2025-2026-1 20231301 《信息安全设计》第十周学习总结
2025-2026-1 20231301 《信息安全设计》第十周学习总结
作业信息
| 作业 | 链接 |
|---|---|
| 作业课程 | <班级>(2025-2026-1 信息安全设计) |
| 作业要求 | <作业>(2025-2026-1 信息安全设计 预习作业要求) |
| 作业目标 | 《Head First C 嗨翻C语⾔》> 预习第十章 |
| 作业正文 | <博客>(第十周学习总结) |
学习内容总结
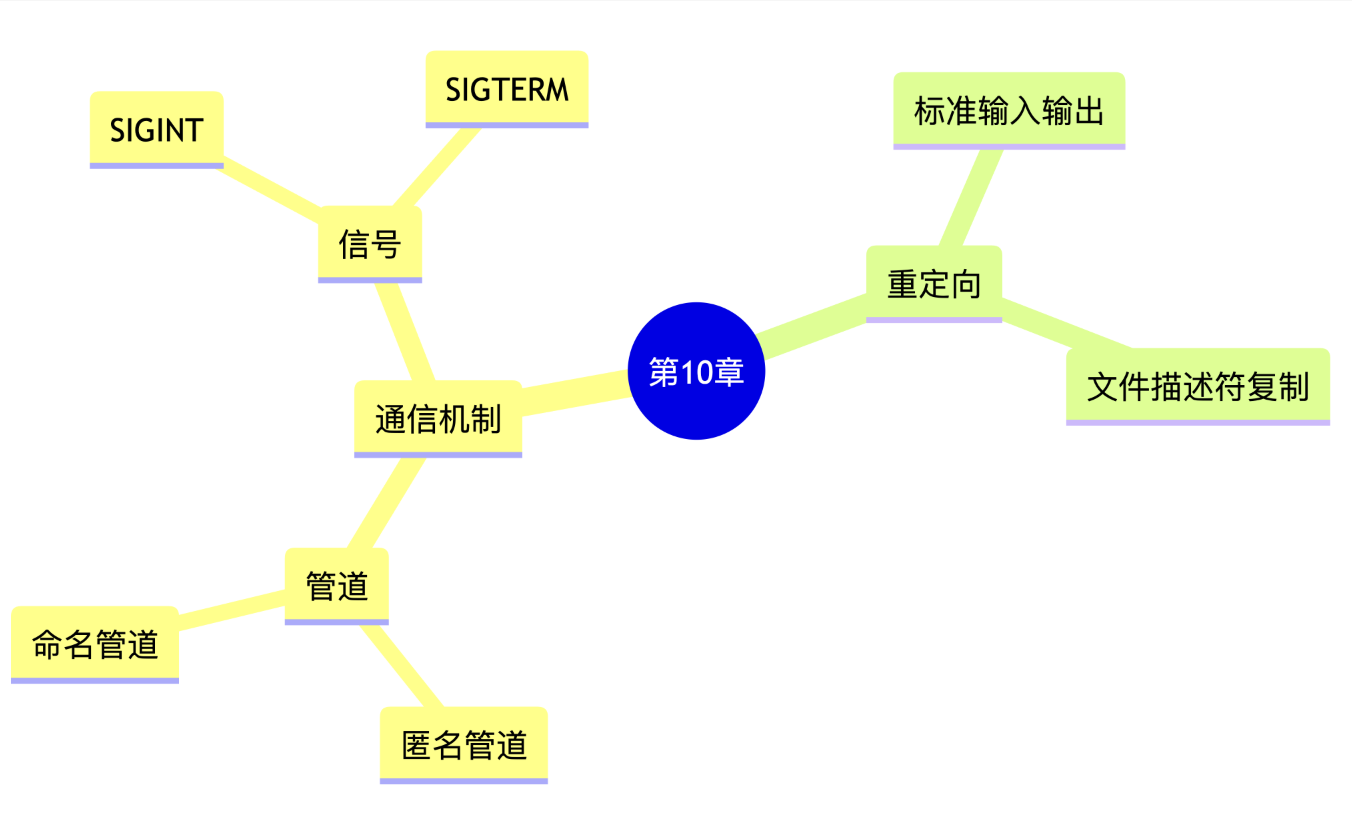
第十章:进程间通信
IPC 机制全面解析
1. 文件描述符深入理解
文件描述符表结构:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void demonstrate_fd_table() {
printf("Standard file descriptors:\n");
printf("STDIN_FILENO = %d\n", STDIN_FILENO); // 0
printf("STDOUT_FILENO = %d\n", STDOUT_FILENO); // 1
printf("STDERR_FILENO = %d\n", STDERR_FILENO); // 2
// 打开新文件会使用最低可用的描述符
FILE* file = fopen("test.txt", "w");
if (file) {
printf("New file descriptor: %d\n", fileno(file));
fclose(file);
}
}
2. 管道通信完整示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <string.h>
void pipe_communication_example() {
int pipefd[2];
pid_t pid;
char buffer[256];
// 创建管道
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) {
perror("pipe");
return;
}
pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
perror("fork");
return;
}
if (pid == 0) {
// 子进程 - 写入端
close(pipefd[0]); // 关闭读取端
const char* message = "Hello from child process!";
write(pipefd[1], message, strlen(message) + 1);
close(pipefd[1]);
_exit(0);
} else {
// 父进程 - 读取端
close(pipefd[1]); // 关闭写入端
ssize_t count = read(pipefd[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (count > 0) {
printf("Parent received: %s\n", buffer);
}
close(pipefd[0]);
wait(NULL); // 等待子进程
}
}
3. 信号处理高级应用
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
volatile sig_atomic_t shutdown_requested = 0;
void graceful_shutdown(int sig) {
shutdown_requested = 1;
printf("\nReceived signal %d - Shutting down gracefully...\n", sig);
}
void setup_signal_handlers() {
struct sigaction action;
