李沐动手学深度学习V2-chapter_convolutional-modern
李沐动手学深度学习V2
文章内容说明
本文主要是自己学习过程中的随手笔记,需要自取
课程参考B站:https://space.bilibili.com/1567748478?spm_id_from=333.788.0.0
课件等信息原视频简介中有
卷积神经网络
经典卷积神经网络LeNet
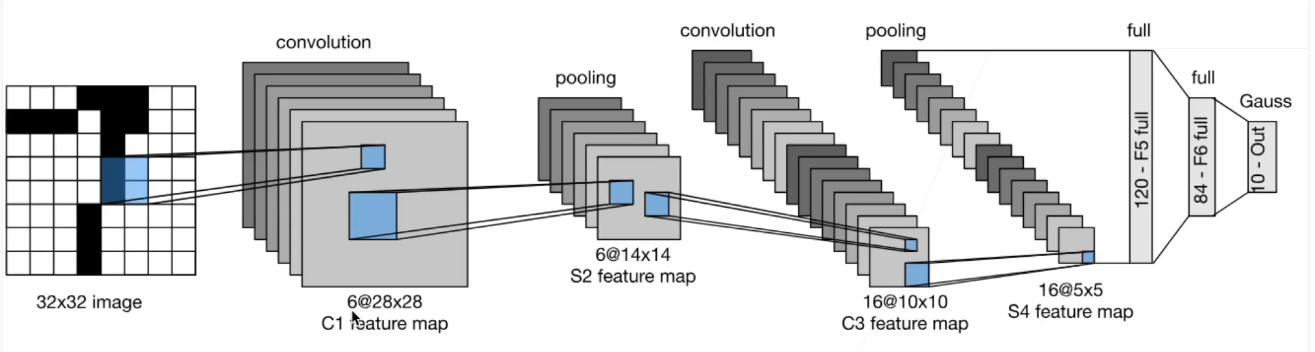

深度卷积神经网络AlexNet
AlexNet与LeNet对比:

1.AlexNet比相对较小的LeNet5要深得多。AlexNet由八层组成:五个卷积层、两个全连接隐藏层和一个全连接输出层。
2.AlexNet使用ReLU而不是sigmoid作为其激活函数。
CODE
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
net = nn.Sequential(
# 这里使用一个11*11的更大窗口来捕捉对象。
# 同时,步幅为4,以减少输出的高度和宽度。
# 另外,输出通道的数目远大于LeNet
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 使用三个连续的卷积层和较小的卷积窗口。
# 除了最后的卷积层,输出通道的数量进一步增加。
# 在前两个卷积层之后,汇聚层不用于减少输入的高度和宽度
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
# 这里,全连接层的输出数量是LeNet中的好几倍。使用dropout层来减轻过拟合
nn.Linear(6400, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
# 最后是输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Linear(4096, 10))
# 观察每一层输出形状
X = torch.randn(1, 1, 224, 224)
for layer in net:
X=layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)
# 读取数据集Fashion-MNIST
batch_size = 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
#训练
lr, num_epochs = 0.01, 10
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())
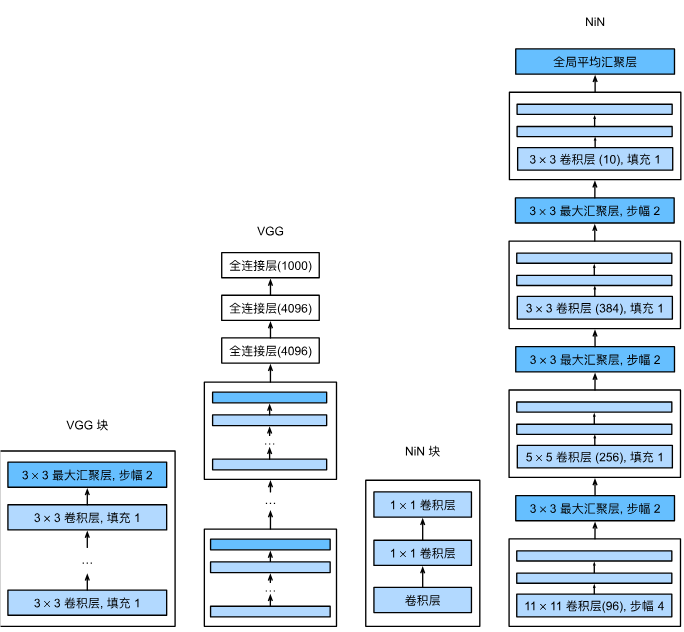
使用块的网络VGG

