Pod高级调度
Pod高级调度:
调度方式:
节点选择器: nodeSelector、nodeName
节点亲和性: nodeAffinity
Pod亲和性: podAffinity
污点: Taint
污点容忍度: Toleration
标签选择器:
等值关系:
=
==
!=
例:
#添加两个测试pod,并添加标签
kubectl label po b1 xxx=123
kubectl label po b1 xxx=abc
kubectl get po -l xxx=123 #仅显示标签xxx=123的pod
集合类型:
key in (v1,v2,...)
key notin (v1,v2,...)
key
!key
例:
kubectl get po -l "xxx in (123,qqq,321)"
kubectl get po -l "xxx notin (123,qqq,321)"
配置清单中标签选择器:
matchLabels: 直接给定键值
matchExpressions: 基于表达式
{key:"key名",operator:"操作",values:[v1,v2]}
操作符:
In、NotIn #values必须非空
Exists、DoesNotExist #values必须为空
Gt、Lt #大于、小于
亲和性
配置语法:
使被调度的pod更倾向于某些节点、pod,或者厌恶某些节点、pod
配置清单中的所有标签选择器用法都是一样的
kubectl explain pod.spec
spec:
nodeName: 节点名 #直接指定节点,不推荐使用,可能节点资源不足,导致调度失败
nodeSelector: #node标签选择器
标签: 值
affinity: <Object> #亲和性
nodeAffinity: <Object> #节点亲和性
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: #软亲和性,能满足最好不能满足尽量
- weight: 权重
preference:
matchExpressions:
- key: #标签值
operator: #操作符
values: #值列表
matchFields:
- key: #标签值
operator: #操作符
values: #值列表
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: #硬亲和性,必须满足
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
...
- matchFields:
...
podAffinity: <Object> #pod亲和性
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: #软亲和,较少使用
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: #硬亲和
labelSelector: <Object> #亲和的pod标签
- matchExpressions:
...
- matchFields:
...
namespaceSelector: <Object> #命名空间标签选择器
namespaces: #亲和的名称空间
topologyKey: 标签 #判断标签,用于判断pod是否在同一位置(筛选node)
podAntiAffinity: <Object> #pod反亲和性
topologyKey方法解读:
- 当pod是亲和性调度时会把pod运行在同一位置,而反亲和性调度时则相反,将pod运行在不同位置,而评判同一位置的标准就是topologyKey给的的标签
- 标签name=A在node1,name=2在node2,topologyKey: name,反亲和调度时,pod正常运行,若node2改为name=A,反亲和的pod就会进入Pending(挂起状态)
案例:
例1: 使用节点标签选择器
1)为节点创建标签
kubectl label nodes 2.2.2.30 disk=ssd
2)创建pod
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: a1
labels:
app: a1
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: a1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: a1
spec:
nodeSelector:
disk: ssd
containers:
- name: a1
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
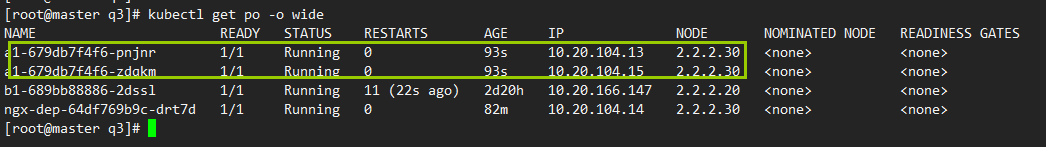
3)查看pod运行状态,是否在2.2.2.30节点
kubectl get po -o wide
例2: 使用节点硬亲和性
1)为节点创建标签
kubectl label nodes 2.2.2.20 zone=qq
2)创建pod
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: a2-dep
labels:
app: a2-dep
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: a2-affinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: a2-affinity
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: zone
operator: In
values:
- qq
- aa
