2024.11.18
设计模式实验十七
软件设计 石家庄铁道大学信息学院
实验17:解释器模式(选作)
本次实验属于模仿型实验,通过本次实验学生将掌握以下内容:
1、理解解释器模式的动机,掌握该模式的结构;
2、能够利用解释器模式解决实际问题。
[实验任务一]:解释器模式
某机器人控制程序包含一些简单的英文指令,其文法规则如下:
expression ::= direction action distance | composite
composite ::= expression and expression
direction ::= ‘up’ | ‘down’ | ‘left’ | ‘right’
action ::= ‘move’ | ‘run’
distance ::= an integer //一个整数值
如输入:up move 5,则输出“向上移动5个单位”;输入:down run 10 and left move 20,则输出“向下移动10个单位再向左移动20个单位”。
实验要求:
1. 提交类图;
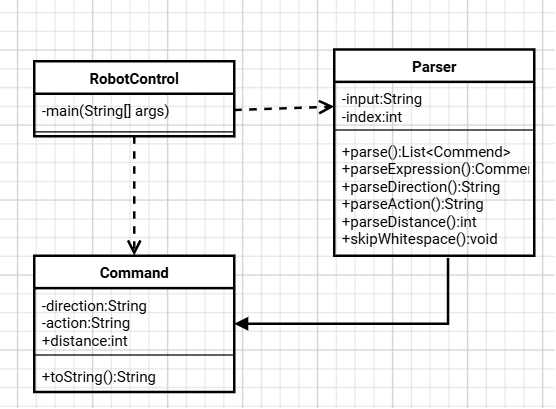
2. 提交源代码;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// Command类:用于表示单条命令
class Command {
private String direction;
private String action;
private int distance;
public Command(String direction, String action, int distance) {
this.direction = direction;
this.action = action;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String directionStr = switch (direction) {
case "up" -> "向上";
case "down" -> "向下";
case "left" -> "向左";
case "right" -> "向右";
default -> "未知方向";
};
String actionStr = switch (action) {
case "move" -> "移动";
case "run" -> "奔跑";
default -> "未知动作";
};
return directionStr + actionStr + distance + "个单位";
}
}
// Parser类:用于解析输入指令
class Parser {
private String input;
private int index;
public Parser(String input) {
this.input = input.trim();
this.index = 0;
}
// 解析完整的指令集合
public List<Command> parse() {
List<Command> commands = new ArrayList<>();
while (index < input.length()) {
Command command = parseExpression();
if (command != null) {
commands.add(command);
}
skipWhitespace();
if (index < input.length() && input.startsWith("and", index)) {
index += 3; // 跳过 "and"
skipWhitespace();
}
}
return commands;
}
// 解析单个表达式
private Command parseExpression() {
String direction = parseDirection();
if (direction == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("方向解析错误");
}
skipWhitespace();
String action = parseAction();
if (action == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("动作解析错误");
}
skipWhitespace();
int distance = parseDistance();
return new Command(direction, action, distance);
}
// 解析方向
private String parseDirection() {
if (input.startsWith("up", index)) {
index += 2;
return "up";
} else if (input.startsWith("down", index)) {
index += 4;
return "down";
} else if (input.startsWith("left", index)) {
index += 4;
return "left";
} else if (input.startsWith("right", index)) {
index += 5;
return "right";
}
return null;
}
// 解析动作
private String parseAction() {
if (input.startsWith("move", index)) {
index += 4;
return "move";
} else if (input.startsWith("run", index)) {
index += 3;
return "run";
}
return null;
}
// 解析距离
private int parseDistance() {
int start = index;
while (index < input.length() && Character.isDigit(input.charAt(index))) {
index++;
}
if (start == index) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("距离解析错误");
}
return Integer.parseInt(input.substring(start, index));
}
// 跳过空白字符
private void skipWhitespace() {
while (index < input.length() && Character.isWhitespace(input.charAt(index))) {
index++;
}
}
}
// RobotControl类:程序入口
public class RobotControl {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input1 = "up move 5";
String input2 = "down run 10 and left move 20";
executeCommands(input1);
executeCommands(input2);
}
private static void executeCommands(String input) {
System.out.println("输入指令: " + input);
Parser parser = new Parser(input);
List<Command> commands = parser.parse();
StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < commands.size(); i++) {
output.append(commands.get(i));
if (i < commands.size() - 1) {
output.append("再");
}
}
System.out.println("输出: " + output);
}
}
3. 注意编程规范。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号