4.2 有向图
一.有向图的表示
1.类似无向图的表示,区别在于,边有方向性。用adj(v)表示由v指出的边所连接的顶点,此时不具有对称性。用addEdge(v,w)表示向有向图添加一条v->w的边
2.代码实现

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; //有向图的表示 public class Digraph { private final int V; //邻接表数组,里面的每个元素都是一个集合类 private Bag<Integer>[] adj; //初始化V个顶点的图 public Digraph(int V) { this.V=V; adj=(Bag<Integer>[])new Bag[V]; //将每个元素初始化,不然会为null for(int v=0;v<V;v++) { adj[v]=new Bag<Integer>(); } } //添加一条由v->w的边 public void addEdge(int v,int w) { adj[v].add(w); } //由v指出的边所连接的所有顶点 public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){ return adj[v]; } public int V() {return V;} //获得反向图 public Digraph reverse() { Digraph R=new Digraph(V); for(int v=0;v<V;v++) //对每个边反向 for(int w:adj(v)) addEdge(w, v); return R; } }
3.性能:

二.有向图搜索
1.有向图的深度优先算法和无向图的搜索方法一样。使用marked判断是否访问过(可达性),使用 edgeTo记录到达它的上一个顶点。(用于判断给定点s到其他点的可达性,以及给出一条可能的路径)
要访问顶点v:
(1)将v标记为已访问
(2)递归的访问所有以v为起点的未标记的顶点
2.代码实现:

package com.cx.graph; import java.util.Stack; public class DirectedDFS { //用于标记是否已访问过该顶点 private boolean[] marked; //用于标记从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点 //边v-w是第一次访问w经过的路径,则edgeTo(w)=v,从而可以记住该路径 private int[] edgeTo; //起点为s private int s; //递归的标记与起点s连通的所有顶点 public DirectedDFS(Digraph G,int s) { marked=new boolean[G.V()]; edgeTo=new int[G.V()]; s=this.s; //找到和s连通的顶点 dfs(G,s); } //标记每一个已访问的顶点,并记录到达它的顶点 private void dfs(Digraph G,int v) { marked[v]=true; for(int w:G.adj(v)) { //访问所有未被标记的邻域顶点 if(!marked[w]) { edgeTo[w]=v; dfs(G, w); } } } //判断任意两个顶点是否连通(可达) public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { return marked[v]; } //找到一条s-v的路径 public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v){ if(!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<Integer> path=new Stack<Integer>(); //从终点逆向得到路径 for(int x=v;v!=s;x=edgeTo[x]) { path.push(x); } path.push(s); return path; } }
3.用途:
(1)流程图,可以用有向图的深度优先算法的可达性来判断有限循环的程序是否可以终止,还有判断是否有些逻辑块永远执行不到(点是框图,边是代码逻辑)
(2)java的垃圾回收机制,程序执行的任何时候有些对象是都可以被直接访问的(例如 stack区),而不能通过这些对象访问到的对象都应该被回收以便释放内存。(点是Object,表示引用)
标记-清除算法:标记所有可达的对象,清除不可达的对象。
4.有向图的广度优先算法也和无向图的一样。(用于得到给定点s到其他点的最短路径)
将起点s加入到队列,如果队列不为空,如果重复下面过程:
(1)将点v移除队列
(2)将以v为起点的所有邻接的未标记的点加入队列,并将它们标记
5.多源最短路径。给定一组源起点,找出以该源起点任意一点出发的其他点的最短路径。
还是使用BFS方法,只是初始化的时候,将这一组源起点都加入到队列中
6.广度优先算法应用:爬网站(BFS with implicit digraph)
(1)选择一个根网站作为起点
(2)维持一个要搜索的网站队列
(3)维持一个集合,来保存已经查找过的网站
(4)先入先出,将它所连接网站(这些网站不在集合中)加入队列。
代码实现:

package com.cx.graph; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue; public class WebCrawler { public static void main(String[] args) { // 保存工作队列 Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>(); // 保存已经处理过的网站 Set<String> discovered = new HashSet<String>(); String root = "http://www.scu.edu.cn"; queue.enqueue(root); discovered.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { String v = queue.dequeue(); System.out.println(v); // 读取整个页面 In in = new In(v); String input = in.readAll(); // 使用正则表达式提取链接 String regexp = "http://(\\w+\\.)*(\\w+)"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regexp); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input); while (matcher.find()) { String w = matcher.group(); // 只处理不在set中的网站 if (!discovered.contains(w)) { discovered.add(w); queue.enqueue(w); } } } } }

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac In.java * Execution: java In (basic test --- see source for required files) * Dependencies: none * * Reads in data of various types from standard input, files, and URLs. * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.URL; import java.net.Socket; // import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.URLConnection; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.InputMismatchException; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /** * <i>Input</i>. This class provides methods for reading strings * and numbers from standard input, file input, URLs, and sockets. * <p> * The Locale used is: language = English, country = US. This is consistent * with the formatting conventions with Java floating-point literals, * command-line arguments (via {@link Double#parseDouble(String)}) * and standard output. * <p> * For additional documentation, see * <a href="http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/31datatype">Section 3.1</a> of * <i>Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach</i> * by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * <p> * Like {@link Scanner}, reading a token also consumes preceding Java * whitespace, reading a full line consumes * the following end-of-line delimeter, while reading a character consumes * nothing extra. * <p> * Whitespace is defined in {@link Character#isWhitespace(char)}. Newlines * consist of \n, \r, \r\n, and Unicode hex code points 0x2028, 0x2029, 0x0085; * see <a href="http://www.docjar.com/html/api/java/util/Scanner.java.html"> * Scanner.java</a> (NB: Java 6u23 and earlier uses only \r, \r, \r\n). * * @author David Pritchard * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne */ public final class In { ///// begin: section (1 of 2) of code duplicated from In to StdIn. // assume Unicode UTF-8 encoding private static final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8"; // assume language = English, country = US for consistency with System.out. private static final Locale LOCALE = Locale.US; // the default token separator; we