PTA题集05-09电梯调度程序分析总结
📌目录
-一、前言
PTA-05
PTA-06
PTA-07
-二、设计与分析
PTA-05分析
PTA-06分析
PTA-07分析
-三、采坑心得
-四、改进建议
-五、总结
🕐一.前言
这三次电梯调度程序很有难度,但是随着每次迭代,从一开始的束手无策到后来的逐渐熟悉,这也是一个很宝贵的学习与进步的过程。通过这三次作业的调度程序能学到很多知
识,慢慢熟悉如何运用arraylist和linkedlist,学会通过测试样例锁定问题和归纳框架。在每次迭代的时候,要求有变时,都能发现虽然看上去要求的改变不大,但实际上对
核心处理逻辑,比如判断下一个请求和判断方向的改变是很大的,需要深度思考和不断测试,不断的去归纳完善整个处理框架,总结出一个通式。
大致预览三次迭代
🟡PTA-05
1.题述要求
设计一个电梯类,具体包含电梯的最大楼层数、最小楼层数(默认为1层)当前楼层、运行方向、运行状态,以及电梯内部乘客的请求队列和电梯外部楼层乘客的请求队列。其中,电梯外部请求队列需要区分上行和下行。电梯运行规则如下:电梯默认停留在1层,状态为静止,当有乘客对电梯发起请求时(各楼层电梯外部乘客按下上行或者下行按钮或者电梯内部乘客按下想要到达的楼层数字按钮),电梯开始移动,当电梯向某个方向移动时,优先处理同方向的请求,当同方向的请求均被处理完毕然后再处理相反方向的请求。电梯运行过程中的状态包括停止、移动中、开门、关门等状态。当电梯停止时,如果有新的请求,就根据请求的方向或位置决定移动方向。电梯在运行到某一楼层时,检查当前是否有请求(访问电梯内请求队列和电梯外请求队列),然后据此决定移动方向。每次移动一个楼层,检查是否有需要停靠的请求,如果有,则开门,处理该楼层的请求,然后关门继续移动。使用键盘模拟输入乘客的请求,此时要注意处理无效请求情况,例如无效楼层请求,比如超过大楼的最高或最低楼层。还需要考虑电梯的空闲状态,当没有请求时,电梯停留在当前楼层。请编写一个Java程序,设计一个电梯类,包含状态管理、请求队列管理以及调度算法。并使用一些测试用例,模拟不同的请求顺序,观察电梯的行为是否符合预期,比如是否优先处理同方向的请求,是否在移动过程中处理顺路的请求等。为了降低编程难度,不考虑同时有多个乘客请求同时发生的情况,即采用串行处理乘客的请求方式(电梯只按照规则响应请求队列中当前的乘客请求,响应结束后再响应下一个请求),具体运行规则详见输入输出样例。
输入格式:
第一行输入最小电梯楼层数。
第二行输入最大电梯楼层数。
从第三行开始每行输入代表一个乘客请求。
电梯内乘客请求格式:<楼层数>
电梯外乘客请求格式:<乘客所在楼层数,乘梯方向>,其中,乘梯方向用UP代表上行,用DOWN代表下行(UP、DOWN必须大写)。
当输入“end”时代表输入结束(end不区分大小写)。
输出格式:
模拟电梯的运行过程,输出方式如下:
运行到某一楼层(不需要停留开门),输出一行文本:
Current Floor: 楼层数 Direction: 方向
运行到某一楼层(需要停留开门)输出两行文本:
Open Door # Floor 楼层数
Close Door
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
20
<3,UP>
<5>
<6,DOWN>
<7>
<3>
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Current Floor: 1 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 2 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 3 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
Current Floor: 4 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 5 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 7 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 7
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 6
Close Door
Current Floor: 5 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 4 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 3 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
//这里结束
2.注解
-没有UML图限制类名和方向枚举,但是还是采用了枚举变量增强代码的可阅读性,方便后面修改拓展
p.s.需要注意的是,由于第一次调度没有UML的要求,这里存储队列数据用的是自定义链 表,没有用arraylist/linkedlist
-类及枚举功能如下:
(1). 枚举类型 Direction:定义了电梯的运行方向,包括上行(UP)、下行(DOWN)和空闲(IDLE)。
(2). 内部请求类 InternalRequest:表示电梯内部的请求,包含目标楼层和指向下一个请求的指针。
(3). 外部请求类 ExternalRequest:表示电梯外部的请求,包含起始楼层、方向和指向下一个请求的指针。
(4). 电梯类(核心类) Elevator:管理电梯的当前状态、请求队列以及处理逻辑。
(5). 主类 Main:处理输入并启动电梯调度。
🟡PTA-06
1.题述要求
对之前电梯调度程序进行迭代性设计,目的为解决电梯类职责过多的问题,类设计要求遵循单一职责原则(SRP),要求必须包含但不限于设计电梯类、乘客请求类、队列类以及控制类,具体设计可参考如下类图。电梯运行规则与前阶段单类设计相同,但要处理如下情况:乘客请求楼层数有误,具体为高于最高楼层数或低于最低楼层数,处理方法:程序自动忽略此类输入,继续执行乘客请求不合理,具体为输入时出现连续的相同请求,例如<3><3><3>或者<5,DOWN><5,DOWN>,处理方法:程序自动忽略相同的多余输入,继续执行,例如<3><3><3>过滤为<3>
输入格式:
第一行输入最小电梯楼层数。
第二行输入最大电梯楼层数。
从第三行开始每行输入代表一个乘客请求。
电梯内乘客请求格式:<楼层数>
电梯外乘客请求格式:<乘客所在楼层数,乘梯方向>,其中,乘梯方向用UP代表上行,用DOWN代表下行(UP、DOWN必须大写)。
当输入“end”时代表输入结束(end不区分大小写)。
输出格式:
模拟电梯的运行过程,输出方式如下:
运行到某一楼层(不需要停留开门),输出一行文本:
Current Floor: 楼层数 Direction: 方向
运行到某一楼层(需要停留开门)输出两行文本:
Open Door # Floor 楼层数
Close Door
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
20
<3,UP>
<5>
<6,DOWN>
<7>
<3>
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Current Floor: 1 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 2 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 3 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
Current Floor: 4 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 5 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 7 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 7
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 6
Close Door
Current Floor: 5 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 4 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 3 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
20
<3,UP>
<3,UP>
<5>
<5>
<5>
<6,DOWN>
<7>
<7>
<3>
<22,DOWN>
<5,DOWN>
<30>
