HDLbits刷题笔记—Exams/ece241 2013 q4
Description
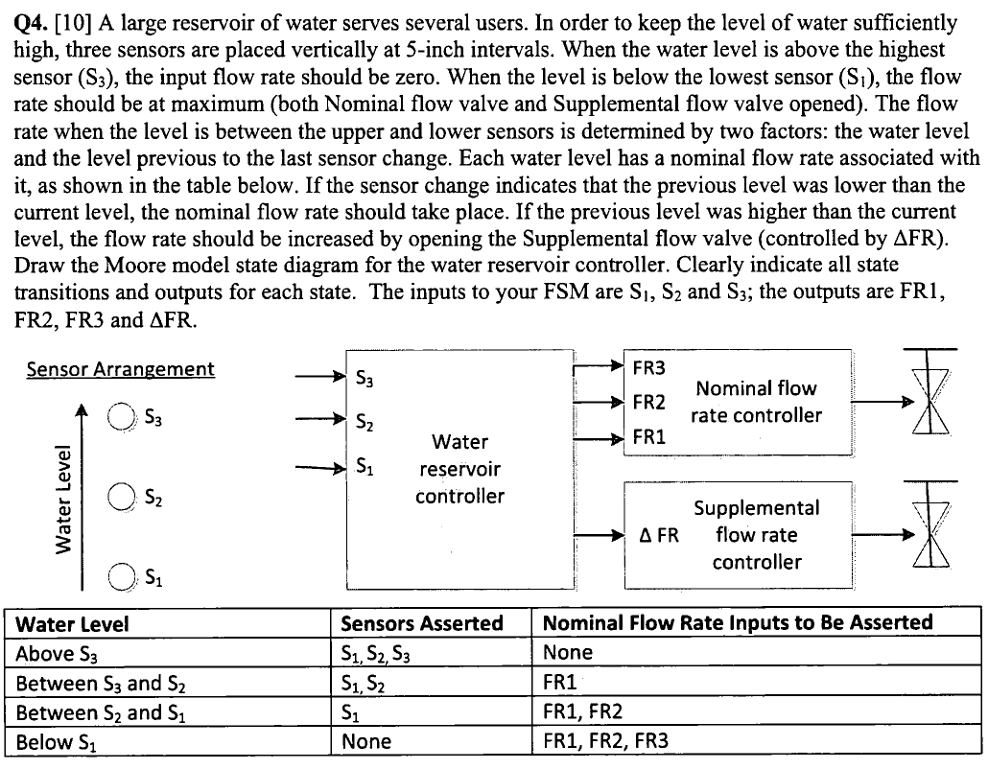
Also include an active-high synchronous reset that resets the state machine to a state equivalent to if the water level had been low for a long time (no sensors asserted, and all four outputs asserted).
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input [3:1] s,
output fr3,
output fr2,
output fr1,
output dfr
);
parameter A=0,B=1,C=2,D=3;
reg [1:0] state,next;
reg l;
always@(*)begin
case(state)
A:case(s)
3'b111:begin next<=A; end
3'b011:begin next<=B; end
3'b001:begin next<=C; end
3'b000:begin next<=D;end
endcase
B:case(s)
3'b111:begin next<=A;;end
3'b011:begin next<=B;end
3'b001:begin next<=C;end
3'b000:begin next<=D;end
endcase
C:case(s)
3'b111:begin next<=A;end
3'b011:begin next<=B;end
3'b001:begin next<=C;end
3'b000:begin next<=D;end
endcase
D:case(s)
3'b111:begin next<=A;end
3'b011:begin next<=B;end
3'b001:begin next<=C;end
3'b000:begin next<=D;end
endcase
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)begin
state<=D;
l<=1;
end
else begin
state<=next;
if(state==next)
l<=l;
else if(state>next)
l<=0;
else if(state<next)
l<=1;
end
end
always@(*)begin
if(l)dfr<=1;else dfr<=0;
case(state)
A:begin {fr3,fr2,fr1}<=3'b000;end
B:begin {fr3,fr2,fr1}<=3'b001;end
C:begin{fr3,fr2,fr1}<=3'b011;end
D:begin{fr3,fr2,fr1}<=3'b111;end
endcase
end
endmodule
另附上官方答案,明显简洁了许多
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input [3:1] s,
output reg fr3,
output reg fr2,
output reg fr1,
output reg dfr
);
// Give state names and assignments. I'm lazy, so I like to use decimal numbers.
// It doesn't really matter what assignment is used, as long as they're unique.
// We have 6 states here.
parameter A2=0, B1=1, B2=2, C1=3, C2=4, D1=5;
reg [2:0] state, next; // Make sure these are big enough to hold the state encodings.
// Edge-triggered always block (DFFs) for state flip-flops. Synchronous reset.
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset) state <= A2;
else state <= next;
end
// Combinational always block for state transition logic. Given the current state and inputs,
// what should be next state be?
// Combinational always block: Use blocking assignments.
always@(*) begin
case (state)
A2: next = s[1] ? B1 : A2;
B1: next = s[2] ? C1 : (s[1] ? B1 : A2);
B2: next = s[2] ? C1 : (s[1] ? B2 : A2);
C1: next = s[3] ? D1 : (s[2] ? C1 : B2);
C2: next = s[3] ? D1 : (s[2] ? C2 : B2);
D1: next = s[3] ? D1 : C2;
default: next = 'x;
endcase
end
// Combinational output logic. In this problem, a procedural block (combinational always block)
// is more convenient. Be careful not to create a latch.
always@(*) begin
case (state)
A2: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 4'b1111;
B1: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 4'b0110;
B2: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 4'b0111;
C1: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 4'b0010;
C2: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 4'b0011;
D1: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 4'b0000;
default: {fr3, fr2, fr1, dfr} = 'x;
endcase
end
endmodule
本文来自博客园,作者:Tao_W,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tao1997/p/15533791.html
个人学习记录,望不吝赐教




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号