maintain the invariant that this value // is held by the scanner's delimiter between calls private static final Pattern WHITESPACE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\p{javaWhitespace}+"); // makes whitespace characters significant private static final Pattern EMPTY_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(""); // used to read the entire input. source: // http://weblogs.java.net/blog/pat/archive/2004/10/stupid_scanner_1.html private static final Pattern EVERYTHING_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\A"); //// end: section (1 of 2) of code duplicated from In to StdIn. private Scanner scanner; /** * Initializes an input stream from standard input. */ public In() { scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in), CHARSET_NAME); scanner.useLocale(LOCALE); } /** * Initializes an input stream from a socket. * * @param socket the socket * @throws IllegalArgumentException if cannot open {@code socket} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code socket} is {@code null} */ public In(Socket socket) { if (socket == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("socket argument is null"); try { InputStream is = socket.getInputStream(); scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(is), CHARSET_NAME); scanner.useLocale(LOCALE); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not open " + socket, ioe); } } /** * Initializes an input stream from a URL. * * @param url the URL * @throws IllegalArgumentException if cannot open {@code url} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code url} is {@code null} */ public In(URL url) { if (url == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url argument is null"); try { URLConnection site = url.openConnection(); InputStream is = site.getInputStream(); scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(is), CHARSET_NAME); scanner.useLocale(LOCALE); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not open " + url, ioe); } } /** * Initializes an input stream from a file. * * @param file the file * @throws IllegalArgumentException if cannot open {@code file} * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code file} is {@code null} */ public In(File file) { if (file == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("file argument is null"); try { // for consistency with StdIn, wrap with BufferedInputStream instead of use // file as argument to Scanner FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(fis), CHARSET_NAME); scanner.useLocale(LOCALE); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not open " + file, ioe); } } /** * Initializes an input stream from a filename or web page name. * * @param name the filename or web page name * @throws IllegalArgumentException if cannot open {@code name} as * a file or URL * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code name} is {@code null} */ public In(String name) { if (name == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); try { // first try to read file from local file system File file = new File(name); if (file.exists()) { // for consistency with StdIn, wrap with BufferedInputStream instead of use // file as argument to Scanner FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(fis), CHARSET_NAME); scanner.useLocale(LOCALE); return; } // next try for files included in jar URL url = getClass().getResource(name); // or URL from web if (url == null) { url = new URL(name); } URLConnection site = url.openConnection(); // in order to set User-Agent, replace above line with these two // HttpURLConnection site = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // site.addRequestProperty("User-Agent", "Mozilla/4.76"); InputStream is = site.getInputStream(); scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(is), CHARSET_NAME); scanner.useLocale(LOCALE); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not open " + name, ioe); } } /** * Initializes an input stream from a given {@link Scanner} source; use with * {@code new Scanner(String)} to read from a string. * <p> * Note that this does not create a defensive copy, so the * scanner will be mutated as you read on. * * @param scanner the scanner * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code scanner} is {@code null} */ public In(Scanner scanner) { if (scanner == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("scanner argument is null"); this.scanner = scanner; } /** * Returns true if this input stream exists. * * @return {@code true} if this input stream exists; {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean exists() { return scanner != null; } //// begin: section (2 of 2) of code duplicated from In to StdIn, //// with all methods changed from "public" to "public static". /** * Returns true if input stream is empty (except possibly whitespace). * Use this to know whether the next call to {@link #readString()}, * {@link #readDouble()}, etc will succeed. * * @return {@code true} if this input stream is empty (except possibly whitespace); * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return !scanner.hasNext(); } /** * Returns true if this input stream has a next line. * Use this method to know whether the * next call to {@link #readLine()} will succeed. * This method is functionally equivalent to {@link #hasNextChar()}. * * @return {@code true} if this input stream has more input (including whitespace); * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean hasNextLine() { return scanner.hasNextLine(); } /** * Returns true if this input stream has more inputy (including whitespace). * Use this method to know whether the next call to {@link #readChar()} will succeed. * This method is functionally equivalent to {@link #hasNextLine()}. * * @return {@code true} if this input stream has more input (including whitespace); * {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean hasNextChar() { scanner.useDelimiter(EMPTY_PATTERN); boolean result = scanner.hasNext(); scanner.useDelimiter(WHITESPACE_PATTERN); return result; } /** * Reads and returns the next line in this input stream. * * @return the next line in this input stream; {@code null} if no such line */ public String readLine() { String line; try { line = scanner.nextLine(); } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { line = null; } return line; } /** * Reads and returns the next character in this input stream. * * @return the next character in this input stream */ public char readChar() { scanner.useDelimiter(EMPTY_PATTERN); String ch = scanner.next(); assert ch.length() == 1 : "Internal (Std)In.readChar() error!" + " Please contact the authors."; scanner.useDelimiter(WHITESPACE_PATTERN); return ch.charAt(0); } /** * Reads and returns the remainder of this input stream, as a string. * * @return the remainder of this input stream, as a string */ public String readAll() { if (!scanner.hasNextLine()) return ""; String result = scanner.useDelimiter(EVERYTHING_PATTERN).next(); // not that important to reset delimeter, since now scanner is empty scanner.useDelimiter(WHITESPACE_PATTERN); // but let's do it anyway return result; } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream and returns it as a {@code String}. * * @return the next {@code String} in this input stream */ public String readString() { return scanner.next(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code int}, * and returns the {@code int}. * * @return the next {@code int} in this input stream */ public int readInt() { return scanner.nextInt(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code double}, * and returns the {@code double}. * * @return the next {@code double} in this input stream */ public double readDouble() { return scanner.nextDouble(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code float}, * and returns the {@code float}. * * @return the next {@code float} in this input stream */ public float readFloat() { return scanner.nextFloat(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code long}, * and returns the {@code long}. * * @return the next {@code long} in this input stream */ public long readLong() { return scanner.nextLong(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code short}, * and returns the {@code short}. * * @return the next {@code short} in this input stream */ public short readShort() { return scanner.nextShort(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code byte}, * and returns the {@code byte}. * <p> * To read binary data, use {@link BinaryIn}. * * @return the next {@code byte} in this input stream */ public byte readByte() { return scanner.nextByte(); } /** * Reads the next token from this input stream, parses it as a {@code boolean} * (interpreting either {@code "true"} or {@code "1"} as {@code true}, * and either {@code "false"} or {@code "0"} as {@code false}). * * @return the next {@code boolean} in this input stream */ public boolean readBoolean() { String s = readString(); if ("true".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) return true; if ("false".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) return false; if ("1".equals(s)) return true; if ("0".equals(s)) return false; throw new InputMismatchException(); } /** * Reads all remaining tokens from this input stream and returns them as * an array of strings. * * @return all remaining tokens in this input stream, as an array of strings */ public String[] readAllStrings() { // we could use readAll.trim().split(), but that's not consistent // since trim() uses characters 0x00..0x20 as whitespace String[] tokens = WHITESPACE_PATTERN.split(readAll()); if (tokens.length == 0 || tokens[0].length() > 0) return tokens; String[] decapitokens = new String[tokens.length-1]; for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length-1; i++) decapitokens[i] = tokens[i+1]; return decapitokens; } /** * Reads all remaining lines from this input stream and returns them as * an array of strings. * * @return all remaining lines in this input stream, as an array of strings */ public String[] readAllLines() { ArrayList<String> lines = new ArrayList<String>(); while (hasNextLine()) { lines.add(readLine()); } return lines.toArray(new String[lines.size()]); } /** * Reads all remaining tokens from this input stream, parses them as integers, * and returns them as an array of integers. * * @return all remaining lines in this input stream, as an array of integers */ public int[] readAllInts() { String[] fields = readAllStrings(); int[] vals = new int[fields.length]; for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) vals[i] = Integer.parseInt(fields[i]); return