END
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Current Floor: 1 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 2 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 3 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
Current Floor: 4 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 5 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 7 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 7
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 6
Close Door
Current Floor: 5 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 4 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 3 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
//这里结束
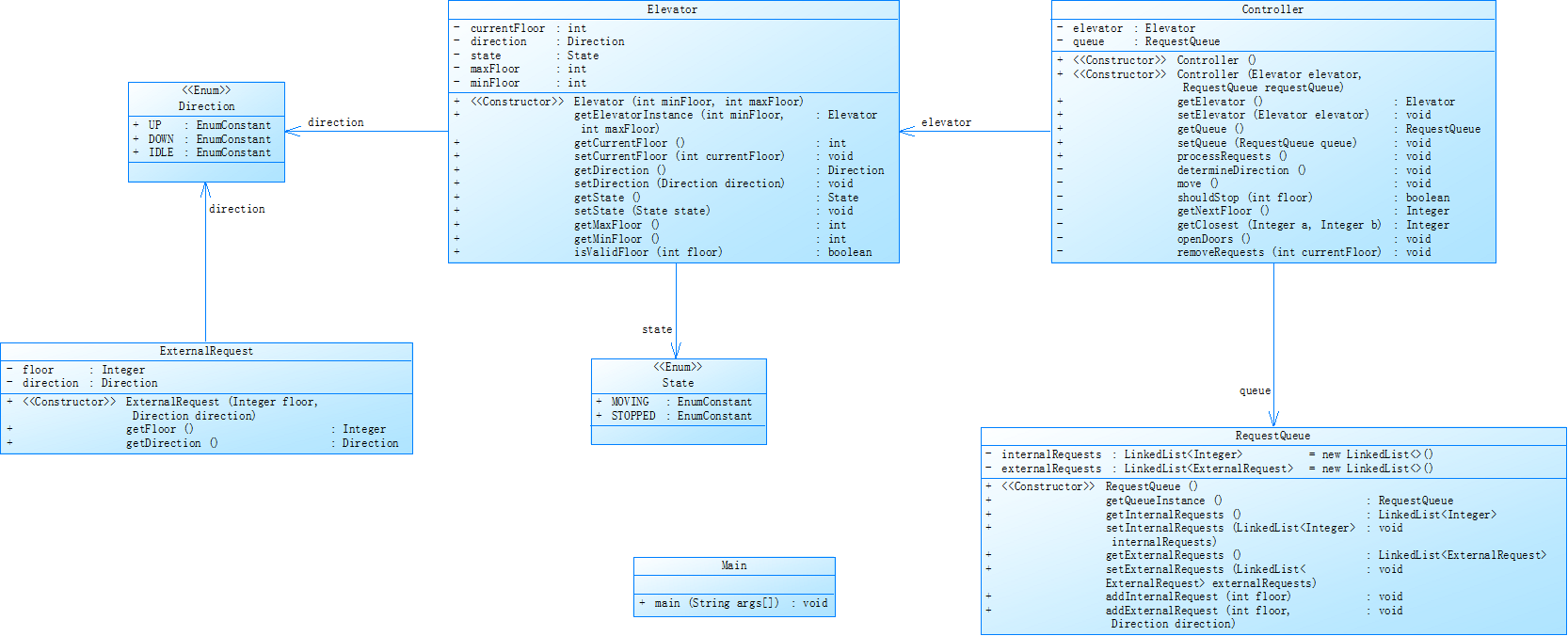
2.注解
-进一步迭代,开始有UML限定必要的枚举和类,同时把上一代Elevator类里冗长的请求队列处理逻辑单独封装在Controller类里
保留外部请求类,删除内部请求类,把内外部请求封装在同一个RequestQueue类里
要求内外队列以linkedlist存储
-类及枚举功能如下:
(1). 枚举类型1 Direction:定义了电梯的运行方向,包括上行(UP)、下行(DOWN)和空闲(IDLE)。
(2). 枚举类型2 State:定义了电梯的运行状态,包括移动(MOVING)和停止(STOPPED)。
(3). 外部请求类 ExternalRequest:封装外部请求(楼层+方向)。
(4). 请求队列类 RequestQueue:管理电梯的内部请求和外部请求。
(5). 电梯类 Elevator:管理电梯状态(楼层、方向、运行状态)。
(6). 控制类(核心类) Controller:管理电梯状态(楼层、方向、运行状态)。
(7). 辅助类 HelpGet:封装一些方法辅助Controller类的处理逻辑,否则Controller类里的主要方法过于重复冗杂。
(8). 主类 Main:处理输入并启动电梯调度。
🟡PTA-07
1.题述要求
对之前电梯调度程序再次进行迭代性设计,加入乘客类(Passenger),取消乘客请求类,类设计要求遵循单一职责原则(SRP),要求必须包含但不限于设计电梯类、乘客类、队列类以及控制类,具体设计可参考如下类图。电梯运行规则与前阶段相同,但有如下变动情况:乘客请求输入变动情况:外部请求由之前的<请求楼层数,请求方向>修改为<请求源楼层,请求目的楼层>对于外部请求,当电梯处理该请求之后(该请求出队),要将<请求源楼层,请求目的楼层>中的请求目的楼层加入到请求内部队列(加到队尾)
输入格式:
第一行输入最小电梯楼层数。
第二行输入最大电梯楼层数。
从第三行开始每行输入代表一个乘客请求。
电梯内乘客请求格式:<楼层数>
电梯外乘客请求格式:<请求源楼层,请求目的楼层>,其中,请求源楼层表示乘客发起请求所在的楼层,请求目的楼层表示乘客想要到达的楼层。
当输入“end”时代表输入结束(end不区分大小写)。
输出格式:
模拟电梯的运行过程,输出方式如下:
运行到某一楼层(不需要停留开门),输出一行文本:
Current Floor: 楼层数 Direction: 方向
运行到某一楼层(需要停留开门)输出两行文本:
Open Door # Floor 楼层数
Close Door
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
20
<5,4>
<5>
<7>
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Current Floor: 1 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 2 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 3 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 4 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 5 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 7 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 7
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 5 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 4 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 4
Close Door
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
20
<5,9>
<8>
<9,3>
<4>
<2>
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Current Floor: 1 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 2 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 3 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 4 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 5 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 5
Close Door
Current Floor: 6 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 7 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 8 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 8
Close Door
Current Floor: 9 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 9
Close Door
Current Floor: 8 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 7 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 6 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 5 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 4 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 4
Close Door
Current Floor: 3 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 2 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 2
Close Door
Current Floor: 3 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 4 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 5 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 6 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 7 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 8 Direction: UP
