T-SQL Logical Query Processing In Brief
Most of us use T-SQL every day, but how does it run step by step? This article will introduces the phase involved in logical processing of query. I will briefly describe each step.
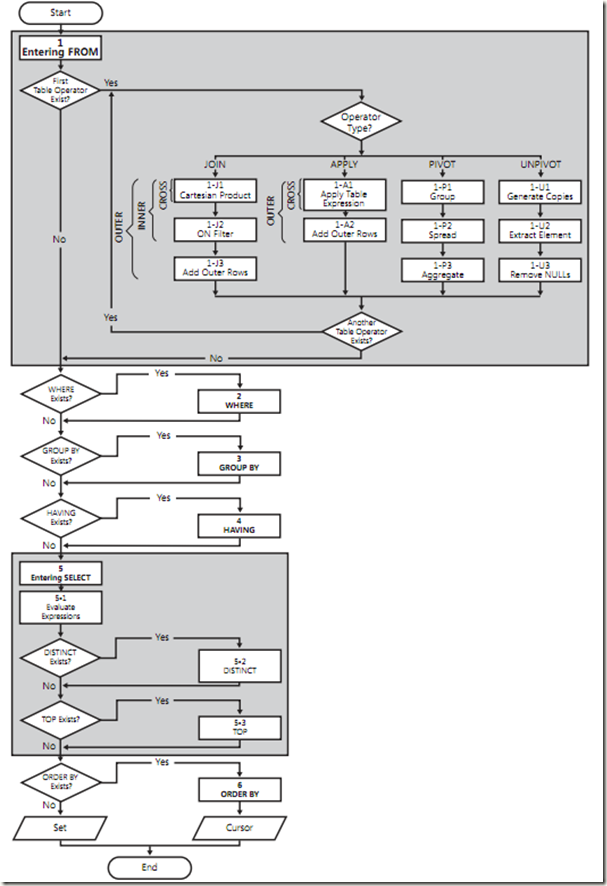
- (1) From The From phase identifieds the query’s source tables and process table operators.
- (1-J1) Cartesian Product This phase performs a Cartesian Product(cross join) between the two tables involved in the table operator, generating VT1-J1.
- (1-J2) On Filter This phase filters the rows from VT1-J1. Only rows for which the predicate evaluates to True are inserted into VT1-J2.
- (1-J3) Add Outer Rows If Outer Join is specified, rows from preserved tables for which a match are not found are added, generating VT1-J3.
- (2) Where This phase filters the rows from VT1 based on the predicated that appears in the Where clause, generating VT2.
- (3) Group By This phase arranges the rows from VT2 in groups based on the columns list specified in the Group By clause, generating VT3. Ultimately, there will be one result row per group.
- (4) Having This phase filters the groups from VT3 based on the predicated that appears in Having clause, generating VT4.
- (5) Select This phase processes the elements in the Select clause, generating VT5
- (5-1) Evaluate Expressions This phase evaluate the expressions in the Select list,generating VT5-1.
- (5-2) Distinct This phase removes the duplicate rows from VT5-1, generating VT5-2.
- (5-3) Top This phase filters the specified top number or percentage of rows from VT5-2 based on the logical ordering defined by the Order By clause,generating VT5-3
- (6) Order By This phase sorts the rows from VT5-3 according to the columns list specified in the Order By clause, generating the cursor VC6. (The Order By clause is the only step where columns alias create in the Select clause can be used.)
Important:
Because this step does return a table(it return a cursor), a query with the presentation Order By clause can’t be used to define a table expression. For example, the queries bellow are invalid and will produces an error:
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Select *
From (Select OrderID, CustomerID From dbo.Orders Order By OrderID Desc) as D
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Create View V_SortedOrder
As
Select OrderID, CustomerID From dbo.Orders Order By OrderID Desc
-----------------------------------------------------------------
However, if a Top query with an Order By clause is used to defined a table expression, is supposed to represent a table with no guaranteed order.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Select *
From (Select Top 3 OrderID, CustomerID From dbo.Orders Order By OrderID Desc) as D
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Conclusion:
This article describes the basic knowledge of Transact-SQL, may be is looks easy, but understanding logical query processing phase and the unique aspects of SQL is important to get into the special mind set required to grogram in SQL. By being familiar with those aspects of language, you can produce efficient solutions and explain your choice. The idea is to master the basics.
Hope it can help you.
Reference:
Inside Microsoft SQL Server 2008 T-SQL Querying (Itzik Ben-Gan)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号