containers:
- name: a2
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
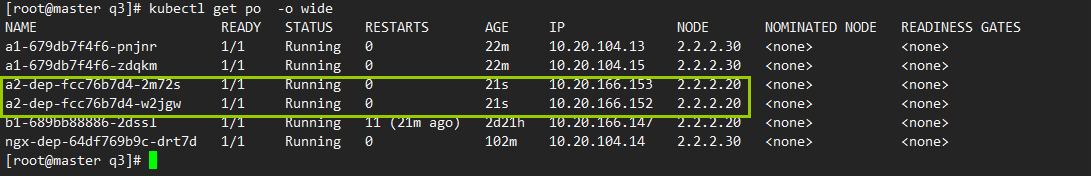
例3: 使用节点软亲和性
1)为2个节点创建标签
kubectl label nodes 2.2.2.20 node=pre
kubectl label nodes 2.2.2.30 node=pre
2)创建pod
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: a3-dep
labels:
app: a3-dep
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: a3-affinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: a3-affinity
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 60
preference:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node
operator: In
values:
- pre
containers:
- name: a3
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
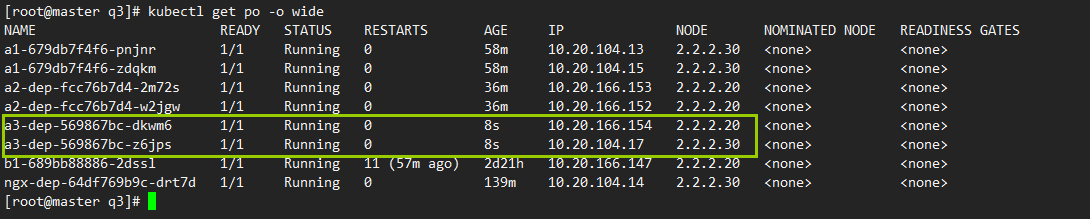
例4: 使用pod硬亲和
运行2个pod,第一个是被依赖者
#pod1
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: p1-dep
labels:
app: p1-dep
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: p1-affinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: p1-affinity
spec:
containers:
- name: p1
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
---
#pod2必须匹配pod1的标签,只要pod1存在的节点,pod2都会在
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: p2-dep
labels:
app: p2-dep
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: p2-affinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: p2-affinity
spec:
containers:
- name: p2
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
affinity:
podAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- {key: app, operator: In, values: ["p1-affinity"]}
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
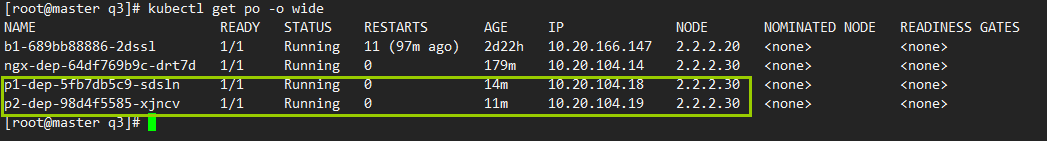
例5: 使用pod的硬反亲和
1)创建pod
两个pod会分开运行,不会在同一个节点
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: p1-dep
labels:
app: p1-dep
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: p1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: p1
spec:
containers:
- name: p1
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: p2-dep
labels:
app: p2-dep
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: p2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: p2
spec:
containers:
- name: p2
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["tail","-f","/etc/hosts"]
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- {key: app, operator: In, values: ["p1"]}
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
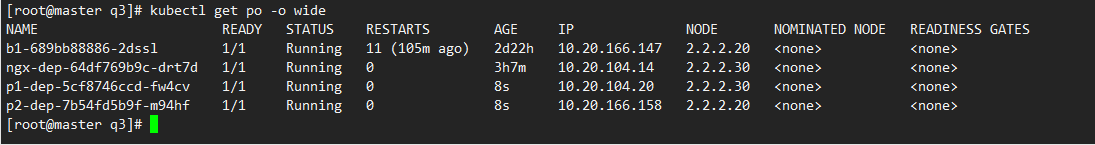
2)测试
两个节点,打同一个标签,给同一个值,那么第二个pod,就会被挂起,因为topologyKey字段匹配不到合适的node
#设置标签
kubectl label nodes 2.2.2.20 zone=qq --overwrite
kubectl label nodes 2.2.2.30 zone=qq --overwrite
#修改
vim a5-pod-notafy.yml
spec:
...