Current Floor: 9 Direction: UP
Open Door # Floor 9
Close Door
Current Floor: 8 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 7 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 6 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 5 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 4 Direction: DOWN
Current Floor: 3 Direction: DOWN
Open Door # Floor 3
Close Door
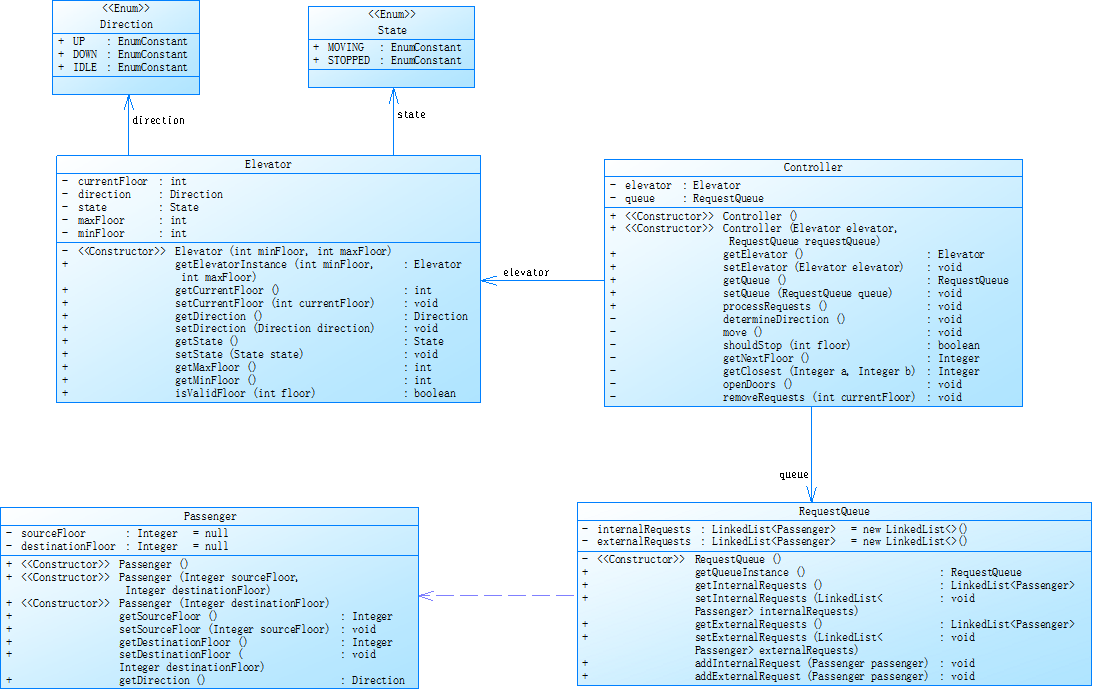
2.注解
再进一步迭代,UML的类删除了ExternalRequest类,增加了Passager类,来专门封装外部请求
最主要的改动:外部的请求不再是<楼层,方向>的形式,而是<源楼层,目标楼层>的形式
也就是说我对外部请求的判断逻辑以及对下一个请求的判断逻辑要有改动,每次处理完,还要记得删除这个外队列,转为内队列
类及枚举功能如下:
(1). 枚举类型1 Direction:定义了电梯的运行方向,包括上行(UP)、下行(DOWN)和空闲(IDLE)。
(2). 枚举类型2 State:定义了电梯的运行状态,包括移动(MOVING)和停止(STOPPED)。
(3). 外部请求类 Passenger:封装外部请求成一个类(源楼层+目标楼层)。
(4). 请求队列类 RequestQueue:管理电梯的内部请求和外部请求。
(5). 电梯类 Elevator:管理电梯状态(楼层、方向、运行状态)。
(6). 控制类(核心类) Controller:管理电梯状态(楼层、方向、运行状态)。
(7). 辅助类 HelpGet:封装一些方法辅助Controller类的处理逻辑,否则Controller类里的主要方法过于重复冗杂。
(8). 主类 Main:处理输入并启动电梯调度。
🕑二.设计与分析
1.🟢PTA-05
(1)源码
//这里主要讨论主要的处理逻辑
public void processRequests() {
// 初始方向确定
if (direction == Direction.IDLE) {
determineInitialDirection();
if (direction != Direction.IDLE) {
System.out.println("Current Floor: 1 Direction: " + direction);
}
}
// 主循环处理所有请求
while (internalHead != null || externalHead != null) {
// 选择下一个要处理的请求
RequestInfo next = selectNextRequest();
/* // 如果没有合适请求,切换方向
if (next == null) {
direction = (direction == Direction.UP) ? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP;
System.out.println("Current Floor: " + currentFloor + " Direction: " + direction);
continue;
}
*/
// 如果没有合适请求,切换方向
if (next == null) {
Direction prevDirection = direction;
direction = (direction == Direction.UP) ? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP;
if (prevDirection != direction) {
// 不输出当前楼层和新方向,直接处理新方向的移动
// System.out.println("Current Floor: " + currentFloor + " Direction: " + direction);
continue;
}
}
// 判断是否需要改变方向
Direction targetDirection = (next.floor > currentFloor) ? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN;
if (targetDirection != direction) {
direction = targetDirection;
// 不输出当前楼层和新方向,直接处理新方向的移动
// System.out.println("Current Floor: " + currentFloor + " Direction: " + direction);
}
// 移动到目标楼层并处理请求
moveToFloor(next.floor);
System.out.println("Open Door # Floor " + currentFloor);
System.out.println("Close Door");
// 移除已处理的请求
removeProcessedRequest(next);
// 检查当前方向是否还有请求
if (!hasRequestsInCurrentDirection()) {
Direction prevDirection = direction;
direction = (direction == Direction.UP) ? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP;
if (prevDirection != direction) {
// 不输出当前楼层和新方向,直接处理新方向的移动
// System.out.println("Current Floor: " + currentFloor + " Direction: " + direction);
}
}
}
}
// 选择下一个要处理的请求
private RequestInfo selectNextRequest() {
// 如果没有请求返回null
if (internalHead == null && externalHead == null) return null;
// 只有外部请求时返回外部请求头节点
if (internalHead == null) return new RequestInfo(externalHead.floor, false);
// 只有内部请求时返回内部请求头节点
if (externalHead == null) return new RequestInfo(internalHead.floor, true);
// 检查两个队列头部请求的方向是否匹配当前方向
boolean internalSameDir = isSameDirection(internalHead.floor, true);
boolean externalSameDir = isSameDirection(externalHead.floor, false);
// 两个请求方向都匹配时,选择距离更近的
if (internalSameDir && externalSameDir) {
return getDistance(internalHead.floor) <= getDistance(externalHead.floor) ?
new RequestInfo(internalHead.floor, true) :
new RequestInfo(externalHead.floor, false);
}
// 只有内部请求方向匹配
else if (internalSameDir) {
return new RequestInfo(internalHead.floor, true);
}
// 只有外部请求方向匹配
else if (externalSameDir) {
return new RequestInfo(externalHead.floor, false);
}
// 都不匹配时选择距离更近的
else {
return getDistance(internalHead.floor) <= getDistance(externalHead.floor) ?
new RequestInfo(internalHead.floor, true) :
new RequestInfo(externalHead.floor, false);
}
}
// 判断请求方向是否与当前方向匹配
