从JAVA源码可以得出有6种状态
NEW、RUNNABLE、BLOCKED、WAITING、TIME_WAITING、TERMINATED
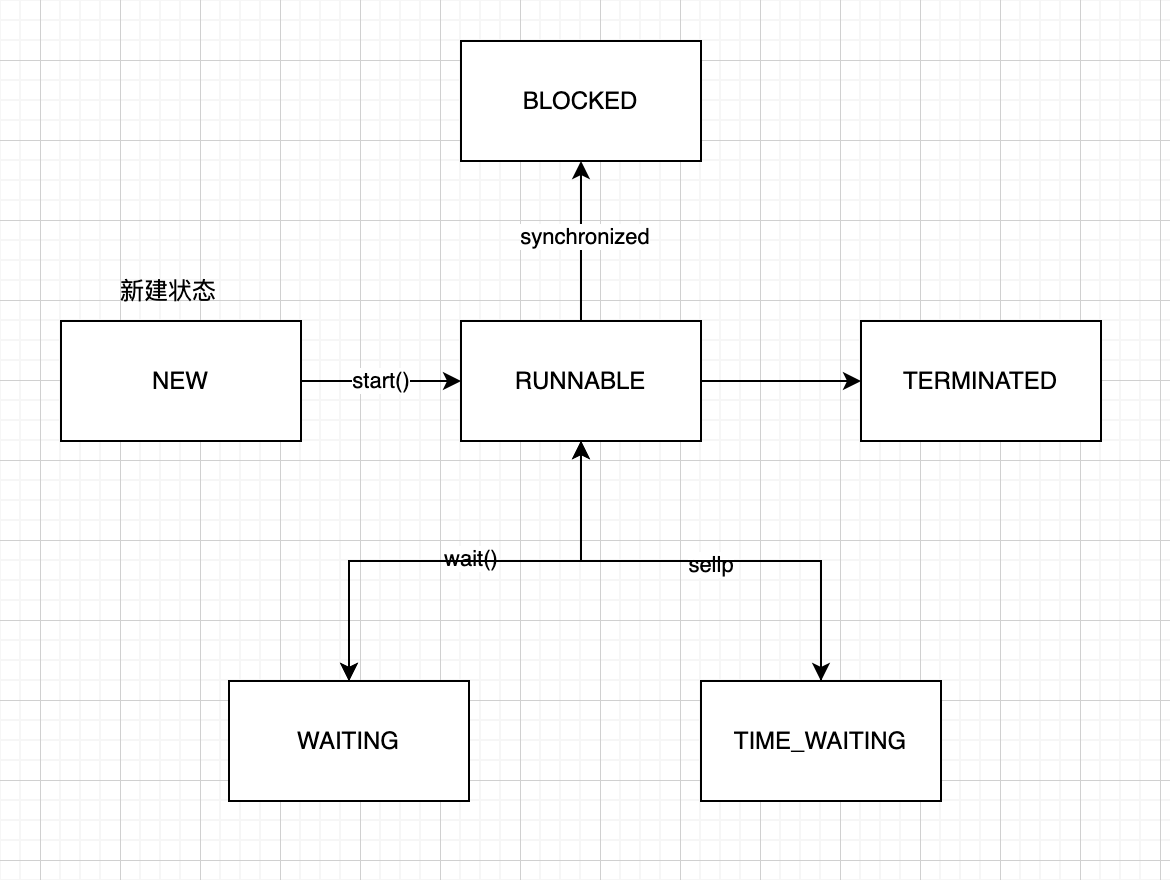
通过代码解释说明
- 初始化状态是NEW
执行结果public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {}); System.out.println(thread.getState()); }NEW - 运行过程的状态是RUNABLE
执行结果的确是RUNNABLEpublic static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { } }); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println(thread.getState()); }RUNNABLE - 主线程被上锁了,创建的线程无法获取锁,此时的状态是BLOCKED
执行结果是BLOCKEDpublic class ThreadStatus { public static Object obj = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (obj) { while (true){ } } }); // 此时住线程持有锁 synchronized (obj){ // 开启新的线程,因为主线程持有锁所以拿不到锁被阻塞 thread.start(); Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println(thread.getState()); } } }BLOCKED - 当创建的线程持有锁时状态是WAITING,
执行结果是public class ThreadStatus { public static Object obj = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Object obj = new Object(); Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { synchronized (obj) { // 步骤2:新线程获取锁 try { obj.wait(); // 步骤3:释放锁,进入WAITING状态 } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } // 步骤6:被唤醒后重新获取锁,继续执行 } }); thread.start(); // 步骤1:启动新线程 Thread.sleep(500); // 步骤4:主线程睡眠 System.out.println(thread.getState()); // 输出:WAITING synchronized (obj) { // 步骤5:主线程可以获取锁(因为新线程已释放) obj.notify(); // 唤醒新线程 } // 主线程释放锁 Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println(thread.getState()); // 输出:TERMINATED } }WAITING TERMINATED - 当线程处于休眠(sleep())中,状态即为TIMED_WAITING
执行结果是public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println(thread.getState()); }TIMED_WAITING - 线程执行结束后状态即为TERMINATED
执行结果public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println(thread.getState()); }TERMINATED



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号