Matlab pulstran关于高斯脉冲的学习
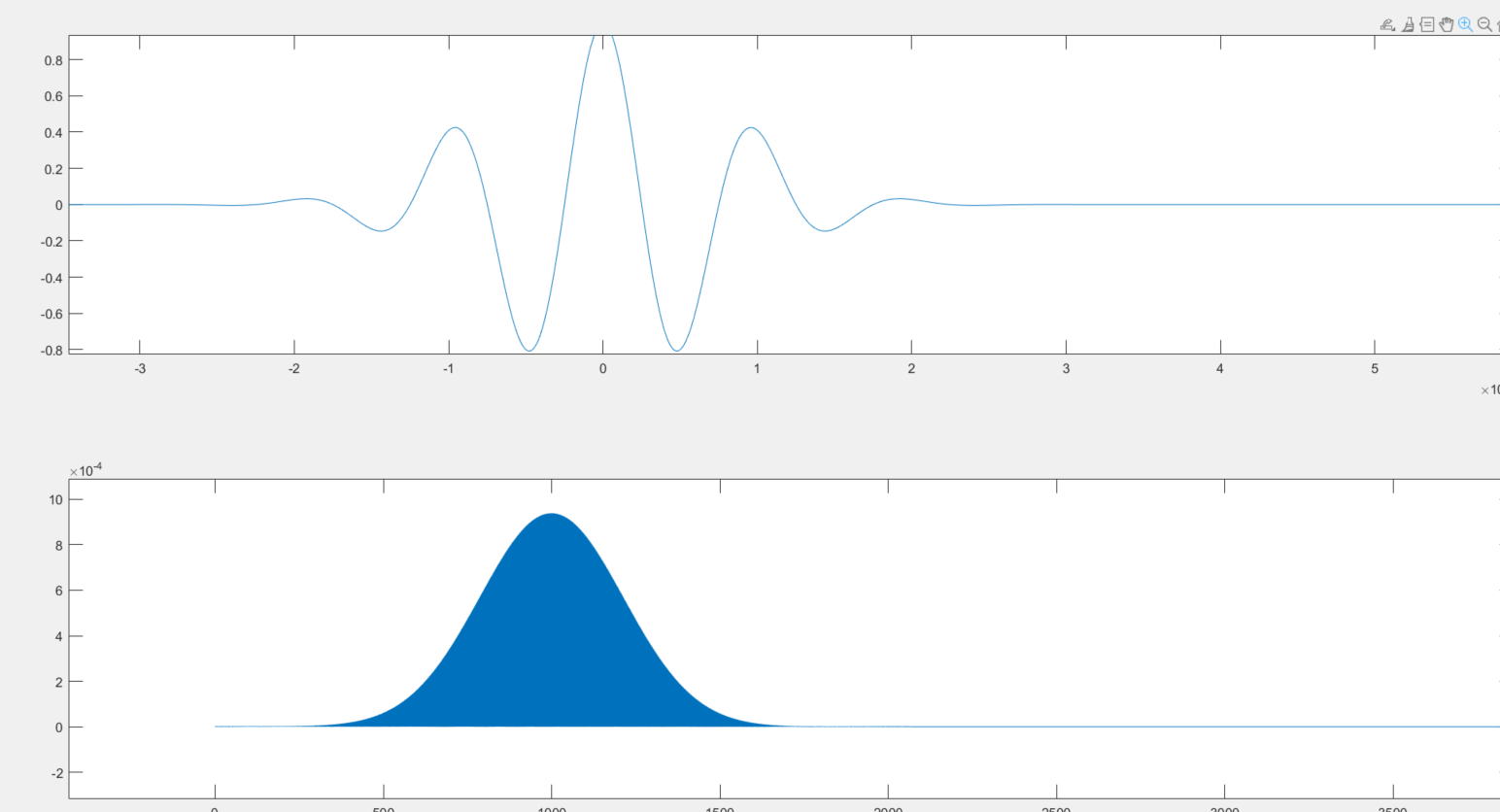
高斯脉冲的频带越小,说明带宽越小(在频域观察,而不是时域)在用matlab中调用pulstran时,如果采用gausplus,那么带宽w代表高斯脉冲频率为中心频率的的两倍
clear
close all
clc
fs = 100e3; % sample freq
T = 10;
t = linspace(-1*T,T,2*fs*T); % signal evaluation time
D1 = linspace(-1*T,T,11); % 脉冲产生的位置
D2 = sin(D1); %赋值的变化向量
D=[D1;D2]'; %将位置和振幅向量合并为一个2维向量
w =0.5; % 脉冲宽度 %当冲击为gauspuls时,脉冲宽度代表了频域中心频率的宽度
gaus_f= 1e3;
% yp = pulstran(t,D,@rectpuls,w); %@rectpuls 方波;tripulse 三角波,
yp = pulstran(t,D1,@gauspuls,gaus_f,w); %@gauspuls
% yp = gauspuls(t,1e3,1);
% 高斯,当冲击为gauspuls时候,必须设定gauspuls的频率
[f,yp_fft]=gfun_2fft(fs,yp);
subplot(211)
plot(t,yp)
subplot(212)
plot(f,yp_fft)
如果gausplus 为1khz,w=0.5则带宽为以1000hz为中心的2khz带宽




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号