vals; } /** * Reads all remaining tokens from this input stream, parses them as longs, * and returns them as an array of longs. * * @return all remaining lines in this input stream, as an array of longs */ public long[] readAllLongs() { String[] fields = readAllStrings(); long[] vals = new long[fields.length]; for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) vals[i] = Long.parseLong(fields[i]); return vals; } /** * Reads all remaining tokens from this input stream, parses them as doubles, * and returns them as an array of doubles. * * @return all remaining lines in this input stream, as an array of doubles */ public double[] readAllDoubles() { String[] fields = readAllStrings(); double[] vals = new double[fields.length]; for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) vals[i] = Double.parseDouble(fields[i]); return vals; } ///// end: section (2 of 2) of code duplicated from In to StdIn */ /** * Closes this input stream. */ public void close() { scanner.close(); } /** * Reads all integers from a file and returns them as * an array of integers. * * @param filename the name of the file * @return the integers in the file * @deprecated Replaced by {@code new In(filename)}.{@link #readAllInts()}. */ @Deprecated public static int[] readInts(String filename) { return new In(filename).readAllInts(); } /** * Reads all doubles from a file and returns them as * an array of doubles. * * @param filename the name of the file * @return the doubles in the file * @deprecated Replaced by {@code new In(filename)}.{@link #readAllDoubles()}. */ @Deprecated public static double[] readDoubles(String filename) { return new In(filename).readAllDoubles(); } /** * Reads all strings from a file and returns them as * an array of strings. * * @param filename the name of the file * @return the strings in the file * @deprecated Replaced by {@code new In(filename)}.{@link #readAllStrings()}. */ @Deprecated public static String[] readStrings(String filename) { return new In(filename).readAllStrings(); } /** * Reads all integers from standard input and returns them * an array of integers. * * @return the integers on standard input * @deprecated Replaced by {@link StdIn#readAllInts()}. */ @Deprecated public static int[] readInts() { return new In().readAllInts(); } /** * Reads all doubles from standard input and returns them as * an array of doubles. * * @return the doubles on standard input * @deprecated Replaced by {@link StdIn#readAllDoubles()}. */ @Deprecated public static double[] readDoubles() { return new In().readAllDoubles(); } /** * Reads all strings from standard input and returns them as * an array of strings. * * @return the strings on standard input * @deprecated Replaced by {@link StdIn#readAllStrings()}. */ @Deprecated public static String[] readStrings() { return new In().readAllStrings(); } /** * Unit tests the {@code In} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { In in; String urlName = "http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/stdlib/InTest.txt"; // read from a URL System.out.println("readAll() from URL " + urlName); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In(urlName); System.out.println(in.readAll()); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); // read one line at a time from URL System.out.println("readLine() from URL " + urlName); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In(urlName); while (!in.isEmpty()) { String s = in.readLine(); System.out.println(s); } } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); // read one string at a time from URL System.out.println("readString() from URL " + urlName); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In(urlName); while (!in.isEmpty()) { String s = in.readString(); System.out.println(s); } } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); // read one line at a time from file in current directory System.out.println("readLine() from current directory"); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In("./InTest.txt"); while (!in.isEmpty()) { String s = in.readLine(); System.out.println(s); } } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); // read one line at a time from file using relative path System.out.println("readLine() from relative path"); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In("../stdlib/InTest.txt"); while (!in.isEmpty()) { String s = in.readLine(); System.out.println(s); } } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); // read one char at a time System.out.println("readChar() from file"); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In("InTest.txt"); while (!in.isEmpty()) { char c = in.readChar(); System.out.print(c); } } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); System.out.println(); // read one line at a time from absolute OS X / Linux path System.out.println("readLine() from absolute OS X / Linux path"); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); in = new In("/n/fs/introcs/www/java/stdlib/InTest.txt"); try { while (!in.isEmpty()) { String s = in.readLine(); System.out.println(s); } } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); // read one line at a time from absolute Windows path System.out.println("readLine() from absolute Windows path"); System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------------------------"); try { in = new In("G:\\www\\introcs\\stdlib\\InTest.txt"); while (!in.isEmpty()) { String s = in.readLine(); System.out.println(s); } System.out.println(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { System.out.println(e); } System.out.println(); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/

