6, 8)) X[:, 2:6] = 0
(2)构造一个卷积核,计算结果为相邻元素相同输出为0,否则为非0,然后计算。
#卷积核K K=torch.tensor([[1.0],[-1.0]]) Y=corr2d(X,K) Y

但这种方法只能检测垂直边缘,无法检测水平边缘。
# 构造一个二维卷积层,它具有1个输出通道和形状为(1,2)的卷积核 conv2d = nn.Conv2d(1,1, kernel_size=(1, 2), bias=False) X = X.reshape((1, 1, 6, 8)) Y = Y.reshape((1, 1, 6, 7)) for i in range(10): Y_hat = conv2d(X) l = (Y_hat - Y) ** 2 conv2d.zero_grad() l.sum().backward() conv2d.weight.data[:] -= 3e-2 * conv2d.weight.grad if (i + 1) % 2 == 0: print(f'batch {i+1}, loss {l.sum():.3f}') conv2d.weight.data.reshape((1, 2))

10轮迭代后,结果很接近我们预估的值。
3.填充和步幅
填充:如果我们添加 Ph行填充和 Pw 列填充,则输出形状将为:
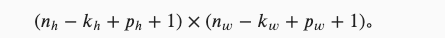
填充的具体操作可以在nn.Conv2d中添加padding
步幅:当垂直步幅为 Sh 、水平步幅为 Sw时,输出形状为:
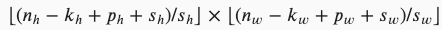
填充的具体操作可以在nn.Conv2d中添加stride
总结:
填充可以增加输出的高度和宽度。这常用来使输出与输入具有相同的高和宽。
步幅可以减小输出的高和宽,例如输出的高和宽仅为输入的高和宽的 1/𝑛1/n( 𝑛n 是一个大于 11 的整数)。
填充和步幅可用于有效地调整数据的维度。
4.多输入输出通道:
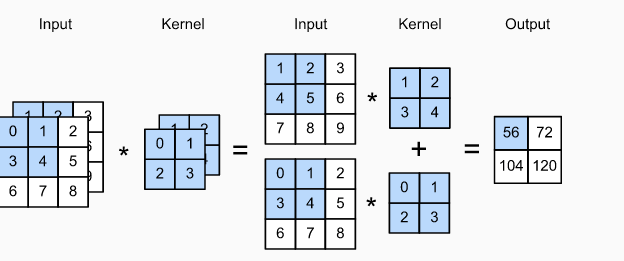
(1)多输入通道:
想关计算:
(2)多输出通道:
我们可以将每个通道看作是对不同特征的响应,因为每个通道不是独立学习的,而是为了共同使用而优化的。因此,多输出通道并不仅是学习多个单通道的检测器。
(3)1*1卷积:
可以改变通道数,可以加入非线形。
5.池化层:
(1).常用的方法有两种:最大值池化和平均值池化
(2)可以对池化层的步幅和填充进行调整:
#参数分别是池化窗口大小,填充大小和步幅大小 pool2d = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 3), padding=(1, 1), stride=(2, 3)) pool2d(X)
(3)在处理多通道输入数据时,池化层对每个通道进行单独运算,并非像卷积层一样在通道上对输入进行汇总,即:池化层的输出通道数和输入通道数相同。
6.LeNet:
(1).大体结构:
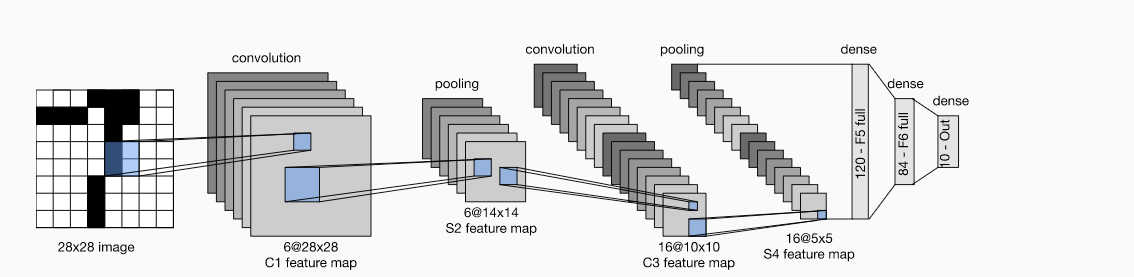
(2)模型实现:
定义网络:
class Reshape(torch.nn.Module): def forward(self, x): return x.view(-1, 1, 28, 28) net = torch.nn.Sequential( Reshape(), nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(), nn.Linear(84, 10))
对网络进行测试:
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32) for layer in net: X = layer(X) print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape: \t',X.shape)

