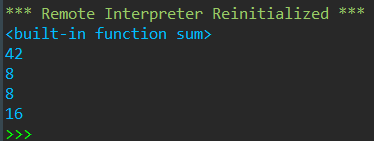
print(sum)
sum=42
print(sum)
def inc(n): sum=n+1 print(sum) return sum sum=inc(7)+inc(7) print(sum)
实验结果:
不代表同一变量名.
一:内置作用域 二:全局作用域 三:局部作用域 四:全局作用域
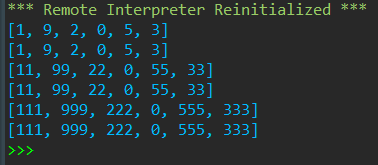
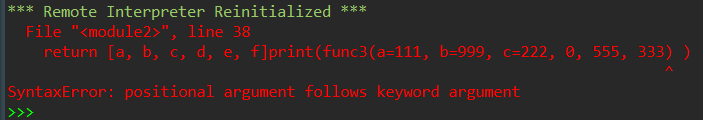
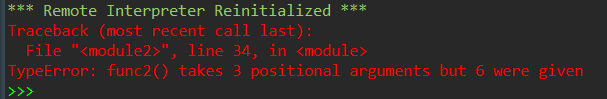
def func1(a, b, c, d, e, f): ''' 返回参数a,b,c,d,e,f构成的列表 默认,参数按位置传递; 也支持关键字传递 ''' return [a, b, c, d, e, f] def func2(a, b, c, *, d, e, f): ''' 返回参数a,b,c,d,e,f构成的列表 *后面的参数只能按关键字传递 ''' return [a, b, c, d, e, f] def func3(a, b, c, /, d, e, f): ''' 返回参数a,b,c,d,e,f构成的列表 /前面的参数只能按位置传递 ''' return [a, b, c, d, e, f] # func1调用:按位置传递、按参数传递都可以 print(func1(a=1, b=9, c=2, d=0, e=5, f=3)) print(func1(1, 9, 2, f=3, d=0, e=5)) # func2调用:d,e,f必须按关键字传递 print(func2(11, 99, 22, d=0, e=55, f=33)) print(func2(a=11, b=99, c=22, d=0, e=55, f=33)) # func3调用:a,b,c必须按位置传递 print(func3(111, 999, 222, 0, 555, 333)) print(func3(111, 999, 222, d=0, e=555, f=333))
运行结果:
list1= [1, 9, 8, 4] print( sorted(list1) ) print( sorted(list1, reverse=True) ) print( sorted(list1, True) )
运行结果:
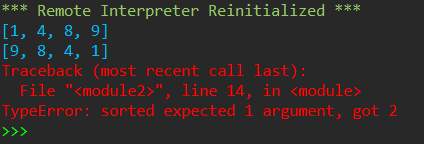
参数reverse的传递方式必须使用关键字传递
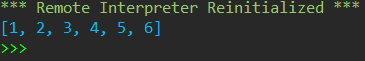
def func(a, b, c, /, *, d, e, f): return( [a,b,c,d,e,f] ) print(func(1, 2, 3, d=4, e=5, f=6))
运行结果:
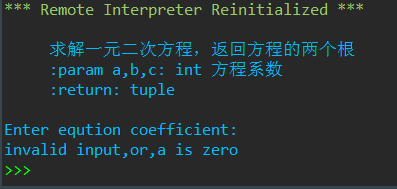
def solve(a,b,c): ''' 求解一元二次方程,返回方程的两个根 :param a,b,c: int 方程系数 :return: tuple ''' delta = b*b-4*a*c delta_sqrt = abs(delta)**0.5 p1 = -b/2/a p2 = delta_sqrt/2/a if delta>=0: root1 = p1 + p2 root2 = p1 - p2 else: root1 = complex(p1,p2) root2 = complex(p1,-p2) return root1,root2 while True: try: a,b,c = eval(input('Enter eqution coefficient:')) if a == 0: raise except: print('invalid input,or,a is zero') break else: root1,root2 = solve(a,b,c) print(f'root1 = {root1:.2f},root2 = {root2:.2f}') print()
运行结果:
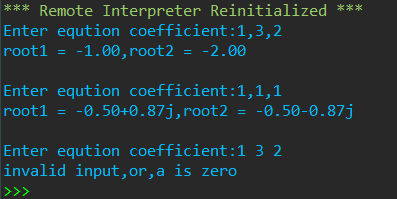
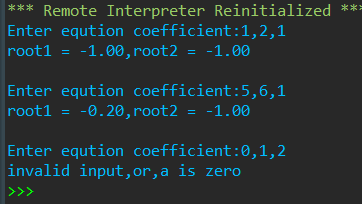
加一行代码
print(solve.__doc__)
运行结果:
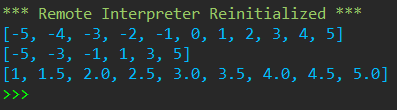
def list_generator(x,y,step=1): list4=[] while x<=y: list4.append(x) x+=step return list4 list1=list_generator(-5, 5) print(list1) list2=list_generator(-5, 5, 2) print(list2) list3=list_generator(1, 5, 0.5) print(list3)
运行结果:
def is_prime(x):
if x<=1:
return False
for i in range(2, int(x**0.5)+1):
if x % i==0 :
return False
else:
return True
for y in range(2,21,2):
for j in range(2,y):
if is_prime(y-j) and is_prime(j):
print(f'{y}={j}+{y-j}')
运行结果:
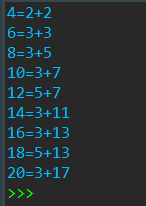
def encoder(s): ls = [] for i in s: x = ord(i) if (x>=97 and x<=117) or (x>=65 and x<=85): ls.append(chr(x+5)) if (x>=86 and x<=90) or (x>=118 and x<=122): ls.append(chr(x-21)) if x<65 or x>122: ls.append(chr(x)) return ''.join(ls) def decoder(s): ls = [] for i in s: x = ord(i) if (x >= 102 and x <= 122) or (x >= 70 and x <= 90): ls.append(chr(x - 5)) if (x >= 65 and x <= 69) or (x >= 97 and x <= 101): ls.append(chr(x+21)) if x < 65 or x > 122: ls.append(chr(x)) return ''.join(ls) x = input('输入英文文本: ') s = encoder(x) print(f'编码后的文本:{s}') print(f'对编码后的文本解码:{decoder(s)}')
运行结果:

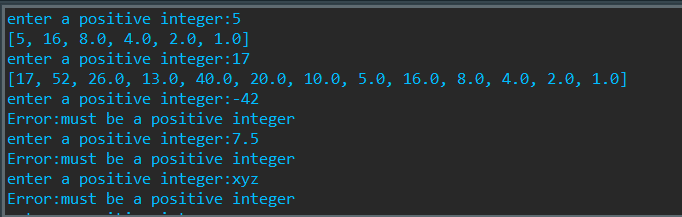
def collatz(n): if n%2 == 0: return n/2 elif n%2!=0: return n*3+1 while True: l = [] try: x = eval(input('enter a positive integer:')) if type(x) is not int or x <= 0: raise NameError except NameError: print('Error:must be a positive integer') else: while x>1: l.append(x) x = collatz(x) l.append(x) print(l)
运行结果:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号