/****************************************************************************** * Compilation: javac Queue.java * Execution: java Queue < input.txt * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks/tobe.txt * * A generic queue, implemented using a linked list. * * % java Queue < tobe.txt * to be or not to be (2 left on queue) * ******************************************************************************/ package edu.princeton.cs.algs4; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; /** * The {@code Queue} class represents a first-in-first-out (FIFO) * queue of generic items. * It supports the usual <em>enqueue</em> and <em>dequeue</em> * operations, along with methods for peeking at the first item, * testing if the queue is empty, and iterating through * the items in FIFO order. * <p> * This implementation uses a singly-linked list with a static nested class for * linked-list nodes. See {@link LinkedQueue} for the version from the * textbook that uses a non-static nested class. * The <em>enqueue</em>, <em>dequeue</em>, <em>peek</em>, <em>size</em>, and <em>is-empty</em> * operations all take constant time in the worst case. * <p> * For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/13stacks">Section 1.3</a> of * <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * @author Robert Sedgewick * @author Kevin Wayne * * @param <Item> the generic type of an item in this queue */ public class Queue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Node<Item> first; // beginning of queue private Node<Item> last; // end of queue private int n; // number of elements on queue // helper linked list class private static class Node<Item> { private Item item; private Node<Item> next; } /** * Initializes an empty queue. */ public Queue() { first = null; last = null; n = 0; } /** * Returns true if this queue is empty. * * @return {@code true} if this queue is empty; {@code false} otherwise */ public boolean isEmpty() { return first == null; } /** * Returns the number of items in this queue. * * @return the number of items in this queue */ public int size() { return n; } /** * Returns the item least recently added to this queue. * * @return the item least recently added to this queue * @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item peek() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); return first.item; } /** * Adds the item to this queue. * * @param item the item to add */ public void enqueue(Item item) { Node<Item> oldlast = last; last = new Node<Item>(); last.item = item; last.next = null; if (isEmpty()) first = last; else oldlast.next = last; n++; } /** * Removes and returns the item on this queue that was least recently added. * * @return the item on this queue that was least recently added * @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty */ public Item dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Queue underflow"); Item item = first.item; first = first.next; n--; if (isEmpty()) last = null; // to avoid loitering return item; } /** * Returns a string representation of this queue. * * @return the sequence of items in FIFO order, separated by spaces */ public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); for (Item item : this) { s.append(item); s.append(' '); } return s.toString(); } /** * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order. * * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this queue in FIFO order */ public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ListIterator<Item>(first); } // an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional private class ListIterator<Item> implements Iterator<Item> { private Node<Item> current; public ListIterator(Node<Item> first) { current = first; } public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Item item = current.item; current = current.next; return item; } } /** * Unit tests the {@code Queue} data type. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>(); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { String item = StdIn.readString(); if (!item.equals("-")) queue.enqueue(item); else if (!queue.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(queue.dequeue() + " "); } StdOut.println("(" + queue.size() + " left on queue)"); } } /****************************************************************************** * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne. * * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook * * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne, * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X. * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu * * * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or * (at your option) any later version. * * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses. ******************************************************************************/
只是一个简单的示意,还存在很多问题,例如有些网站禁止访问,则会错,还有有些视频网站也会报错。
7.为什么不使用深度优先爬网站而是使用广度优先?