private boolean isSameDirection(int floor, boolean isInternal) {
// IDLE状态时所有请求都视为匹配
if (direction == Direction.IDLE) return true;
if (isInternal) {
// 内部请求:根据目标楼层与当前楼层的关系判断方向
return (direction == Direction.UP && floor > currentFloor) ||
(direction == Direction.DOWN && floor < currentFloor);
} else {
// 外部请求:直接比较方向
ExternalRequest req = externalHead;
// 查找对应的外部请求节点
while (req != null && req.floor != floor) req = req.next;
return req != null && req.direction == direction;
}
}
// 计算距离
private int getDistance(int floor) {
return Math.abs(floor - currentFloor);
}
// 移除已处理的请求
private void removeProcessedRequest(RequestInfo req) {
if (req.isInternal) {
// 移除内部请求头节点
internalHead = internalHead.next;
} else {
// 移除外部请求头节点
externalHead = externalHead.next;
}
}
private void determineInitialDirection() {
// 优先处理内部请求
if (internalHead != null) {
direction = internalHead.floor > currentFloor ? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN;
}
// 其次处理外部请求
else if (externalHead != null) {
direction = externalHead.direction;
}
}
// 移动到目标楼层
private void moveToFloor(int targetFloor) {
// 确定移动步长(1或-1)
int step = targetFloor > currentFloor ? 1 : -1;
// 逐层移动并输出状态
while (currentFloor != targetFloor) {
currentFloor += step;
System.out.println("Current Floor: " + currentFloor + " Direction: " + direction);
}
}
}
(2)逻辑分析
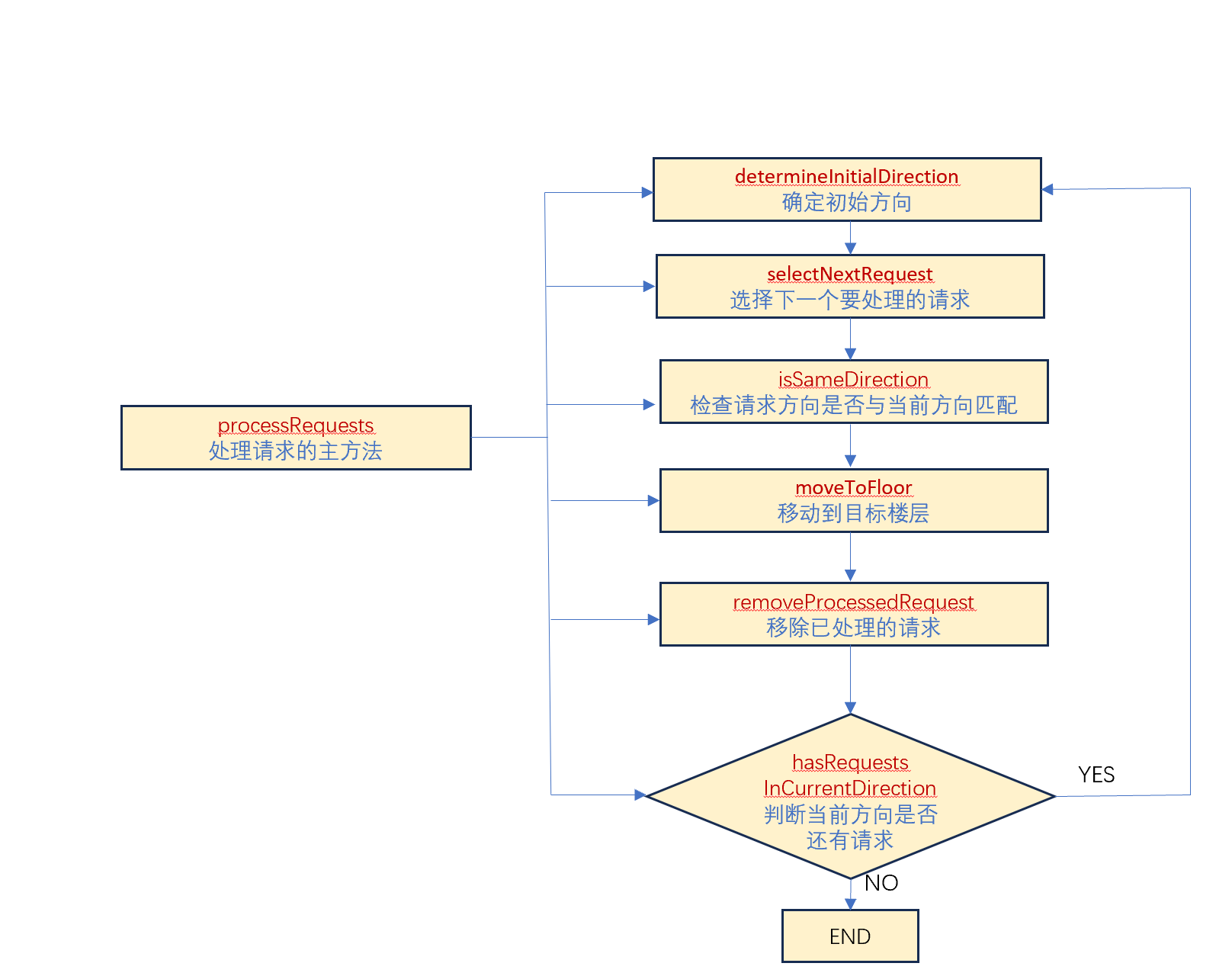
首先确定初始方向,然后进入主循环处理所有请求。主循环中,选择下一个要处理的请求,移动电梯到目标楼层,处理请求后移除该请求,并检查是否需要改变方向。
接下来我们重点分析请求处理的逻辑,特别是如何选择下一个请求以及方向的判断。
首先,初始方向的确定由determineInitialDirection方法处理。它会优先考虑内部请求,如果存在内部请求,根据目标楼层与当前楼层的关系设置方向;否则,如果有外部请求,使用外部请求的方向。如果都没有,方向保持IDLE。
在处理请求的主循环中,首先调用selectNextRequest方法选择下一个请求。这个方法会检查内部和外部请求链表的头节点,比较它们是否符合当前方向,并选择距离更近的一个。如果都不符合当前方向,可能返回null,这时会切换方向。
然后,判断是否需要改变方向的逻辑。根据目标楼层和当前楼层的关系,确定目标方向。如果目标方向与当前方向不同,则改变方向。
在移动到目标楼层后,电梯开门关门,并移除已处理的请求。之后,检查当前方向是否还有请求,如果没有,再次切换方向。例如,如果电梯在上行方向处理完所有请求后,会切换为下行,检查是否有下行请求。
接下来,我需要仔细看selectNextRequest方法。它比较内部和外部请求链表的头节点,判断它们的方向是否与当前方向一致,然后选择更近的一个。
a. 初始方向确定
优先级:优先处理内部请求。若存在内部请求,根据其目标楼层与当前楼层的关系(高于或低于)设置方向;否则,使用外部请求的方向。
空闲状态:若无请求,方向保持IDLE。
b. 主循环processRequests
选择下一个请求selectNextRequest:
内部请求:判断目标楼层是否与当前方向一致。例如,电梯上行时仅处理高于当前楼层的请求。
外部请求:判断请求方向是否与电梯当前方向一致。
比较逻辑:若内部和外部请求均符合方向,选择距离更近的;若仅一方符合,选择对应的请求;若均不符合,返回null。
方向调整:
若无合适请求,切换方向(UP↔DOWN)。
若目标楼层与当前方向相反,调整方向。
移动与处理请求:
逐层移动并输出状态,到达目标楼层后开门、关门。
移除已处理的请求(链表头节点)。
方向再检查:
处理完请求后,若当前方向无其他请求,再次切换方向。
(3)报表
2.🟢PTA-06
(1)源码
class Controller {
private Elevator elevator;
private RequestQueue queue;
//测试
public void testInput() {
for(ExternalRequest request : queue.getExternalRequests()) {
System.out.println(request.getDirection()+" "+request.getFloor());
}
for (Integer floor : queue.getInternalRequests()) {
System.out.println(floor);
}
}
// 有参构造
public Controller(Elevator elevator, RequestQueue queue) {
this.elevator = elevator;
this.queue = queue;
}
//getter和setter
public Elevator getElevator() {
return elevator;
}
public void setElevator(Elevator elevator) {
this.elevator = elevator;
}
public RequestQueue getQueue() {
return queue;
}
public void setQueue(RequestQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
// 主体函数:处理请求队列中所有请求的方法
public void processRequests() {
// 初始方向确定
if (elevator.getDirection() == Direction.IDLE) {
determineDirection();
if (elevator.getDirection() != Direction.IDLE) {
System.out.println("Current Floor: " + elevator.getCurrentFloor() + " Direction: " + elevator.getDirection());
}
}
// 主循环处理所有请求
while (!queue.getInternalRequests().isEmpty() ||!queue.getExternalRequests().isEmpty()) {
// 选择下一个要处理的请求
HelpGet next = whatToDisposedDNext();
// 如果没有合适请求,切换方向
if (next == null) {
Direction prevDirection = elevator.getDirection();
elevator.setDirection((elevator.getDirection() == Direction.UP)? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP);
if (prevDirection != elevator.getDirection()) {
continue;
}
}
// 判断是否需要改变方向
Direction targetDirection = (next.floor > elevator.getCurrentFloor())? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN;
