Java数据结构——二叉树



1.二叉树的遍历
前序遍历——根 左 右
中序遍历——左 根 右
后序遍历——左 右 根
2.二叉树的实现
class Stack_BinaryTree{
private int maxSize; //栈的长度
private Node[] stackArray; //创建栈的数组的引用
private int top; //创建栈顶的引用
public Stack_BinaryTree(int s) { //构造函数
this.maxSize = s;
stackArray = new Node[maxSize]; //创建对象
top = -1; //栈顶等于-1
}
public void push(Node j){ //入栈操作
stackArray[++top] = j; //先把top=-1自加成0,再入栈
}
public Node pop(){
return stackArray[top--]; //弹出当前栈顶的元素后,再自减
}
public Node peek(){
return stackArray[top]; //返回当前栈顶的元素
}
public boolean isEmpty(){ //栈顶为-1,即栈为空
return (top == -1);
}
public boolean isFull(){ //栈顶为maxSize-1,即栈为满
return (top == maxSize-1);
}
}
class Node{
int iData;
double fData;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public void display(){
System.out.println('{');
System.out.println(iData);
System.out.println(',');
System.out.println(fData);
System.out.println('}');
}
}
class Tree{
public Node root;
public Tree(){
root = null;
}
public Node find(int key){ //查找关键字的节点
Node current = root;
while(current.iData != key){ //不等于就一直循环
if(key<current.iData){
current = current.leftChild;
}else{
current = current.rightChild;
}
if(current == null){
return null;
}
}
return current;
}
public void insert(int id,double dd){ //插入新的节点
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.iData = id;
newNode.fData = dd;
if(root == null){
root = newNode;
}else{
Node current = root;
Node parent;
while(true){
parent = current;
if(newNode.iData<current.iData){ //如果插入的节点的数据小于当前节点的数据
current = current.leftChild;
if(current == null){
parent.leftChild = newNode; //把父亲节点的左孩子设为新节点
return;
}
}else{ //如果插入的节点的数据大于当前节点的数据
current = current.rightChild;
if(current == null){
parent.rightChild = newNode; //把父亲节点的右孩子设为新节点
return;
}
}
}
}
}
public void displayTree(){ //显示整个二叉树
Stack_BinaryTree globalStack = new Stack_BinaryTree(128); //用来放置每一层的二叉树
globalStack.push(root); //入栈
int nBlanks = 32;
boolean isRowEmpty = false;
System.out.println(".............................................");
while(isRowEmpty==false){
Stack_BinaryTree localStack = new Stack_BinaryTree(128); //用来放置下一层的二叉树
isRowEmpty = true;
for(int j=0;j<nBlanks;j++){
System.out.print(' ');
}
while(globalStack.isEmpty()==false){ //当globalStack不为空,就一直出栈
Node temp = (Node)globalStack.pop(); //temp等于globalStack出栈的节点
if(temp!=null){
System.out.print(temp.iData); //当当前的节点不为空的时候,输出节点的值
localStack.push(temp.leftChild); //入栈globalStack的左孩子到下一层
localStack.push(temp.rightChild); //入栈globalStack的右孩子到下一层
if(temp.leftChild != null || temp.rightChild != null){
isRowEmpty = false; //只要有一个子节点不为空,就把isRowEmpty置为false
}
}
else{ //否则输出--,并把下一层置为空
System.out.print("--");
localStack.push(null);
localStack.push(null);
}
for(int j=0;j<nBlanks*2-2;j++){
System.out.print(' ');
}
}
System.out.println();
nBlanks /= 2; //输出的空格数减半
while(localStack.isEmpty() == false){
globalStack.push(localStack.pop()); //还原本来的层
}
}
System.out.println(".............................................");
}
public void preOrder(Node localRoot){ //前序遍历
if(localRoot != null){
System.out.print(localRoot.iData+" ");
preOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
preOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
}
}
public void inOrder(Node localRoot){ //中序遍历
if(localRoot != null){
inOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
System.out.print(localRoot.iData+" ");
inOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
}
}
public void postOrder(Node localRoot){ //后序遍历
if(localRoot != null){
postOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
postOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
System.out.print(localRoot.iData+" ");
}
}
public Node minimum(){ //找到最小的节点
Node current;
Node last = null;
current = root;
while(current != null){
last = current;
current = current.leftChild;
}
return last;
}
public Node maxmum(){ //找到最大的节点
Node current;
Node last = null;
current = root;
while(current != null){
last = current;
current = current.rightChild;
}
return last;
}
public boolean delete(int key){
Node current = root;
Node parent = root;
boolean isLeftChild = true;
while(current.iData != key){//查找要删除的节点,并把其置为current,如果没有返回null
parent = current;
if(key<current.iData){
current = current.leftChild;
isLeftChild = true; //当前current节点的parent节点有左孩子节点
}else{
current = current.rightChild;
isLeftChild = false; //当前current节点的parent节点没有左孩子节点
}
if(current == null){
return false;
}
}
//进入以下的时候,说明current已经匹配到要删除的节点
//如果匹配的current节点没有孩子节点
if(current.leftChild == null && current.rightChild == null){
if(current == root){ //如果这个节点就是根节点
root = null;
}else if(isLeftChild){
parent.leftChild = null; //父节点断开左孩子节点
}else{
parent.rightChild = null; //父节点断开右孩子节点
}
}
//如果current没有右孩子,则要把左子树上移
else if(current.rightChild == null){
if(current == root){ //如果是根节点
root = current.leftChild;
}else if(isLeftChild){ //如果current节点是左孩子,则把current的左孩子放到parent的左孩子位置
parent.leftChild = current.leftChild;
}else{ //如果current节点是右孩子,则把current的左孩子放到parent的右孩子位置
parent.rightChild = current.leftChild;
}
}
//如果current没有左孩子,则要把右子树上移
else if(current.leftChild == null){
if(current == root){ //如果是根节点
root = current.rightChild;
}else if(isLeftChild){ //如果current节点是左孩子,则把current的右孩子放到parent的左孩子位置
parent.leftChild = current.rightChild;
}else{ //如果current节点是右孩子,则把current的右孩子放到parent的右孩子位置
parent.rightChild = current.rightChild;
}
}
//如果current有左右孩子
else{
Node successor = getSuccessor(current);
if(current == root){ //如果要删除的节点是根节点
root = successor;
}else if(isLeftChild){ //如果要删除的节点是左孩子
parent.leftChild = successor;
}else{ //如果要删除的节点是右孩子
parent.rightChild = successor;
}
successor.leftChild = current.leftChild;//把最小的值的节点连接到要删除节点的左子树上
}
return true;
}
private Node getSuccessor(Node delNode){
Node successorParent = delNode;
Node successor = delNode;
Node current = delNode.rightChild;
while(current != null){ //循环,直到返回右子树中最小的值
successorParent = successor;
successor = current;
current = current.leftChild;
}
if(successor != delNode.rightChild){
successorParent.leftChild = successor.rightChild; //把最小的值的右孩子放到该最小值的位置
successor.rightChild = delNode.rightChild; //把最小的值连接到要删除的节点的右子树上
}
return successor;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
int value;
Tree theTree = new Tree();
theTree.insert(50, 1.5);
theTree.insert(25, 1.4);
theTree.insert(75, 1.3);
theTree.insert(12, 1.6);
theTree.insert(37, 1.7);
//theTree.insert(43, 1.2);
theTree.insert(60, 1.1);
theTree.insert(85, 1.1);
theTree.insert(77, 1.1);
theTree.displayTree();
System.out.println("查找节点的值:"+theTree.find(77).iData);
theTree.preOrder(theTree.root);
System.out.println();
theTree.inOrder(theTree.root);
System.out.println();
theTree.postOrder(theTree.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("最小的节点:"+theTree.minimum().iData);
System.out.println("最大的节点:"+theTree.maxmum().iData);
theTree.delete(75);
theTree.displayTree();
}
}
3.树、森林和二叉树之间的转换
树转换为二叉树
1. 加线
在所有兄弟结点之间加一条连线。
2. 去线
树中的每个结点,只保留它与第一个孩子结点的连线,删除它与其它孩子结点之间的连线。
3. 层次调整
以树的根节点为轴心,将整棵树顺时针旋转一定角度,使之结构层次分明。(注意第一个孩子是结点的左孩子,兄弟转换过来的孩子是结点的右孩子)