深度优先搜素算法:不全部保留结点,占用空间少;有回溯操作(即有入栈、出栈操作),运行速度慢。
广度优先搜索算法:保留全部结点,占用空间大; 无回溯操作(即无入栈、出栈操作),运行速度快。
另外,重要的网页往往离root比较近,例如我们打开新闻网站的时候往往是最热门的新闻,随着不断的深入冲浪,所看到的网页的重要性越来越低。
三.拓扑排序(topological sorting)
1.拓扑排序:给定一幅有向图。将所有的顶点排序,是的所有的边均从排到前面的元素指向排到后面的元素。
2.应用:优先级调度问题。给定一组需要完成的任务以及完成任务的优先级限制,应该如何安排并完成所有任务?(使用点表示任务,使用有向边表示优先级顺序)
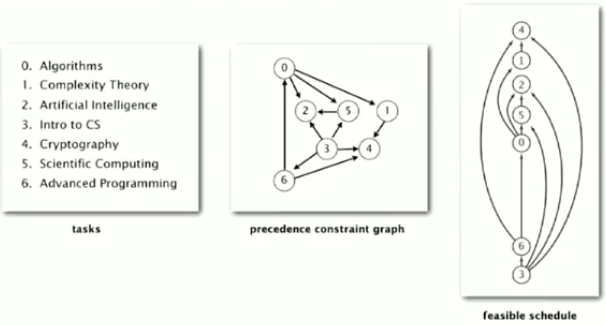
3.优先级限制的问题中存在有向环,那么这个问题无解。因此,解决优先级限制的问题需要确保处理的是DAG,即有向无环图(Directed acyclic graph)。
4.拓扑排序的思想
(1)使用深度优先搜索
(2)将顶点以逆后序的方式返回(处理完一个即压栈)
具体过程如图所示:
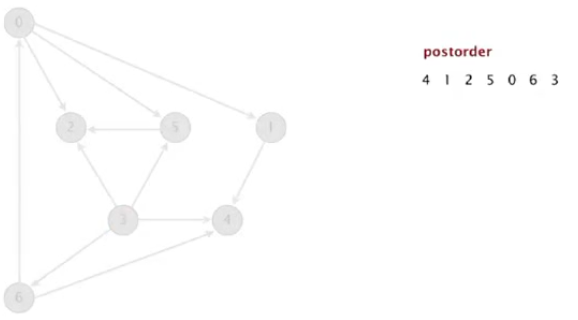

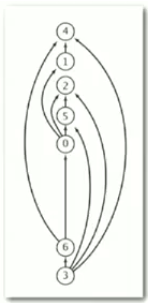
5.说明:
(1)逆后序:在递归调用之后将顶点压入栈。
(2)一副有向无环图的拓扑顺序即为所有顶点的逆后序排序。
6.代码实现:

package com.cx.graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; public class DepthFirstOrder { private boolean[] marked; private Stack<Integer> reversePost; public DepthFirstOrder(Digraph G) { reversePost=new Stack<Integer>(); marked=new boolean[G.V()]; for(int v=0;v<G.V();v++) if(!marked[v]) dfs(G,v); } private void dfs(Digraph G,int v) { marked[v]=true; for(int w:G.adj(v)) if(!marked[w]) dfs(G, w); //逆后序 //递归调用以后将顶点压入栈,也就是优先级低最后才能出栈 reversePost.push(v); } public Iterable<Integer> reversePost(){ return reversePost(); } }
7.有向图的环检测
四.强连通分量
1.几个概念:
(1)强连通性:如果有一条v->w的有向路径,也有一条w->v的有向路径,则顶点v和w是强连通的。
(2)强连通分量:强连通点的最大子集。