if (targetDirection != elevator.getDirection()) {
elevator.setDirection(targetDirection);
}
// 移动到目标楼层并处理请求
move(next.floor);
openDoors();
removeRequests(next.floor, next.isInternal);
// 检查当前是否还有请求
if (!ifStillHave()) {
Direction prevDirection = elevator.getDirection();
elevator.setDirection((elevator.getDirection() == Direction.UP)? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP);
if (prevDirection != elevator.getDirection()) {
}
}
}
}
// 关键函数:处理确定方向
public void determineDirection() {
LinkedList<Integer> internalRequests = queue.getInternalRequests();
LinkedList<ExternalRequest> externalRequests = queue.getExternalRequests();
//内
if (!internalRequests.isEmpty()) {
elevator.setDirection(internalRequests.peek() > elevator.getCurrentFloor()? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN);
}
//外
else if (!externalRequests.isEmpty()) {
elevator.setDirection(externalRequests.peek().getDirection());
}
}
//关键函数:移动楼层并输出
public void move(int targetFloor) {
int step = targetFloor > elevator.getCurrentFloor()? 1 : -1;//记得创实例
while (elevator.getCurrentFloor() != targetFloor) {
int temp=elevator.getCurrentFloor();
temp+= step;
elevator.setCurrentFloor(temp);//更新
System.out.println("Current Floor: " + elevator.getCurrentFloor() + " Direction: " + elevator.getDirection());//逐层移动输出
}
}
// 辅助函数:判断电梯是否应该在指定楼层停止
public void shouldStop() {
LinkedList<Integer> internalRequests = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<ExternalRequest> externalRequests = new LinkedList<>(); // 存储电梯内外请求的链表
int randomNumber = (int) (Math.random() * 100);
if (randomNumber % 2 == 0) {
internalRequests.add(-1);
externalRequests.add(new ExternalRequest(-1, Direction.IDLE));
}
internalRequests.removeIf(integer -> integer == -1);
externalRequests.removeIf(request -> request.getFloor() == -1);
}
// 关键函数:开关门
public void openDoors() {
System.out.println("Open Door # Floor " + elevator.getCurrentFloor());
System.out.println("Close Door");
}
// 关键函数:删除刚处理完的请求
public void removeRequests(int currentFloor, boolean isInternal) {
if (isInternal) {
// 移除 internalRequests 的头节点(FIFO)
if (!queue.getInternalRequests().isEmpty()) {
queue.getInternalRequests().remove(0);
}
} else {
// 移除 externalRequests 的头节点(FIFO)
if (!queue.getExternalRequests().isEmpty()) {
queue.getExternalRequests().remove(0);
}
}
}
// 关键函数:接着判断下一个请求
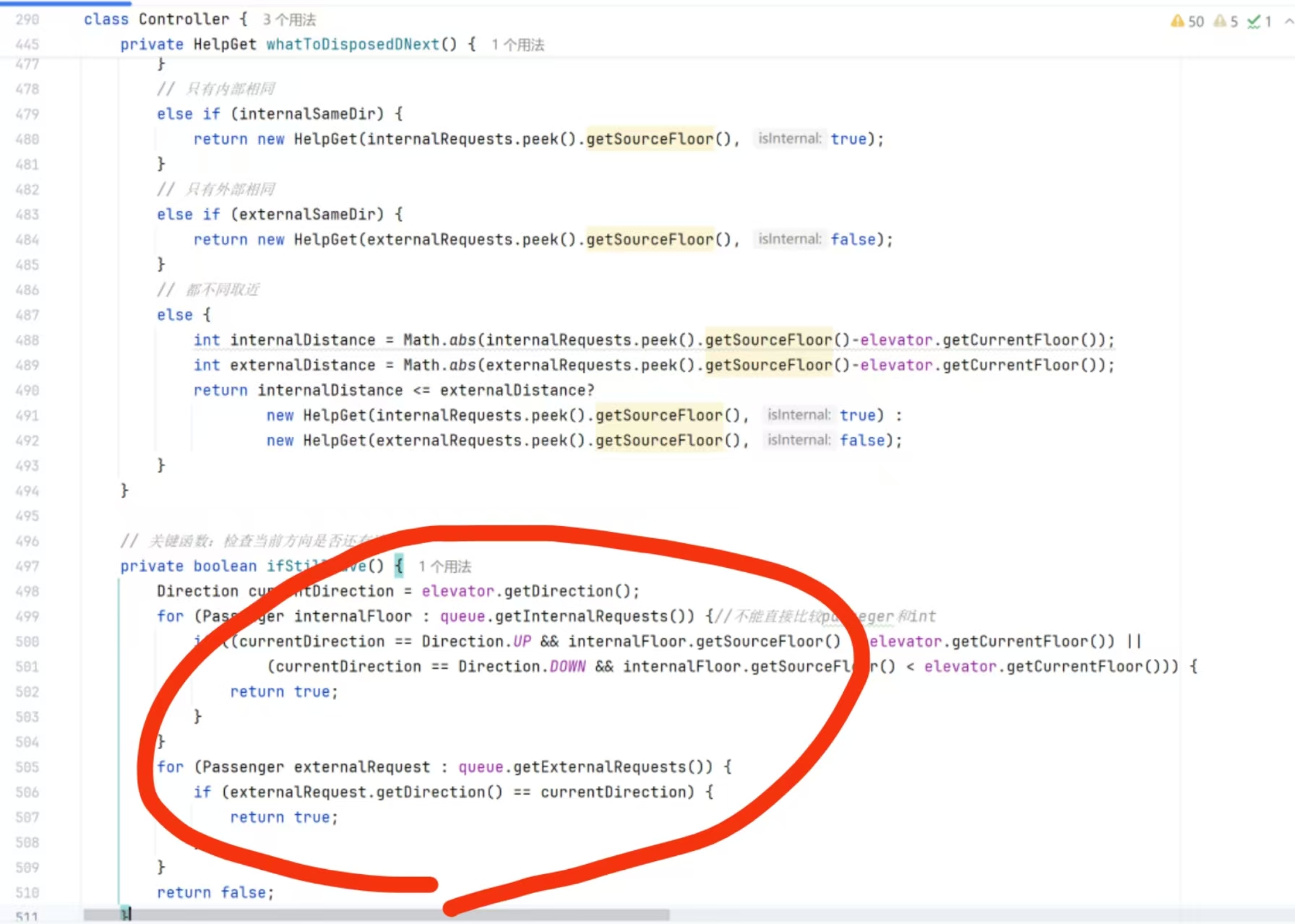
private HelpGet whatToDisposedDNext() {
LinkedList<Integer> internalRequests = queue.getInternalRequests();
LinkedList<ExternalRequest> externalRequests = queue.getExternalRequests();
// 全空请求返回null
if (internalRequests.isEmpty() && externalRequests.isEmpty()) return null;
// 只有外返回外
if (internalRequests.isEmpty()) {
ExternalRequest req = externalRequests.peek();
return new HelpGet(req.getFloor(), false);
}
// 只有内返回内
if (externalRequests.isEmpty()) {
return new HelpGet(internalRequests.peek(), true);
}
// 检查两个队列头部请求的方向是否匹配当前方向
boolean internalSameDir = isSameDirection(internalRequests.peek(), true);
boolean externalSameDir = isSameDirection(externalRequests.peek().getFloor(), false);
// 内外都相同取近
if (internalSameDir && externalSameDir) {
int internalDistance = Math.abs(internalRequests.peek()-elevator.getCurrentFloor());
int externalDistance = Math.abs(externalRequests.peek().getFloor()-elevator.getCurrentFloor());
return internalDistance <= externalDistance?
new HelpGet(internalRequests.peek(), true) :
new HelpGet(externalRequests.peek().getFloor(), false);
}
// 只有内部相同
else if (internalSameDir) {
return new HelpGet(internalRequests.peek(), true);
}
// 只有外部相同
else if (externalSameDir) {
return new HelpGet(externalRequests.peek().getFloor(), false);
}
// 都不同取近
else {
int internalDistance = Math.abs(internalRequests.peek()-elevator.getCurrentFloor());
int externalDistance = Math.abs(externalRequests.peek().getFloor()-elevator.getCurrentFloor());
return internalDistance <= externalDistance?