topologyKey: zone #改为新标签
kubectl apply -f a5-pod-notafy.yml
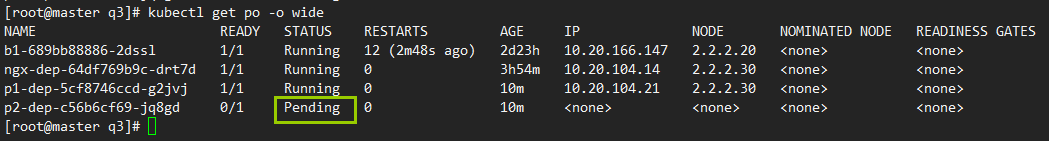
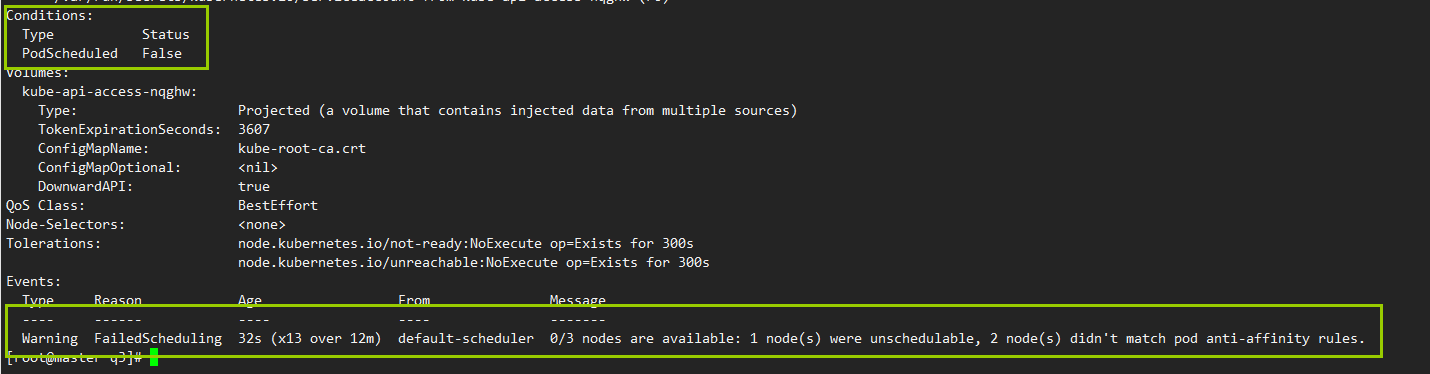
#此时,p2的pod,被挂起,且显示调度失败
kubectl get po -o wide
污点和容忍度:
污点(Taint)定义在node上,使节点能够排斥一类特定的 Pod
容忍度(Toleration) 是应用于 Pod 上,容忍度允许调度器调度带有对应污点的 Pod。 容忍度允许调度但并不保证调度
污点和容忍度都可以有多个
污点可理解为A的不良习惯,如抽烟、酗酒
污点容忍可理解为B能够忍受的习惯,如B容忍A抽烟
污点效果:
对pod产生的影响
- NoSchedule: 仅影响调度的过程,对已经运行的pod不产生影响
- NoExecute: 影响调度过程,也影响已经运行的pod,节点上出现不能容忍的,pod将被驱逐
- PreferNoSchedule: 实在是没有节点能满足了,只好将就了
污点配置语法:
kubectl explain nodes.spec
spec:
providerID
taints: <[]Object>
- effect: 污点效果
#NoSchedule
#NoExecute
#PreferNoSchedule
key: 名称
value:
timeAdded: 时间 #添加污点的时间。 仅适用于NoExecute污点
unschedulable
命令行定义:
kubectl taint node 节点名 污点名称=污点:污点效果 #创建污点
kubectl taint node 节点名 污点名称=污点:污点效果- #删除污点
例1: 为节点创建污点,并运行pod
1)为node2创建一个污点
kubectl taint node 2.2.2.20 node-type=prod:NoSchedule
2)创建pod
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ngx-dep
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ngx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ngx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
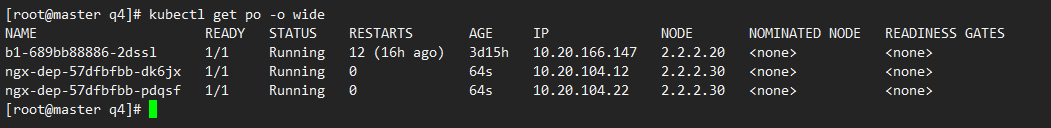
3)查看效果
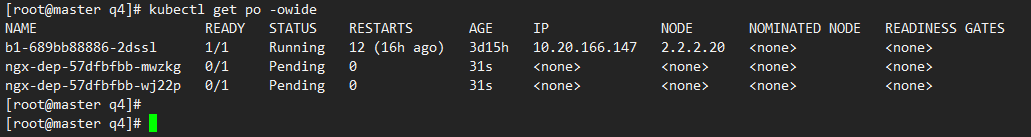
此时创建的pod都运行在node3,没有node2,因为pod没有容忍node2的污点
kubectl get po -o wide
4)为node3也添加污点,再次查看
2.2.2.30添加污点后,pod被挂起,因为没有pod没有做任何污点容忍
kubectl taint node 2.2.2.30 node-type=dev:NoSchedule
kubectl get po -owide
容忍度配置语法:
kubectl explain pod.spec
spec:
tolerations: <[]Object>
- key: #容忍的污点名称