// 设置 SIGINT (Ctrl+C) 处理器
action.sa_handler = graceful_shutdown;
sigemptyset(&action.sa_mask);
action.sa_flags = 0;
if (sigaction(SIGINT, &action, NULL) == -1) {
perror("sigaction");
exit(1);
}
// 忽略 SIGPIPE (避免写入已关闭的管道时程序退出)
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
}
void signal_demo() {
setup_signal_handlers();
printf("Program running. Press Ctrl+C to test signal handling.\n");
while (!shutdown_requested) {
printf("Working...\n");
sleep(2);
}
printf("Cleanup completed. Exiting.\n");
}
高级 IPC 模式
双向进程通信
void bidirectional_pipe_communication() {
int parent_to_child[2], child_to_parent[2];
pid_t pid;
char buffer[256];
// 创建两个管道
if (pipe(parent_to_child) == -1 || pipe(child_to_parent) == -1) {
perror("pipe");
return;
}
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
// 子进程
close(parent_to_child[1]); // 关闭父→子的写入端
close(child_to_parent[0]); // 关闭子→父的读取端
// 从父进程读取
ssize_t count = read(parent_to_child[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (count > 0) {
printf("Child received: %s", buffer);
// 回复父进程
const char* reply = "Message received by child\n";
write(child_to_parent[1], reply, strlen(reply));
}
close(parent_to_child[0]);
close(child_to_parent[1]);
_exit(0);
} else {
// 父进程
close(parent_to_child[0]); // 关闭父→子的读取端
close(child_to_parent[1]); // 关闭子→父的写入端
// 向子进程发送消息
const char* message = "Hello child process!\n";
write(parent_to_child[1], message, strlen(message));
// 等待子进程回复
ssize_t count = read(child_to_parent[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (count > 0) {
printf("Parent received reply: %s", buffer);
}
close(parent_to_child[1]);
close(child_to_parent[0]);
wait(NULL);
}
}
思维导图
posted on 2025-09-30 21:59 20231301周子昂 阅读(9) 评论(0) 收藏 举报

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号