new HelpGet(internalRequests.peek(), true) :
new HelpGet(externalRequests.peek().getFloor(), false);
}
}
// 关键函数:检查当前方向是否还有请求
private boolean ifStillHave() {
Direction currentDirection = elevator.getDirection();
for (Integer internalFloor : queue.getInternalRequests()) {
if ((currentDirection == Direction.UP && internalFloor > elevator.getCurrentFloor()) ||
(currentDirection == Direction.DOWN && internalFloor < elevator.getCurrentFloor())) {
return true;
}
}
for (ExternalRequest externalRequest : queue.getExternalRequests()) {
if (externalRequest.getDirection() == currentDirection) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 关键函数:判断请求方向是否与当前方向匹配
private boolean isSameDirection(int floor, boolean isInternal) {
Direction currentDirection = elevator.getDirection();
if (currentDirection == Direction.IDLE) return true;
if (isInternal) {
return (currentDirection == Direction.UP && floor > elevator.getCurrentFloor()) ||
(currentDirection == Direction.DOWN && floor < elevator.getCurrentFloor());
} else {
int floorDiff = floor - elevator.getCurrentFloor();
if (currentDirection == Direction.UP) {
return floorDiff > 0 &&
queue.getExternalRequests().stream()
.anyMatch(req -> req.getFloor() == floor && req.getDirection() == currentDirection);
} else if (currentDirection == Direction.DOWN) {
return floorDiff < 0 &&
queue.getExternalRequests().stream()
.anyMatch(req -> req.getFloor() == floor && req.getDirection() == currentDirection);
}
return false;
}
}
}
(2)逻辑分析
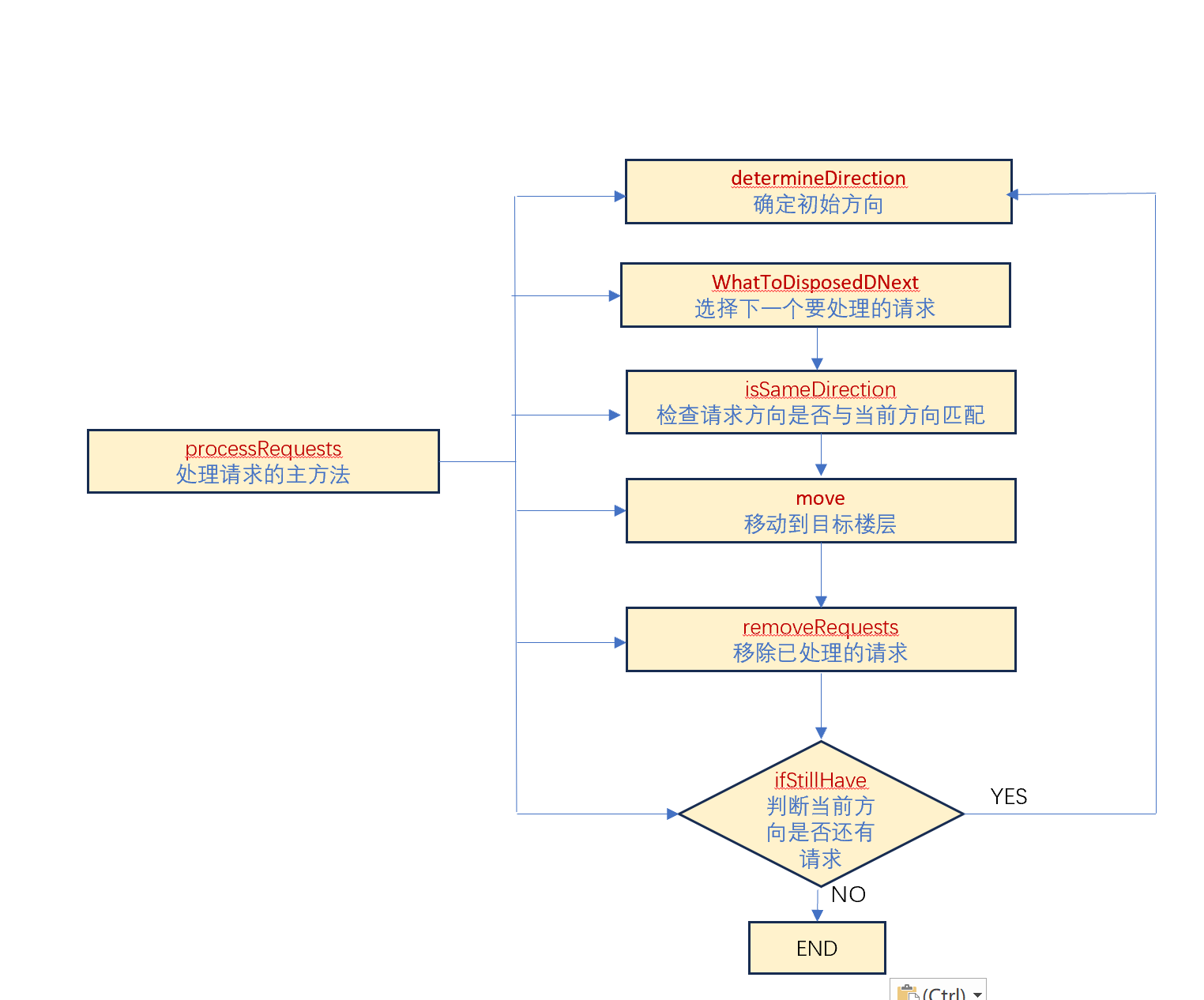
初始方向确定:determineDirection方法,当电梯处于 IDLE 状态时调用,内部请求优先,取队列第一个内部请求的楼层,若高于当前楼层则方向设为 UP,否则 DOWN。外部请求次优:直接采用第一个外部请求的方向。
选择下一个请求whatToDisposedDNext:比较内/外队列头节点,优先选择符合当前方向且距离更近的请求。若均不符合方向,选择距离更近的请求并切换方向。
移动电梯move方法:逐层更新 currentFloor,输出移动状态。并处理请求:开门、关门。
移除已处理的请求removeRequests:移除已处理的请求,内外队列都直接移除队列头部请求(FIFO),其中外部请求删除后还要根据目标楼层生成新的内部请求。
检查剩余请求ifStillHave:检查当前方向是否还有待处理的请求,决定是否切换方向。遍历内部请求队列,检查是否存在楼层在电梯当前路径上(如 UP 时楼层 > 当前楼层)。
遍历外部请求队列,检查是否存在方向匹配且楼层在路径上的请求。
主循环处理processRequests方法:调用上述方法,核心的处理逻辑是:初始方向确定 → 选择请求 → 移动电梯 → 处理请求 → 删除请求 → 检查剩余请求。
(3)报表
3.🟢PTA-07
(1)源码
class Controller {
private Elevator elevator;
private RequestQueue queue;
public Controller(Elevator elevator, RequestQueue queue) { // 有参构造
this.elevator = elevator;
this.queue = queue;
}
public void processRequests() { // 主体函数:处理请求队列中所有请求的方法
if (elevator.getDirection() == Direction.IDLE) {
determineDirection();
if (elevator.getDirection() != Direction.IDLE) {
System.out.println("Current Floor: " + elevator.getCurrentFloor() + " Direction: " + elevator.getDirection());
}
}
// 主循环处理所有请求
while (!queue.getInternalRequests().isEmpty() ||!queue.getExternalRequests().isEmpty()) {
// 选择下一个要处理的请求
HelpGet next = whatToDisposedDNext();
// 如果没有合适请求,切换方向
if (next == null) {
Direction prevDirection = elevator.getDirection();
elevator.setDirection((elevator.getDirection() == Direction.UP)? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP);
if (prevDirection != elevator.getDirection()) {
continue;
}
}
// 判断是否需要改变方向
Direction targetDirection = (next.floor > elevator.getCurrentFloor())? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN;
if (targetDirection != elevator.getDirection()) {
elevator.setDirection(targetDirection);
}
// 移动到目标楼层并处理请求
move(next.floor);
openDoors();
removeRequests(next.floor, next.isInternal);
// 检查当前是否还有请求
if (!ifStillHave()) {
Direction prevDirection = elevator.getDirection();
elevator.setDirection((elevator.getDirection() == Direction.UP)? Direction.DOWN : Direction.UP);
if (prevDirection != elevator.getDirection()) {
}
}
}
}
public void determineDirection() { // 关键函数:处理确定方向
LinkedList<Passenger> internalRequests = queue.getInternalRequests();
LinkedList<Passenger> externalRequests = queue.getExternalRequests();
if (!internalRequests.isEmpty()) {//内
int targetFloor = internalRequests.getFirst().getDestinationFloor();
elevator.setDirection(targetFloor > elevator.getCurrentFloor() ? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN);
}
else if (!externalRequests.isEmpty()) {//外(注意这里对外部队列方向的判断)
Passenger firstExternalRequest = externalRequests.getFirst();
int sourceFloor = firstExternalRequest.getSourceFloor();
int destinationFloor = firstExternalRequest.getDestinationFloor();
elevator.setDirection(destinationFloor > sourceFloor? Direction.UP : Direction.DOWN);
}
}
public void move(int targetFloor) { //辅助函数:移动楼层并输出
int step = targetFloor > elevator.getCurrentFloor()? 1 : -1;//记得创实例
while (elevator.getCurrentFloor() != targetFloor) {
int temp=elevator.getCurrentFloor();
temp+= step;
elevator.setCurrentFloor(temp);//更新
System.out.println("Current Floor: " + elevator.getCurrentFloor() + " Direction: " + elevator.getDirection());//逐层移动输出
}
}
public void openDoors() { // 辅助函数:开关门
System.out.println("Open Door # Floor " + elevator.getCurrentFloor());
System.out.println("Close Door");
}
public void removeRequests(int currentFloor, boolean isInternal) { // 关键函数:删除刚处理完的请求
if (isInternal) {
if (!queue.getInternalRequests().isEmpty()) {
queue.getInternalRequests().remove(0);// 移除 internalRequests 的头节点(FIFO)
}
} else {
if (!queue.getExternalRequests().isEmpty()) {
Passenger removedExternal = queue.getExternalRequests().remove(0);// 1.获取并移除 externalRequests 的头节点(FIFO)
Passenger newInternalRequest = new Passenger(currentFloor,removedExternal.getDestinationFloor());//2.源楼层为当前楼层(currentFloor),目标楼层为外部请求的 destinationFloor
queue.addInternalRequest(newInternalRequest);//3.将新请求添加到内部队列尾部
}
}
}
private HelpGet whatToDisposedDNext() {
LinkedList<Passenger> internals = queue.getInternalRequests();
LinkedList<Passenger> externals = queue.getExternalRequests();
if (internals.isEmpty() && externals.isEmpty()) return null;
// 单队列处理
if (internals.isEmpty()) return new HelpGet(externals.peek().getSourceFloor(), false);
if (externals.isEmpty()) return new HelpGet(internals.peek().getDestinationFloor(), true);
// 核心变量提取
Passenger internal = internals.peek();
Passenger external = externals.peek();
int current = elevator.getCurrentFloor();
Direction dir = elevator.getDirection();
int iFloor = internal.getDestinationFloor();
int eFloor = external.getSourceFloor();
// 方向判断
boolean iSameDir = isSameDirection(iFloor, true);
boolean eSameDir = isSameDirection(eFloor, false);
// 逻辑分支简化
if (iSameDir || eSameDir) { // 至少一方方向匹配
if (iSameDir && eSameDir) { // 双方同向
return closer(iFloor, eFloor, current) ?
