Andrew 算法求凸包
Andrew 算法求凸包
参考资料:
- \(a\) 与 \(b\) 相对位置
- \(b\) 在 \(a\) 的逆时针方向: \(a \times b>0\)
- 顺负逆正(其实就是高中数学对于正负角的定义)
- 伪代码
while(右旋){
标记原来的栈顶为不在凸包上
}
标记新点在栈顶上
加入栈中
- 一般是叉积小于0则不合法(=0是平的,但合法)
二维凸包
定义
凸多边形
凸多边形是指所有内角大小都在 \([0,\pi]\) 范围内的 简单多边形。
凸包
在平面上能包含所有给定点的最小凸多边形叫做凸包。
实际上可以理解为用一个橡皮筋包含住所有给定点的形态。
凸包用最小的周长围住了给定的所有点。如果一个凹多边形围住了所有的点,它的周长一定不是最小,如下图。根据三角不等式,凸多边形在周长上一定是最优的。
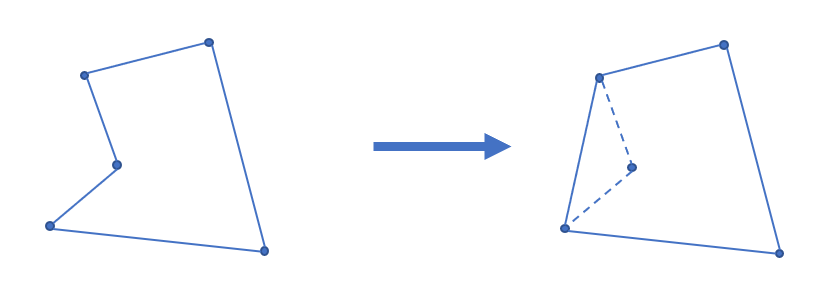
Andrew 算法求凸包
过程:
1、首先以 \(x\) 为第一关键字, \(y\) 为第二关键字排序
2、显然排序后最小的元素和最大的元素一定在凸包上。而且因为是凸多边形,我们如果从一个点出发逆时针走,轨迹总是「左拐」的,一旦出现右拐,就说明这一段不在凸包上。因此我们可以用一个单调栈来维护上下凸壳。
因为从左向右看,上下凸壳所旋转的方向不同,为了让单调栈起作用,我们首先 升序枚举 求出下凸壳,然后 降序 求出上凸壳。
- 左右旋的判定:叉积的正负(左旋为正角,右旋为负角,0证明是平的一段)
二维凸包模板:Luogu P2742 Fencing the Cows
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define F(i,l,r) for(int i(l);i<=r;++i)
#define G(i,r,l) for(int i(r);i>=l;--i)
#define double long double
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N=1e5+105;
struct node{
double x,y;
node operator - (const node &o)const{
node z=(node){x-o.x,y-o.y};
return z;
}
double operator * (const node &o)const{
return x*o.y-y*o.x;
}
bool operator < (const node &o)const{
return x==o.x ? y<o.y : x<o.x;
}
}w[N];
double dis(node a){
return __builtin_sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y);
}
int tp=0,n;
int stk[N<<1];
bool used[N];
double ans=0;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>n; F(i,1,n) cin>>w[i].x>>w[i].y;
sort(w+1,w+n+1);
stk[++tp]=1;//used不打标记方便最后封闭
F(i,2,n){
while(tp>=2 && (w[stk[tp]]-w[stk[tp-1]])*(w[i]-w[stk[tp]])<0) used[stk[tp--]]=0;
//注意叉积小于0,一定不能写成小于等于!
used[i]=1;
stk[++tp]=i;
}
G(i,n,1){
if(used[i]) continue;
while(tp>=2 && (w[stk[tp]]-w[stk[tp-1]])*(w[i]-w[stk[tp]])<0) used[stk[tp--]]=0;
used[i]=1;
stk[++tp]=i;
}
F(i,1,tp-1) ans+=dis(w[stk[i+1]]-w[stk[i]]);//凸包周长的求法
ans+=dis(w[stk[1]]-w[stk[tp]]);
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<ans<<"\n";
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号