可以多个VGG块串一起组建更深的网络,块中的3×3卷积层可以n次

CODE
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
# VGG块
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
layers = []
for _ in range(num_convs):
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
# VGG网络_VGG-11(多个块串在一起)
conv_arch = ((1, 64), (1, 128), (2, 256), (2, 512), (2, 512))
def vgg(conv_arch):
conv_blks = []
in_channels = 1
# 卷积层部分
for (num_convs, out_channels) in conv_arch:
conv_blks.append(vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(
*conv_blks, nn.Flatten(),
# 全连接层部分
nn.Linear(out_channels * 7 * 7, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 10))
net = vgg(conv_arch)
# 观察每层输出情况
X = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224, 224))
for blk in net:
X = blk(X)
print(blk.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)
# 训练模型
# 减少通道数(计算量大故减少)
ratio = 4
small_conv_arch = [(pair[0], pair[1] // ratio) for pair in conv_arch]
net = vgg(small_conv_arch)
# 训练
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.05, 10, 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())

网络中的网络NiN
全连接层参数太多了,nin直接用卷积层替代全连接层,通过步长为2的池化层减半大小
CODE
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
# nin块
def nin_block(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, strides, padding):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, strides, padding),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1), nn.ReLU())
# nin网络模型
net = nn.Sequential(
nin_block(1, 96, kernel_size=11, strides=4, padding=0),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nin_block(96, 256, kernel_size=5, strides=1, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nin_block(256, 384, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding=1),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
# 标签类别数是10
nin_block(384, 10, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding=1),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
# 将四维的输出转成二维的输出,其形状为(批量大小,10)
nn.Flatten())
# 每个块输出形状
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 224, 224))
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t', X.shape)
# 训练模型
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.1, 10, 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())

含并行连结的网络GoogleNet/Inception V3
Inception块(盗梦空间inception)
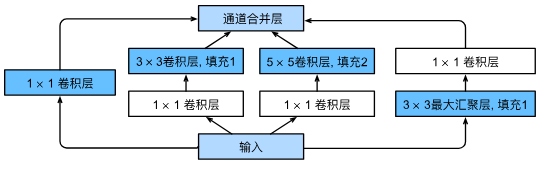
GoogLeNet模型(模型参数小,内存少)
用了9个inception块,其中构造不一,详细看视频讲解