new HelpGet(iFloor, true) : new HelpGet(eFloor, false);
}
return iSameDir ?
new HelpGet(iFloor, true) : new HelpGet(eFloor, false);
}
// 无方向匹配时的智能路径选择
return handleNoDirectionMatch(iFloor, eFloor, current, dir, external);
}
// 辅助方法1:距离比较
private boolean closer(int a, int b, int current) {
return Math.abs(a - current) <= Math.abs(b - current);
}
// 辅助方法2:处理无方向匹配的情况
private HelpGet handleNoDirectionMatch(int iFloor, int eFloor, int current,
Direction dir, Passenger external) {
// 同一侧请求处理
if ((iFloor > current && eFloor > current) || (iFloor < current && eFloor < current)) {
if (closer(eFloor, iFloor, current)) {
int dest = external.getDestinationFloor();
addUniqueInternal(current, dest); // 去重添加逻辑
return (dir == Direction.UP && dest > current) || (dir == Direction.DOWN && dest < current) ?
new HelpGet(eFloor, false) : new HelpGet(iFloor, true);
}
return new HelpGet(iFloor, true);
}
// 异侧请求处理
if (dir == Direction.UP && eFloor > current) {
addUniqueInternal(current, external.getDestinationFloor());
return new HelpGet(eFloor, false);
}
return new HelpGet(iFloor, true);
}
// 辅助方法3:去重添加内部请求
private void addUniqueInternal(int source, int dest) {
if (queue.getInternalRequests().stream().noneMatch(p -> p.getDestinationFloor() == dest)) {
queue.addInternalRequest(new Passenger(source, dest));
}
}
private boolean ifStillHave() {// 关键函数:检查当前方向是否还有请求
Direction currentDirection = elevator.getDirection();
LinkedList<Passenger> internalRequests = queue.getInternalRequests();
LinkedList<Passenger> externalRequests = queue.getExternalRequests();
// 检查内部请求队列的头元素
if (!internalRequests.isEmpty()) {
Passenger internalRequest = internalRequests.peek();//peek获取头队列
int destinationFloor = internalRequest.getDestinationFloor();//获取目标楼层
if ((currentDirection == Direction.UP && destinationFloor > elevator.getCurrentFloor()) ||
(currentDirection == Direction.DOWN && destinationFloor < elevator.getCurrentFloor())) {
return true;
}
}
// 检查外部请求队列的头元素
if (!externalRequests.isEmpty()) {
Passenger externalRequest = externalRequests.peek();
int reqFloor = externalRequest.getSourceFloor();
boolean isOnPath = (currentDirection == Direction.UP && reqFloor >= elevator.getCurrentFloor()) ||
(currentDirection == Direction.DOWN && reqFloor <= elevator.getCurrentFloor());// 关键:路径有效性优先于方向匹配性
if (isOnPath) {
return true;//在路径上就返回 true
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean isSameDirection(int floor, boolean isInternal) {// 关键函数:判断请求方向是否与当前方向匹配
Direction currentDirection = elevator.getDirection();
if (currentDirection == Direction.IDLE) return true;
if (isInternal) {
return (currentDirection == Direction.UP && floor > elevator.getCurrentFloor()) ||
(currentDirection == Direction.DOWN && floor < elevator.getCurrentFloor());
} else {
int floorDiff = floor - elevator.getCurrentFloor();
