unsorted_segment_sum源码追溯
unsorted_segment_sum
在tensorflow中遇到了unsorted_segment_sum作用差不多的几个算子,追溯了一下源码,mark一下。
tf.math.unsorted_segment_sum版本
tf.math.unsorted_segment_sum(
data, # <tf.Tensor 'wide_deep/deep/mul_4:0' shape=(?, ?, 32) dtype=float32>
segment_ids,# <tf.Tensor 'wide_deep/deep/add_4:0' shape=(?, ?) dtype=int64>
num_segments,# <tf.Tensor 'wide_deep/deep/Cast_9:0' shape=() dtype=int64>
name=None # None
)
参数解释:
data :
A
Tensor. Must be one of the following types:float32,float64,int32,uint8,int16,int8,complex64,int64,qint8,quint8,qint32,bfloat16,uint16,complex128,half,uint32,uint64.
segment_ids : 分段索引数组,shape要求是data.shape的前缀。
A
Tensor. Must be one of the following types:int32,int64. A tensor whose shape is a prefix ofdata.shape.
num_segments : 分段数目。
A
Tensor. Must be one of the following types:int32,int64.
name :
A name for the operation (optional).
返回:类型与data相同,维度为(num_segments, data.shape(segment_ids.dims()), ... ,data.shape(data.dims()))
A
Tensor. Has the same type asdata.
作用
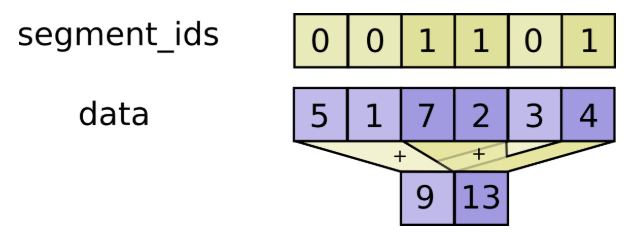
c = tf.constant([[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8], [4,3,2,1]])
tf.unsorted_segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1, 0]), num_segments=2)
# ==> [[ 0所属分段和 ], [ 1所属分段和 ]]
# ==> [[ c[0] + c[2]], [c1]]
# ==> [[ 5, 5, 5, 5], [5, 6, 7, 8]]
实现
tensorflow 1.14.0版本python端:
tensorflow/python/ops/gen_math_ops.py(11767)unsorted_segment_sum()
gen_math_ops.py是编译后生成的python文件,实际上是通过_pywrap_tensorflow.TFE_Py_FastPathExecute调用C++代码:
tensorflow/core/ops/math_ops.cc(1252)REGISTER_OP("UnsortedSegmentSum")
UnsortedSegmentSum类比较复杂,且有多个版本,这里以GPU版本为例,首先通过REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL_UNSORTEDSEGMENT间接定义:
tensorflow/core/kernels/segment_reduction_ops.cc(584)REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL_UNSORTEDSEGMENT("UnsortedSegmentSum", type, index_type, functor::Zero<type>, functor::SumOpGpu<type>)
REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL_UNSORTEDSEGMENT宏最终通过REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER调用UnsortedSegmentReductionOp类:
tensorflow/core/kernels/segment_reduction_ops.cc(467)class UnsortedSegmentReductionOp
具体实现在Compute函数中:
tensorflow/core/kernels/segment_reduction_ops.cc(472)Compute()
在REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL_UNSORTEDSEGMENT中指定了DeviceReductionFunctor为functor::UnsortedSegmentFunctor这里直接调用:
tensorflow\core\kernels\segment_reduction_ops_gpu.cu.cc(176)struct UnsortedSegmentFunctor
UnsortedSegmentFunctor调用了两个CUDA kernel:
第一个kernel为 SetToValue设定返回tensor的值全0(functor::Zero,在REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL_UNSORTEDSEGMENT指定的):
tensorflow/core/util/gpu_device_functions.h(472)SetToValue()
tensorflow/core/kernels/segment_reduction_ops.h(107)struct Zero
第二个kernel为UnsortedSegmentCustomKernel对每个元素调用functor::SumOpGpu(REGISTER_GPU_KERNEL_UNSORTEDSEGMENT指定的):
tensorflow/core/kernels/segment_reduction_ops_gpu.cu.cc(109)UnsortedSegmentCustomKernel()
tensorflow/core/kernels/segment_reduction_ops.h(72)struct SumOpGpu
实际上就是对每个元素调用CudaAtomicAdd函数。
C++代码文件.cc等都只能在编译前的源码中找到,编译后成了.so文件。
tf.scatter_add版本
tf.scatter_add(
ref, # <tf.Tensor 'wide_deep/deep/transpose:0' shape=(32, ?, 6) dtype=float32>
indices, # <tf.Tensor 'wide_deep/deep/transpose_1:0' shape=(32, ?, ?) dtype=int64>
updates, # <tf.Tensor 'wide_deep/deep/mul_4:0' shape=(?, ?, 32) dtype=float32>
use_locking=False, #False
name=None #None
)
参数解释
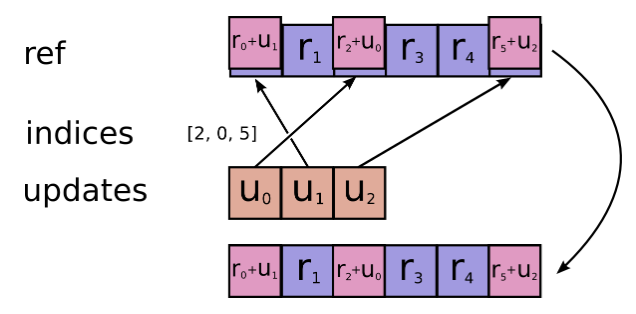
ref: 目标值,类型与updates相同,这里输入为全0 tensor,。
A
Variable.