CODE
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
# Inception块
class Inception(nn.Module):
# c1--c4是每条路径的输出通道数
def __init__(self, in_channels, c1, c2, c3, c4, **kwargs):
super(Inception, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# 线路1,单1x1卷积层
self.p1_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c1, kernel_size=1)
# 线路2,1x1卷积层后接3x3卷积层
self.p2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c2[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p2_2 = nn.Conv2d(c2[0], c2[1], kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 线路3,1x1卷积层后接5x5卷积层
self.p3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c3[0], kernel_size=1)
self.p3_2 = nn.Conv2d(c3[0], c3[1], kernel_size=5, padding=2)
# 线路4,3x3最大汇聚层后接1x1卷积层
self.p4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.p4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c4, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
p1 = F.relu(self.p1_1(x))
p2 = F.relu(self.p2_2(F.relu(self.p2_1(x))))
p3 = F.relu(self.p3_2(F.relu(self.p3_1(x))))
p4 = F.relu(self.p4_2(self.p4_1(x)))
# 在通道维度上连结输出
return torch.cat((p1, p2, p3, p4), dim=1)
# 实现GoogLeNet模型每个模块
b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b3 = nn.Sequential(Inception(192, 64, (96, 128), (16, 32), 32),
Inception(256, 128, (128, 192), (32, 96), 64),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b4 = nn.Sequential(Inception(480, 192, (96, 208), (16, 48), 64),
Inception(512, 160, (112, 224), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 128, (128, 256), (24, 64), 64),
Inception(512, 112, (144, 288), (32, 64), 64),
Inception(528, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
b5 = nn.Sequential(Inception(832, 256, (160, 320), (32, 128), 128),
Inception(832, 384, (192, 384), (48, 128), 128),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)),
nn.Flatten())
net = nn.Sequential(b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, nn.Linear(1024, 10))
# 输出形状变化
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 96, 96))
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t', X.shape)
# 训练模型
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.1, 10, 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())

ResNet残差网络
为防止越大的模型偏离最优值
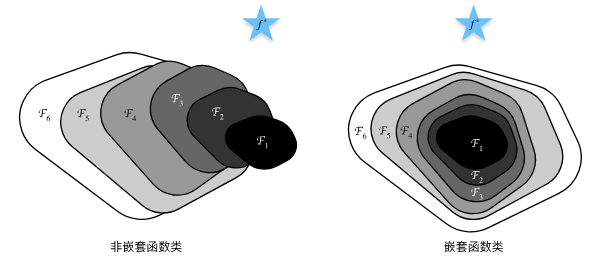
使其变为f(x) = x + g(x)
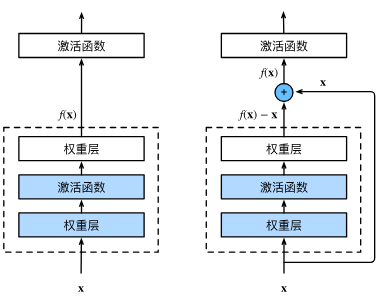

下面为ResNet-18架构,4个由残差块组成的模块
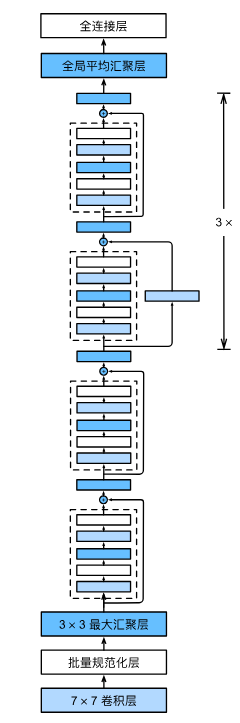
CODE
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
class Residual(nn.Module): #@save
def __init__(self, input_channels, num_channels,
use_1x1conv=False, strides=1):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=strides)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=strides)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.bn2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3:
X = self.conv3(X)
Y += X
return F.relu(Y)
# 输入输出形状一致情况
blk = Residual(3,3)
X = torch.rand(4, 3, 6, 6)
Y = blk(X)
Y.shape
# 增加输出通道数的同时,减半输出的高和宽
blk = Residual(3,6, use_1x1conv=True, strides=2)
blk(X).shape
# ResNet模型
b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
def resnet_block(input_channels, num_channels, num_residuals,
first_block=False):
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(Residual(input_channels, num_channels,
use_1x1conv=True, strides=2))
else:
blk.append(Residual(num_channels, num_channels))
return blk
# 在ResNet加入所有残差块,这里每个模块使用2个残差块
b2 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
b3 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
b4 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
b5 = nn.Sequential(*resnet_block(256, 512, 2))
net = nn.Sequential(b1, b2, b3, b4, b5,
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)),
nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(512, 10))
# 输出形状变化
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 224, 224))
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t', X.shape)
# 模型训练
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.05, 10, 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=96)
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号