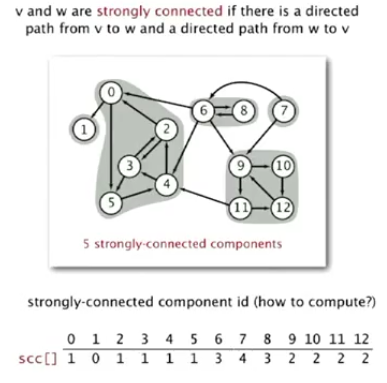
2.强连通分量,能够在线性时间(E+V)内进行划分,并且在常数时间内判断两个顶点是否是强连通的。
3.两个性质:
(1)G和反向图GR具有相同的强连通分量。
(2)kernel DAG:将每一个强连通分量缩小为一个单一的顶点。经过这种处理后,可以得到一个DAG无环图

4.算法的思想:
(1)计算GR的逆后序(即拓扑排序)
(2)在G中运行DFS,对尚未标记的点使用GR的逆后序排序的顺序来访问,而不是之前的自然顺序。
5.具体步骤:
(1)计算GR的逆后序,如图所示,逆后序为:1,0,2,4,5,3,11,9,12,10,6,7,8
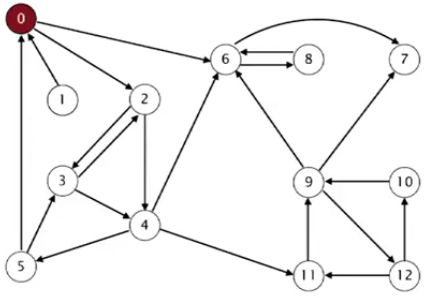
(2)在G中运行DFS,对尚未标记的点使用(1)得到的顺序来访问,而不是之前的自然顺序。
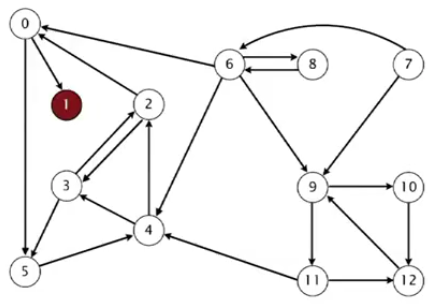

6.代码实现,和无向图的CC类似,只是不是使用自然顺序而已。结合上面拓扑顺序的实现,可以得到如下代码:

package com.cx.graph; import java.util.stream.IntStream; public class KosarajuSharirSCC { private boolean[] marked; //v所在的连通分量的标识符 private int[] id; //连通分量个数 private int count; public KosarajuSharirSCC(Digraph G) { marked=new boolean[G.V()]; id=new int[G.V()]; //对反向图取拓扑顺序 DepthFirstOrder dfo=new DepthFirstOrder(G.reverse()); //按照指定的顺序执行dfs操作进行标记,而不是自然顺序 for(int s:dfo.reversePost()) { //对未标记的执行dfs if(!marked[s]) { dfs(G,s); count++; } } } private void dfs(Digraph G,int v) { marked[v]=true; id[v]=count; for(int w:G.adj(v)) { if(!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } } //判断是否强连通 public boolean stronglyConnected(int v,int w) { return id[v]==id[w]; } public int id(int v) { return id[v]; } public int count() { return count; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号