indices: 索引id,与data中的元素一一对应,表示updates要加到ref中的哪个位置。
A
Tensor. Must be one of the following types:int32,int64. A tensor of indices into the first dimension ofref.
updates: 即data,维度与indices相同。A Tensor.
Must have the same type as
ref.A tensor of updated values to store inref.
use_locking: ref+=updates时是否加锁。
An optional
bool. Defaults toFalse. If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
name:
A name for the operation (optional).
返回:
Same as
ref. Returned as a convenience for operations that want to use the updated values after the update is done.
限制:
updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]
作用
# Scalar indices
ref[indices, ...] += updates[...]
# Vector indices (for each i)
ref[indices[i], ...] += updates[i, ...]
# High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] += updates[i, ..., j, ...]
实现
tensorflow 1.14.0版本python端:
tensorflow/python/ops/gen_state_ops.py(719)scatter_add()
gen_state_ops.py是编译后生成的python文件,实际上是通过_op_def_lib._apply_op_helper调用C++代码:
tensorflow/core/ops/state_ops.cc(146)REGISTER_OP("ScatterAdd")
ScatterAdd类的实现比较复杂,该class并不是直接定义的,而是通过REGISTER_SCATTER_KERNEL间接定义的:
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_op.cc(256)REGISTER_SCATTER_KERNEL(type, dev, "ScatterAdd", scatter_op::UpdateOp::ADD);
该宏定义最终通过REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER调用ScatterUpdateOp类:
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_op.cc(73)class ScatterUpdateOp
具体实现在Compute中:
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_op.cc(84)Compute()
而Compute只是判断是否加锁并最终调用DoCompute函数:
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_op.cc(97)DoCompute()
DoCompute函数其实也只是检查参数,具体实现由functor::ScatterFunctor,只看GPU版本的实现:
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_functor_gpu.cu.h(118)struct ScatterFunctor
该算子只调用了一个CUDA kernel scatter_op_gpu::ScatterOpCustomKernel:
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_functor_gpu.cu.h(73)ScatterOpCustomKernel()
该kernel对每一个元素调用ScatterOpKernelBody运算,这里调用的是scatter_op::UpdateOp::ADD版本(REGISTER_SCATTER_KERNEL指定的):
tensorflow/core/kernels/scatter_functor_gpu.cu.h(43)struct ScatterOpKernelBody
实际上就是对每个元素调用CudaAtomicAdd操作。
C++代码文件.cc等都只能在编译前的源码中找到,编译后成了.so文件。
torch.scatter_add版本
torch.scatter_add(
dim,
index,
src
)
参数解释
self(tensor) : 调用scatter_add的对象,通常由一个tensor元素调用。
dim (int) : 单个int值,src要加到self的哪个维度。
the axis along which to index.
index (LongTensor) : 索引id,src加到self的dim维的index位置,大小要么为空,要么与src的维度相同。
the indices of elements to scatter and add, can be either empty or the same size of src. When empty, the operation returns identity.
src (Tensor) : 要加的元素 。
the source elements to scatter and add.
返回:
一个tensor,维度与self的维度相同。
限制:
index.size(d) <= src.size(d)for all dimensionsd, and thatindex.size(d) <= self.size(d)for all dimensionsd != dim.
作用
self[index[i][j][k]][j][k] += src[i][j][k] # if dim == 0
self[i][index[i][j][k]][k] += src[i][j][k] # if dim == 1
self[i][j][index[i][j][k]] += src[i][j][k] # if dim == 2
实现
pytorch 1.5.1版本python端:
torch/onnx/symbolic_opset9.py(1938)scatter_add()
从python源代码可以直接看到,scatter_add的实现分为三步:
第一步先生成一个大小与self相同的全0 tensor to_add。
sizes = self.type().sizes()
to_add = g.op("Constant", value_t=torch.zeros(sizes, dtype=dtype))
第二步通过scatter操作将src的元素按index赋值到to_add的dim维对应位置处。
to_add = sym_help._scatter_helper(g, to_add, dim, index, src)
最后将to_add加到self中。
add(g, self, to_add)
具体C++代码和CUDA代码实现从pytorch源码中并没有找到。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号