使用Fashion-MNIST数据集进行训练:
batch_size = 256 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size=batch_size) def evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, data_iter, device=None): #@save if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module): net.eval() if not device: device = next(iter(net.parameters())).device # 正确预测的数量,总预测的数量 metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) for X, y in data_iter: if isinstance(X, list): X = [x.to(device) for x in X] else: X = X.to(device) y = y.to(device) metric.add(d2l.accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel()) return metric[0] / metric[1]
#@save def train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, device): def init_weights(m): if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d: nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight) net.apply(init_weights) print('training on', device) net.to(device) optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc']) timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter) for epoch in range(num_epochs): metric = d2l.Accumulator(3) net.train() for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter): timer.start() optimizer.zero_grad() X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device) y_hat = net(X) l = loss(y_hat, y) l.backward() optimizer.step() with torch.no_grad(): metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0]) timer.stop() train_l = metric[0] / metric[2] train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2] if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1: animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches, (train_l, train_acc, None)) test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter) animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc)) print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, ' f'test acc {test_acc:.3f}') print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec ' f'on {str(device)}')
lr, num_epochs = 0.9, 10
train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())
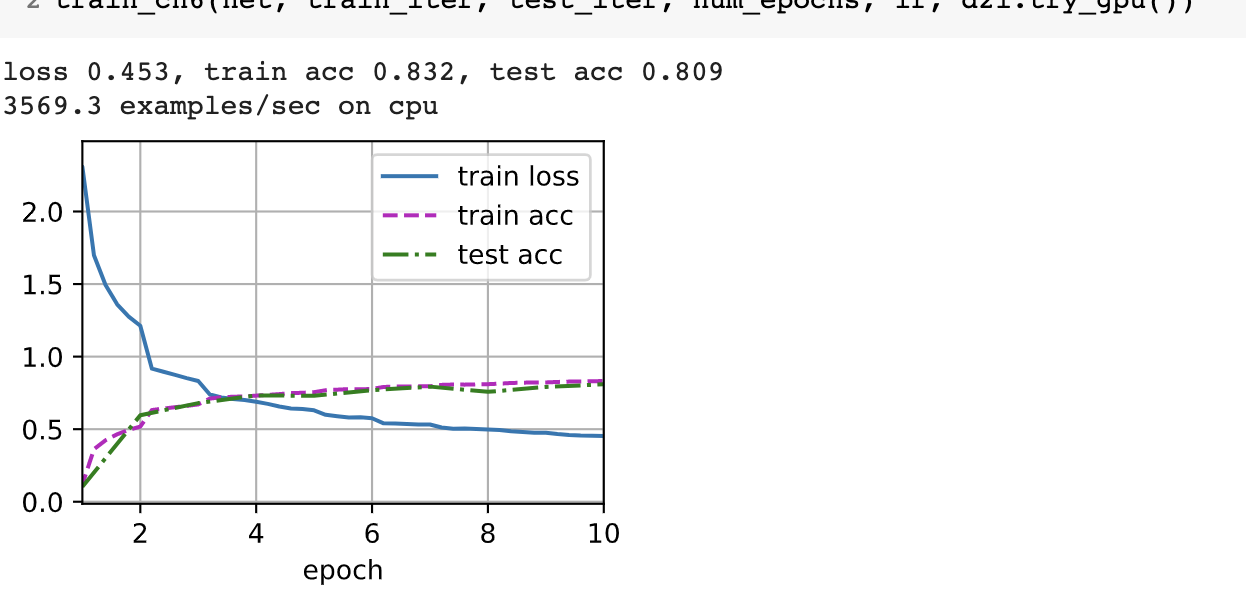
训练结果还可以
三.猫狗大战:
1.导入数据:
!wget http://fenggao-image.stor.sinaapp.com/dogscats.zip !unzip dogscats.zip !wget https://static.leiphone.com/cat_dog.rar !unrar x /content/cat_dog.rar
2.定义网络:
import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5) self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(44944, 120) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 2) def forward(self, x): x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x))) x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x))) x = x.view(-1, 44944) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) x = self.fc3(x) return x # 网络放到GPU上 net = Net().to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.001)
3.训练:
for epoch in range(10): # 重复多轮训练 for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(loader_train): inputs = inputs.to(device) labels = labels.to(device) # 优化器梯度归零 optimizer.zero_grad() # 正向传播 + 反向传播 + 优化 outputs = net(inputs) loss = criterion(outputs, labels) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # 输出统计信息 if i % 100 == 0: print('Epoch: %d Minibatch: %5d loss: %.3f' %(epoch + 1, i + 1, loss.item())) print('Finished Training')

4.在比赛用的测试集上进行测试:
loader_test = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dsets, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=0) def test(model,dataloader,size): model.eval() cnt = 0 #count for inputs,_ in dataloader: if cnt < size: inputs = inputs.to(device) outputs = model(inputs) _,preds = torch.max(outputs.data,1) key = dsets.imgs[cnt][0].split("/")[-1].split('.')[0] final[key] = preds[0] cnt += 1 else: break; print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%' % ( 100 * correct / total)) test(net,loader_test,size=2000)
5.保存数据:
with open("/content/test.csv",'a+') as f: for key in range(2000): f.write("{},{}\n".format(key,final[str(key)]))
6.上交结果:


训练了两次,结果相差不多,但都并非很理想。
复习使用了VGGNET进行了一次训练:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号