if (currentDirection == Direction.UP) {
return floorDiff > 0 &&
queue.getExternalRequests().stream()
.anyMatch(req -> req.getSourceFloor() == floor && req.getDirection() == currentDirection);
} else if (currentDirection == Direction.DOWN) {
return floorDiff < 0 &&
queue.getExternalRequests().stream()
.anyMatch(req -> req.getSourceFloor() == floor && req.getDirection() == currentDirection);
}
return false;
}
}
}
(2)逻辑分析
p.s.流程图与PTA-06相似
分析determineDirection方法。该方法用于确定电梯的初始方向。优先处理内部请求,如果没有内部请求,则处理外部请求。
接下来,whatToDisposedDNext方法是选择下一个要处理的请求的关键。代码中处理了内外部请求队列,比较它们的楼层是否符合当前方向,并选择更近的请求。在无方向匹配
时,handleNoDirectionMatch方法尝试智能选择,例如处理同侧请求或异侧请求。
在removeRequests方法中,处理外部请求时会将其转换为内部请求,也即乘客进入电梯后,原本的外部请求完成,会被删除,其目标楼层成为内部请求。
ifStillHave方法用于检查当前方向是否还有请求。这里对内部请求检查目标楼层是否在路径上,而外部请求则检查源楼层是否在路径上。
在isSameDirection方法中,判断外部请求是否与当前方向一致时,不仅检查方向是否匹配,还检查源楼层是否在电梯当前方向的路径上。例如,电梯在上行时,外部请求的源楼层必须高于当前楼层且方向一致。
(3)报表
🕒三.采坑心得
1.关于只删除头节点
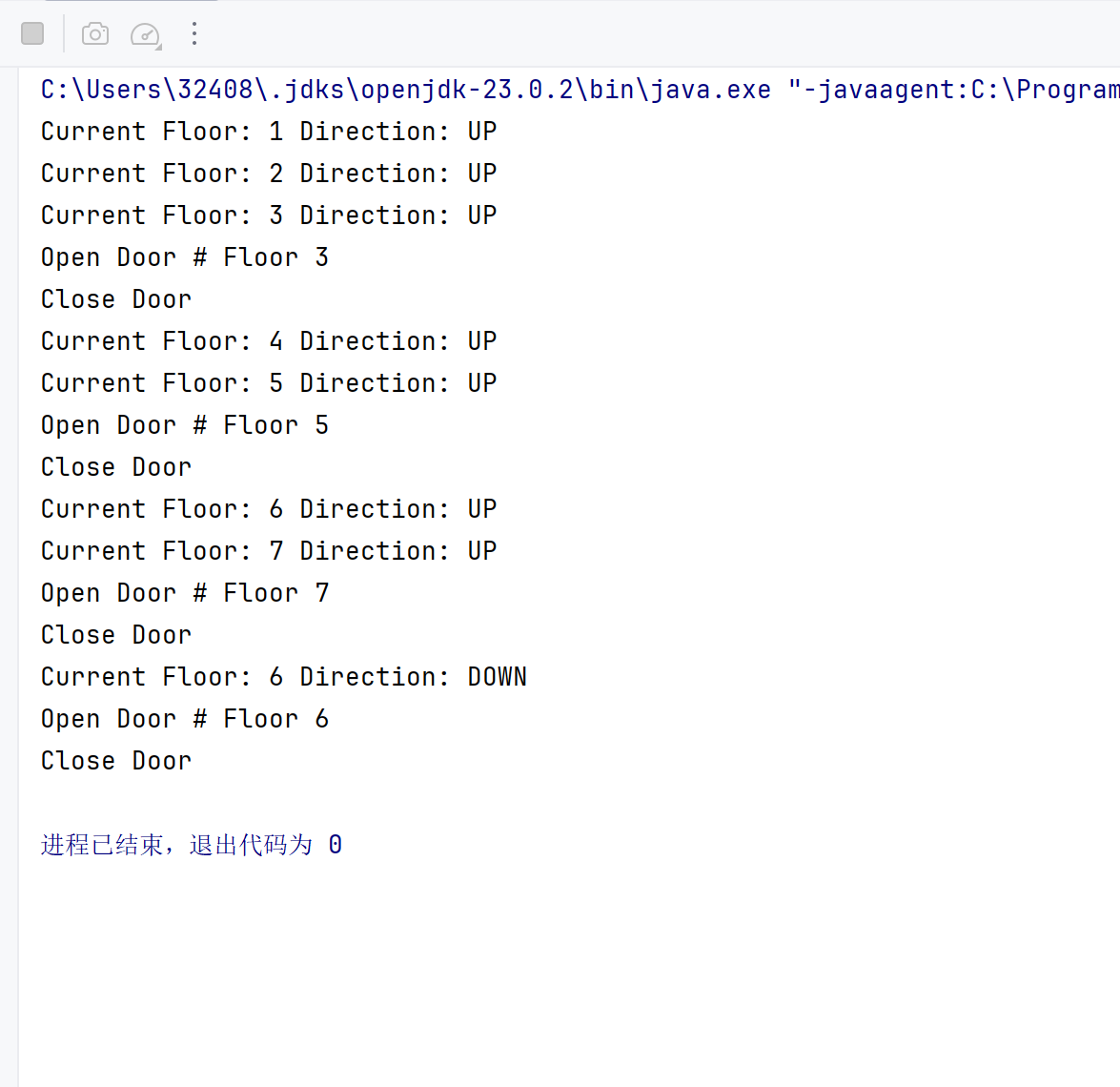
一开始的删除逻辑是根据楼层来删除,比如,外队列<3,UP>,内队列<5>和<4>和<3>,我从一楼上行肯定先到3楼,由于<3,UP>是头队列,我肯定先执行头队列,处理完后我会删除3楼对应的所有匹配请求,也就是说<3,UP>和<3>都会删除,但如果<3>被删除了,最后电梯下行的时候到4楼就停了,我的期望是只删除<3,UP>,所以这里只能删除头节点,而不能按楼层删除。
比如我输入:
1
20
<3,UP>
<5>
<6,DOWN>
<7>
<3>
end
最后下行时未能停在3楼
2.关于新增的Passenger类
外部请求的请求方式改变了,对于外部请求的判断,与当前方向不同不能只看谁近,比如,现在在3楼,方向是上行,外部队列的头队列是<5,1>,内部队列的头队列是<2>,对于<5,1>来说方向是DOWN,会先处理<2>,但是实际上电梯要线上到2,在去往5,也就是说还要看楼层差,也就是相对高度来判断方向,这就是为什么直接用原来的逻辑会乱序
🕓四.改进建议
1.关于代码改进
(1)输入验证增强
可以检查外部请求的源楼层是否合法
(2) 统一请求模型
内部请求 (Passenger) 和外部请求的 (ExternalRequest) 合并为统一请求类
(3)消除重复代码
可以对whatToDisposedDNext() 中方向匹配和距离计算的逻辑进行封装
(4) 分离关注点
handleNoDirectionMatch() 方法过于臃肿,可以想办法改变算法使其更精简
2.关于测试点/样例改进
(1)把测试点细化,分的再细一点多一点,这样就能更精准的定位问题测试点没有名字,不然不知道没过的测试点到底有什么意义,是哪一块,有时候调试了很多遍还是找不出问题在哪儿
(2)给出更多的样例以方便检测程序漏洞,比如专门有一个测试样例的文件,同时在给样例的时候标注样例的不同之处,用于检测什么
✔️五.总结
1. 基础优先级规则
外部请求为空时:执行内部请求(FIFO)。
内部请求为空时:执行外部请求(FIFO),并将目标楼层转为内部请求(需去重)。
内外均非空时:根据请求方向和位置综合判断。
2. 内外请求均非空时的逻辑
大条件:内外请求在同一侧
上方同侧:内外请求楼层均 > 当前楼层。
下方同侧:内外请求楼层均 < 当前楼层。
处理规则
距离更近者优先:
若外部请求更近,需满足 方向条件:
上方同侧:外部请求方向为 UP(目标楼层 > 当前楼层)。
下方同侧:外部请求方向为 DOWN(目标楼层 < 当前楼层)。
若内部请求更近或无有效外部请求,优先内部请求。
距离相等时的特殊处理:
将外部请求的目标楼层转为内部请求(需去重),同时处理内外请求。
大条件:内外请求在异侧
电梯方向 UP:
仅处理 上方外部请求(无论其方向),转为内部请求(需去重)。
其他情况优先处理内部请求。
电梯方向 DOWN:
仅处理 下方外部请求(无论其方向),转为内部请求(需去重)。
其他情况优先处理内部请求。
3. 核心流程图解
开始
│
├── 内部空? → 处理外部请求 → 转为内部(记得去重)
│
├── 外部空? → 处理内部请求
│
└── 内外均非空 → 判断同侧/异侧
│
├── 同侧 → 比较距离 + 方向验证 → 处理更近者
│
└── 异侧 → 仅处理与电梯方向一致的异侧请求
4. 关键逻辑验证样例
场景1:电梯在5楼,方向UP
外部请求:<7,3>(楼层7,方向DOWN)
内部请求:<6>(目标6楼)
逻辑判断:
同侧(7 > 5,6 > 5)。
外部更近(7-5=2 vs 6-5=1 ❌ 外部更远)。
方向验证:外部请求方向DOWN ❌(其实需UP)。
结果:优先处理内部请求 <6>。
场景2:电梯在3楼,方向UP
外部请求:<5,9>(楼层5,方向UP)
内部请求:<4>(目标4楼)
逻辑判断:
同侧(5 > 3,4 > 3)。
外部更近(5-3=2 vs 4-3=1 ❌ 外部更远)。
方向验证:外部方向UP ✔️。
结果:优先处理内部请求 <4>。
场景3:电梯在5楼,方向DOWN
外部请求:<3,8>(楼层3,方向UP)
内部请求:<2>(目标2楼)
逻辑判断:
异侧(3 < 5,2 < 5)。
电梯方向DOWN,外部请求在下方且方向UP ❌。
结果:优先处理内部请求 <2>。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号