Verilog combinational logical 中 basic gate代码总结
Truthtable1
本题考察真值表转换为逻辑表达式,翻了翻以前数电的笔记后了解到:
真值表->表达式有三个步骤:
1.找出真值表中使得Y=1的输入变量组合。
2.将每个取值组合写成一个与项,其中取值为1的写原变量,为0的写反变量。
3.将这些与项相或并简化后获得最终的真值表达式。
题目内容:
In the previous exercises, we used simple logic gates and combinations of several logic gates. These circuits are examples of combinational circuits. Combinational means the outputs of the circuit is a function (in the mathematics sense) of only its inputs. This means that for any given input value, there is only one possible output value. Thus, one way to describe the behaviour of a combinational function is to explicitly list what the output should be for every possible value of the inputs. This is a truth table.
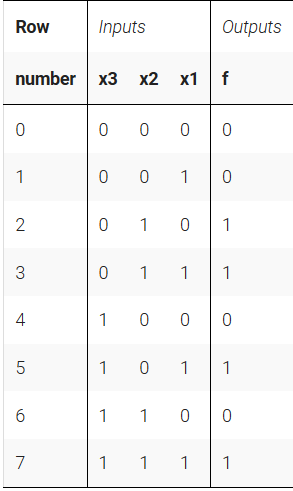
我们取A=x3; B=x2; C=x1; Y=f;
按照上面的做法有:Y = A'BC' + A'BC + AB'C + ABC
化简后有Y = A'B + AC
整理为代码如下所示:
答案:
1 module top_module( 2 input x3, 3 input x2, 4 input x1, // three inputs 5 output f // one output 6 ); 7 8 assign f = ((~x3)&x2) | (x1&x3); 9 10 endmodule
Thermostat
题目:
A heating/cooling thermostat controls both a heater (during winter) and an air conditioner (during summer). Implement a circuit that will turn on and off the heater, air conditioning, and blower fan as appropriate.
The thermostat can be in one of two modes: heating (mode = 1) and cooling (mode = 0). In heating mode, turn the heater on when it is too cold (too_cold = 1) but do not use the air conditioner. In cooling mode, turn the air conditioner on when it is too hot (too_hot = 1), but do not turn on the heater. When the heater or air conditioner are on, also turn on the fan to circulate the air. In addition, the user can also request the fan to turn on (fan_on = 1), even if the heater and air conditioner are off.
Try to use only assign statements, to see whether you can translate a problem description into a collection of logic gates.
答案:
1 module top_module ( 2 input too_cold, 3 input too_hot, 4 input mode, 5 input fan_on, 6 output heater, 7 output aircon, 8 output fan 9 ); 10 assign heater = mode&too_cold; 11 assign aircon = (~mode)&too_hot; 12 assign fan = mode&(~((~too_cold)&(~fan_on))) | (~mode)&(~((~too_hot)&(~fan_on))); 13 14 endmodule
Gatesv
题目:
You are given a four-bit input vector in[3:0]. We want to know some relationships between each bit and its neighbour:
- out_both: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether both the corresponding input bit and its neighbour to the left (higher index) are '1'. For example, out_both[2] should indicate if in[2] and in[3] are both 1. Since in[3] has no neighbour to the left, the answer is obvious so we don't need to know out_both[3].
- out_any: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether any of the corresponding input bit and its neighbour to the right are '1'. For example, out_any[2] should indicate if either in[2] or in[1] are 1. Since in[0] has no neighbour to the right, the answer is obvious so we don't need to know out_any[0].
- out_different: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether the corresponding input bit is different from its neighbour to the left. For example, out_different[2] should indicate if in[2] is different from in[3]. For this part, treat the vector as wrapping around, so in[3]'s neighbour to the left is in[0].
答案:
1 module top_module( 2 input [3:0] in, 3 output [2:0] out_both, 4 output [3:1] out_any, 5 output [3:0] out_different ); 6 assign out_both = in[3:1]&in[2:0]; 7 assign out_any = in[3:1]|in[2:0]; 8 assign out_different[2:0] = in[3:1]^in[2:0]; 9 assign out_different[3] = in[3]^in[0]; 10 11 endmodule
做这道题我差点用了case语句,还是要多动动脑子,能少写很多代码。
标准答案里,different用了下面的句子
assign out_different = in ^ {in[0], in[3:1]};
有点循环移位的意思。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号