5.1 activity的跳转 service
活动代表了一个具有用户界面的单一屏幕,如 Java 的窗口或者帧。
Android 的活动是 ContextThemeWrapper 类的子类。
如果你曾经用 C,C++ 或者 Java 语言编程,你应该知道这些程序从 main() 函数开始。很类似的,Android 系统初始化它的程序是通过活动中的 onCreate() 回调的调用开始的。存在有一序列的回调方法来启动一个活动,同时有一序列的方法来关闭活动。
两界面跳转的例子:
文件结构如下:
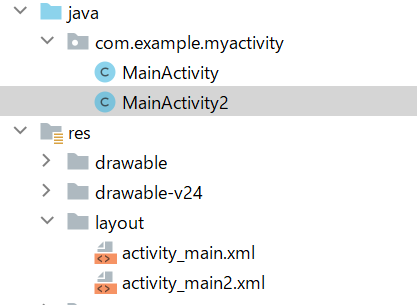
从activity_main.xml通过点击Button跳转到activity_main2.xml页面
具体的跳转逻辑和页面渲染由各自的java代码负责
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn1" android:onClick="toOtherPage" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="跳转到另一个activity" /> </LinearLayout>
activity_main2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity2"> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:text="成功跳转过来了"/> </LinearLayout>
MainActivity.class
package com.example.myactivity; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } public void toOtherPage(View view) { Button button = findViewById(R.id.btn1); button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { startActivity(new Intent(MainActivity.this,MainActivity2.class)); } }); } }
MainActivity2.class
package com.example.myactivity; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; public class MainActivity2 extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2); } }
认识service
服务在后台默默的运行,是不可见的
执行长时间运行且不需要用户交互的任务,比如退回主界面音乐播放器依然在唱歌。
但是service依赖于创建service时所在的应用程序进程,当某个应用进程被杀掉时,所有依赖于该进程的service也会停止运行。
一个普通的类继承了Service就变成了服务
小例子
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/startService_btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="startServiceClick"
android:text="开启服务"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/endService_btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="stopServiceClick"
android:text="停止服务"/>
</LinearLayout>
FirstService.class
package com.example.myservice.services;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class FirstService extends Service {
public final String TAG = this.getClass().getName();
public FirstService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d(TAG,"onCreate创建.......");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d(TAG,"onDestroy销毁.......");
}
}
别忘了去AndroidManifest.xml里去注册
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.myactivity"> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/Theme.MyActivity"> <!-- 默认activity --> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:exported="true"> <!-- 激活默认的activity --> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <!--注册一下Service--> <service android:name=".MyService"/> </application> </manifest>
MainActivity.class
package com.example.myservice;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import com.example.myservice.services.FirstService;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
//开启服务
public void startServiceClick(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(this,FirstService.class);
startService(intent);
}
//停止服务
public void stopServiceClick(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(this,FirstService.class);
stopService(intent);
}
}






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号