operator: #对污点的判断操作
#Exists,污点名存在即可,不关注值
#Equal,精确匹配容忍值,默认
value: #容忍的污点内容
effect: 污点效果 #空为匹配所有污点效果
tolerationSeconds: #容忍时间,被驱逐时,多少秒后再赶,默认0s,立即驱逐
topologySpreadConstraints: <[]Object> #pod跨拓扑域分布
两种特殊情况说明:
容忍度的key为空且operator为Exists, 表示容忍度与任意key、value、effect都匹配,即能容忍任何污点
effect为空,则可以与指定key名的所有效果匹配
案例:
例1: 为pod定义污点容忍,允许到node2运行
1)结合之前的污点
kubectl taint node 2.2.2.20 node-type=prod:NoSchedule
2)创建pod
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ngx-dep
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ngx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ngx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
tolerations:
- key: "node-type"
operator: "Equal"
value: "prod"
effect: "NoSchedule"
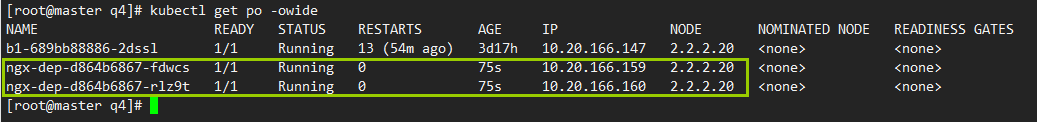
3)查看pod是否运行
前面污点的例子中,pod由于没有容忍度,被调度到node2,后面node2又加了新污点,所以处于挂起状态,现在可以运行
kubectl get po -owide
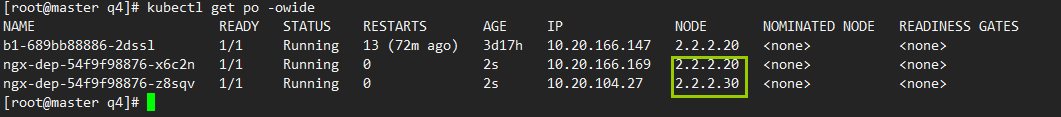
例2: 修改pod的污点容忍操作
1)修改pod配置
达到只要有key为node-type,且效果是为NoScheduleDe
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ngx-dep
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ngx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ngx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
tolerations:
- key: "node-type"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
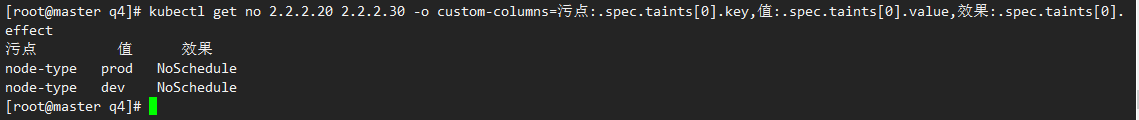
2)查看
kubectl get no 2.2.2.20 2.2.2.30 -o custom-columns=污点:.spec.taints[0].key,值:.spec.taints[0].value,效果:.spec.taints[0].effect




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号