森林转换为二叉树
1. 把每棵树转换为二叉树。
2. 第一棵二叉树不动,从第二棵二叉树开始,依次把后一棵二叉树的根结点作为前一棵二叉树的根结点的右孩子,用线连接起来。

二叉树转换为树
是树转换为二叉树的逆过程。
1. 加线
若某结点X的左孩子结点存在,则将这个左孩子的右孩子结点、右孩子的右孩子结点、右孩子的右孩子的右孩子结点…,都作为结点X的孩子。将结点X与这些右孩子结点用线连接起来。
2. 去线
删除原二叉树中所有结点与其右孩子结点的连线。
3. 层次调整。

二叉树转换为森林
假如一棵二叉树的根节点有右孩子,则这棵二叉树能够转换为森林,否则将转换为一棵树。
1. 从根节点开始,若右孩子存在,则把与右孩子结点的连线删除。再查看分离后的二叉树,若其根节点的右孩子存在,则连线删除…。直到所有这些根节点与右孩子的连线都删除为止。
2. 将每棵分离后的二叉树转换为树。

4.平衡二叉树的平衡因子
若向平衡二叉树中插入一个新结点后破坏了平衡二叉树的平衡性。首先要找出插入新结点后失去平衡的最小子树根结点的指针。然后再调整这个子树中有关结点之间的链接关系,使之成为新的平衡子树。当失去平衡的最小子树被调整为平衡子树后,原有其他所有不平衡子树无需调整,整个二叉排序树就又成为一棵平衡二叉树。
失去平衡的最小子树是指以离插入结点最近,且平衡因子绝对值大于 1 的结点作为根的子树。假设用 A 表示失去平衡的最小子树的根结点,则调整该子树的操作可归纳为下列四种情况。
( 1 ) LL 型平衡旋转法
由于在 A 的左孩子 B 的左子树上插入结点 F ,使 A 的平衡因子由 1 增至 2 而失去平衡。故需进行一次顺时针旋转操作。 即将 A 的左孩子 B 向右上旋转代替 A 作为根结点, A 向右下旋转成为 B 的右子树的根结点。而原来 B 的右子树则变成 A 的左子树。
( 2 ) RR 型平衡旋转法
由于在 A 的右孩子 C 的右子树上插入结点 F ,使 A 的平衡因子由 -1 减至 -2 而失去平衡。故需进行一次逆时针旋转操作。即将 A 的右孩子 C 向左上旋转代替 A 作为根结点, A 向左下旋转成为 C 的左子树的根结点。而原来 C 的左子树则变成 A 的右子树。
( 3 ) LR 型平衡旋转法
由于在 A 的左孩子 B 的右子数上插入结点 F ,使 A 的平衡因子由 1 增至 2 而失去平衡。故需进行两次旋转操作(先逆时针,后顺时针)。即先将 A 结点的左孩子 B 的右子树的根结点 D 向左上旋转提升到 B 结点的位置,然后再把该 D 结点向右上旋转提升到 A 结点的位置。即先使之成为 LL 型,再按 LL 型处理 。
如图中所示,即先将圆圈部分先调整为平衡树,然后将其以根结点接到 A 的左子树上,此时成为 LL 型,再按 LL 型处理成平衡型。
( 4 ) RL 型平衡旋转法
由于在 A 的右孩子 C 的左子树上插入结点 F ,使 A 的平衡因子由 -1 减至 -2 而失去平衡。故需进行两次旋转操作(先顺时针,后逆时针),即先将 A 结点的右孩子 C 的左子树的根结点 D 向右上旋转提升到 C 结点的位置,然后再把该 D 结点向左上旋转提升到 A 结点的位置。即先使之成为 RR 型,再按 RR 型处理。
如图中所示,即先将圆圈部分先调整为平衡树,然后将其以根结点接到 A 的左子树上,此时成为 RR 型,再按 RR 型处理成平衡型。
平衡化靠的是旋转。 参与旋转的是 3 个节点(其中一个可能是外部节点 NULL ),旋转就是把这 3 个节点转个位置。注意的是,左旋的时候 p->right 一定不为空,右旋的时候 p->left 一定不为空,这是显而易见的。
如果从空树开始建立,并时刻保持平衡,那么不平衡只会发生在插入删除操作上,而不平衡的标志就是出现 bf == 2 或者 bf == -2 的节点。
5.树的三种存储结构
(转自http://blog.csdn.net/x1247600186/article/details/24670775)
说到存储结构,我们就会想到常用的两种存储方式:顺序存储和链式存储两种。
先来看看顺序存储,用一段地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中数据元素,这对于线性表来说是很自然的,但是对于树这种一对多的结构而言是否适合呢?
树中某个结点的孩子可以有多个,这就意味着,无论用哪种顺序将树中所有的结点存储到数组中,结点的存储位置都无法直接反映逻辑关系,试想一下,数据元素挨个存储,那么谁是谁的双亲,谁是谁的孩子呢?所以简单的顺序存储是不能满足树的实现要求的。
不过可以充分利用顺序存储和链式存储结构的特点,完全可以实现对树的存储结构的表示。
下面介绍三种不同的树的表示法:双亲表示法,、孩子表示法,、孩子兄弟表示法。
1、双亲表示法:
我们假设以一组连续空间存储树的结点,同时在每个结点中,附设一个指示器指向其双亲结点到链表中的位置。也就是说每个结点除了知道自己之外还需要知道它的双亲在哪里。
它的结构特点是如图所示:

以下是我们的双亲表示法的结构定义代码:
/*树的双亲表示法结点结构定义 */
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType; //树结点的数据类型,暂定为整形
typedef struct PTNode //结点结构
{
ElemType data; //结点数据
int parent; //双亲位置
}PTNode;
typedef struct
{
PTNode nodes[MAXSIZE]; //结点数组
int r,n; //根的位置和结点数
}PTree;
2、孩子表示法
换一种不同的考虑方法。由于每个结点可能有多棵子树,可以考虑使用多重链表,即每个结点有多个指针域,其中每个指针指向一棵子树的根结点,我们把这种方法叫做多重链表表示法。不过树的每个结点的度,也就是它的孩子个数是不同的。所以可以设计两种方案来解决。
方案一:
一种是指针域的个数就等于树的度(树的度是树的各个结点度的最大值)
其结构如图所示:
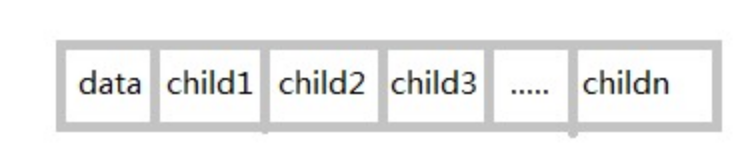
不过这种结构由于每个结点的孩子数目不同,当差异较大时,很多结点的指针域就都为空,显然是浪费空间的,不过若树的各结点度相差很小时,那就意味着开辟的空间都被利用了,这时这种缺点反而变成了优点。
方案二:
第二种方案是每个结点指针域的个数等于该结点的度,我们专门取一个位置来存储结点指针域的个数。
其结构如图所示:
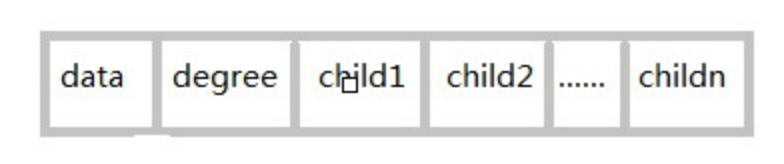
这种方法克服了浪费空间的缺点,对空间的利用率是很高了,但是由于各个结点的链表是不相同的结构,加上要维护结点的度的数值,在运算上就会带来时间上的损耗。
能否有更好的方法呢,既可以减少空指针的浪费,又能是结点结构相同。
说到这大家肯定就知道是有的麦,那就是孩子表示法。
具体办法是,把每个结点的孩子排列起来,以单链表做存储结构,则n个结点有n个孩子链表,如果是叶子结点则此单链表为空。然后n个头指针有组成一个线性表,采用顺序存储结构,存放进入一个一维数组中。
为此,设计两种结点结构,
一个是孩子链表的孩子结点,如下所示:

其中child是数据域,用来存储某个结点在表头数组中的下标。next是指针域,用来存储指向某结点的下一个孩子结点的指针。
另一个是表头结点,如下所示:
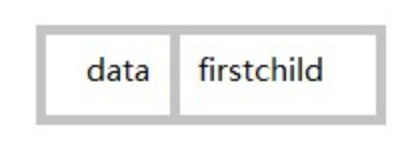
其中data是数据域,存储某结点的数据信息。firstchild是头指针域,存储该结点的孩子链表的头指针。
以下是孩子表示法的结构定义代码:
/*树的孩子表示法结点结构定义 */
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType; //树结点的数据类型,暂定为整形
typedef struct CTNode //孩子结点
{
int child;
struct CTNode *next;
}*ChildPtr;
typedef struct //表头结构
{
ElemType data;
ChildPtr firstchild;
}CTBox;
typedef struct //树结构
{
CTBox nodes[MAXSIZE]; //结点数组
int r,n; //根结点的位置和结点数
}CTree;
3、孩子兄弟表示法
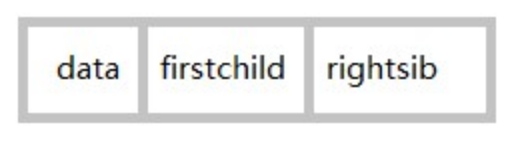
我们发现,任意一颗树,它的结点的第一个孩子如果存在就是的,它的右兄弟如果存在也是唯一的。因此,我们设置两个指针,分别指向该结点的第一个孩子和此结点的右兄弟。
其结点结构如图所示:
以下是孩子兄弟表示法的结构定义代码:
/*树的孩子兄弟表示法结构定义 */
typedef struct CSNode
{
ElemType data;
struct CSNode *firstchild, *rightsib;
}CSNode, *CSTree;
本文只发表于博客园和tonglin0325的博客,作者:tonglin0325,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tonglin0325/p/5379021.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号